Kubernetes HPA Controller源码分析
Author: [email protected]
源码目录结构分析
HorizontalPodAutoscaler(以下简称HPA)的主要代码如下,主要涉及的文件不多。
cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/autoscaling.go // HPA Controller的启动代码
/pkg/controller/podautoscaler
.
├── BUILD
├── OWNERS
├── doc.go
├── horizontal.go // podautoscaler的核心代码,包括其创建和运行的代码
├── horizontal_test.go
├── metrics
│ ├── BUILD
│ ├── metrics_client.go
│ ├── metrics_client_test.go
│ ├── metrics_client_test.go.orig
│ ├── metrics_client_test.go.rej
│ └── utilization.go
├── replica_calculator.go // ReplicaCaculator的创建,以及根据cpu/metrics计算replicas的方法
└── replica_calculator_test.go
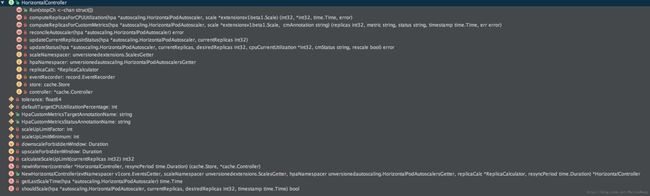
其中,horizontal.go和replica_calculator.go是最核心的文件,他们对应的Structure如下:
源码分析
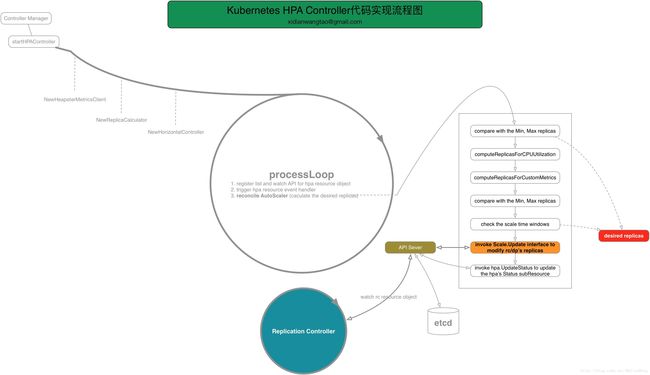
HPA Controller同其他Controller一样,都是在kube-controller-manager启动时完成初始化并启动的,如下代码所示。
cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go:224
func newControllerInitializers() map[string]InitFunc {
controllers := map[string]InitFunc{}
...
controllers["horizontalpodautoscaling"] = startHPAController
...
return controllers
}kube-controller-manager启动时会initial一堆的controllers,对于HPA controller,它的启动就交给startHPAController了。
cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/autoscaling.go:29
func startHPAController(ctx ControllerContext) (bool, error) {
...
// HPA Controller需要集群已经部署Heapster,由Heapster提供监控数据,来进行replicas的计算。
metricsClient := metrics.NewHeapsterMetricsClient(
hpaClient,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterNamespace,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterScheme,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterService,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterPort,
)
// 创建ReplicaCaculator,后面会用它来计算desired replicas。
replicaCalc := podautoscaler.NewReplicaCalculator(metricsClient, hpaClient.Core())
// 创建HPA Controller,并启动goroutine执行其Run方法,开始工作。
go podautoscaler.NewHorizontalController(
hpaClient.Core(),
hpaClient.Extensions(),
hpaClient.Autoscaling(),
replicaCalc,
ctx.Options.HorizontalPodAutoscalerSyncPeriod.Duration,
).Run(ctx.Stop)
return true, nil
}首先我们来看看NewHorizontalController创建HPA Controller的代码。
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:112
func NewHorizontalController(evtNamespacer v1core.EventsGetter, scaleNamespacer unversionedextensions.ScalesGetter, hpaNamespacer unversionedautoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscalersGetter, replicaCalc *ReplicaCalculator, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *HorizontalController {
...
// 构建HPA Controller
controller := &HorizontalController{
replicaCalc: replicaCalc,
eventRecorder: recorder,
scaleNamespacer: scaleNamespacer,
hpaNamespacer: hpaNamespacer,
}
// 创建Informer,配置对应的ListWatch Func,及其对应的EventHandler,用来监控HPA Resource的Add和Update事件。newInformer是HPA的核心代码入口。
store, frameworkController := newInformer(controller, resyncPeriod)
controller.store = store
controller.controller = frameworkController
return controller
}我们有必要来看看HPA Controller struct的定义:
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:59
type HorizontalController struct {
scaleNamespacer unversionedextensions.ScalesGetter
hpaNamespacer unversionedautoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscalersGetter
replicaCalc *ReplicaCalculator
eventRecorder record.EventRecorder
// A store of HPA objects, populated by the controller.
store cache.Store
// Watches changes to all HPA objects.
controller *cache.Controller
}- scaleNamespacer其实是一个ScaleInterface,包括Scale subresource的Get和Update接口。
- hpaNamespacer是HorizontalPodAutoscalerInterface,包括HorizontalPodAutoscaler的Create, Update, UpdateStatus, Delete, Get, List, Watch等接口。
replicaCalc根据Heapster提供的监控数据,计算对应desired replicas。
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go:31 type ReplicaCalculator struct { metricsClient metricsclient.MetricsClient podsGetter v1core.PodsGetter }- store和controller:controller用来watch HPA objects,并更新到store这个cache中。
上面提到了Scale subresource,那是个什么东西?好吧,我们得看看Scale的定义。
pkg/apis/extensions/v1beta1/types.go:56
// represents a scaling request for a resource.
type Scale struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard object metadata; More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#metadata.
// +optional
v1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// defines the behavior of the scale. More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status.
// +optional
Spec ScaleSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// current status of the scale. More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status. Read-only.
// +optional
Status ScaleStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
// describes the attributes of a scale subresource
type ScaleSpec struct {
// desired number of instances for the scaled object.
Replicas int `json:"replicas,omitempty"`
}
// represents the current status of a scale subresource.
type ScaleStatus struct {
// actual number of observed instances of the scaled object.
Replicas int `json:"replicas"`
// label query over pods that should match the replicas count.
Selector map[string]string `json:"selector,omitempty"`
}- Scale struct作为一次scale动作的请求数据。
- 其中Spec定义的是desired replicas number。
- ScaleStatus定义了current replicas number。
看完了HorizontalController的结构后,接着看看NewHorizontalController中调用的newInformer。在上面的注释中,我提到newInformer是整个HPA的核心代码入口。
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:75
func newInformer(controller *HorizontalController, resyncPeriod time.Duration) (cache.Store, *cache.Controller) {
return cache.NewInformer(
// 配置ListFucn和WatchFunc,用来定期List和watch HPA resource。
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return controller.hpaNamespacer.HorizontalPodAutoscalers(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return controller.hpaNamespacer.HorizontalPodAutoscalers(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
// 定义期望收到的object为HorizontalPodAutoscaler
&autoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscaler{},
// 定义定期List的周期
resyncPeriod,
// 配置HPA resource event的Handler(AddFunc, UpdateFunc)
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
hpa := obj.(*autoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscaler)
hasCPUPolicy := hpa.Spec.TargetCPUUtilizationPercentage != nil
_, hasCustomMetricsPolicy := hpa.Annotations[HpaCustomMetricsTargetAnnotationName]
if !hasCPUPolicy && !hasCustomMetricsPolicy {
controller.eventRecorder.Event(hpa, v1.EventTypeNormal, "DefaultPolicy", "No scaling policy specified - will use default one. See documentation for details")
}
// 根据监控调整hpa的数据
err := controller.reconcileAutoscaler(hpa)
if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("Failed to reconcile %s: %v", hpa.Name, err)
}
},
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {
hpa := cur.(*autoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscaler)
// 根据监控调整hpa的数据
err := controller.reconcileAutoscaler(hpa)
if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("Failed to reconcile %s: %v", hpa.Name, err)
}
},
// We are not interested in deletions.
},
)
}newInformer的代码也不长嘛,简单说来,就是配置了HPA resource的ListWatch的Func,注册HPA resource 的Add和Update Event的handler Func。
最终通过调用reconcileAutoscaler来矫正hpa的数据。
上面代码中,将HPA resource的ListWatch Func注册为HorizontalPodAutoscaler Interface定义的List和Watch接口。
等等,说了这么多,怎么还没看到HorizontalPodAutoscaler struct的定义呢!好吧,下面就来看看,正好HorizontalPodAutoscaler Interface中出现了。
pkg/apis/autoscaling/v1/types.go:76
// configuration of a horizontal pod autoscaler.
type HorizontalPodAutoscaler struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard object metadata. More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
v1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// behaviour of autoscaler. More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status.
// +optional
Spec HorizontalPodAutoscalerSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// current information about the autoscaler.
// +optional
Status HorizontalPodAutoscalerStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}Spec HorizontalPodAutoscalerSpec存的是hpa的描述信息,是可以通过kube-controller-manager配置对应flag的信息。包括最小副本数MinReplicas,最大副本数MaxReplicas,hpa对应的所有pods的平均的百分比形式的目标CPU利用率TargetCPUUtilizationPercentage。pkg/apis/autoscaling/v1/types.go:36 // specification of a horizontal pod autoscaler. type HorizontalPodAutoscalerSpec struct { // reference to scaled resource; horizontal pod autoscaler will learn the current resource consumption // and will set the desired number of pods by using its Scale subresource. ScaleTargetRef CrossVersionObjectReference `json:"scaleTargetRef" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=scaleTargetRef"` // lower limit for the number of pods that can be set by the autoscaler, default 1. // +optional MinReplicas *int32 `json:"minReplicas,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=minReplicas"` // upper limit for the number of pods that can be set by the autoscaler; cannot be smaller than MinReplicas. MaxReplicas int32 `json:"maxReplicas" protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=maxReplicas"` // target average CPU utilization (represented as a percentage of requested CPU) over all the pods; // if not specified the default autoscaling policy will be used. // +optional TargetCPUUtilizationPercentage *int32 `json:"targetCPUUtilizationPercentage,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=targetCPUUtilizationPercentage"` }Status HorizontalPodAutoscalerStatu存的是HPA的当前状态数据,包括前后两次scale的时间间隔ObservedGeneration,上一次scale的时间戳LastScaleTime,当前副本数CurrentReplicas,期望副本数DesiredReplicas,hpa对应的所有pods的平均的百分比形式的当前CPU利用率。pkg/apis/autoscaling/v1/types.go:52 // current status of a horizontal pod autoscaler type HorizontalPodAutoscalerStatus struct { // most recent generation observed by this autoscaler. // +optional ObservedGeneration *int64 `json:"observedGeneration,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=observedGeneration"` // last time the HorizontalPodAutoscaler scaled the number of pods; // used by the autoscaler to control how often the number of pods is changed. // +optional LastScaleTime *metav1.Time `json:"lastScaleTime,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=lastScaleTime"` // current number of replicas of pods managed by this autoscaler. CurrentReplicas int32 `json:"currentReplicas" protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=currentReplicas"` // desired number of replicas of pods managed by this autoscaler. DesiredReplicas int32 `json:"desiredReplicas" protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=desiredReplicas"` // current average CPU utilization over all pods, represented as a percentage of requested CPU, // e.g. 70 means that an average pod is using now 70% of its requested CPU. // +optional CurrentCPUUtilizationPercentage *int32 `json:"currentCPUUtilizationPercentage,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,5,opt,name=currentCPUUtilizationPercentage"` }
newInformer的代码可见,不管hpa resource的event为Add或者update,最终都是调用reconcileAutoscaler来触发HorizontalPodAutoscaler数据的更新。
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:272
func (a *HorizontalController) reconcileAutoscaler(hpa *autoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscaler) error {
...
// 获取对应resource的scale subresource数据。
scale, err := a.scaleNamespacer.Scales(hpa.Namespace).Get(hpa.Spec.ScaleTargetRef.Kind, hpa.Spec.ScaleTargetRef.Name)
...
// 得到当前副本数
currentReplicas := scale.Status.Replicas
cpuDesiredReplicas := int32(0)
cpuCurrentUtilization := new(int32)
cpuTimestamp := time.Time{}
cmDesiredReplicas := int32(0)
cmMetric := ""
cmStatus := ""
cmTimestamp := time.Time{}
desiredReplicas := int32(0)
rescaleReason := ""
timestamp := time.Now()
rescale := true
// 如果期望副本数为0,这不进行scale操作。
if scale.Spec.Replicas == 0 {
// Autoscaling is disabled for this resource
desiredReplicas = 0
rescale = false
}
// 期望副本数不能超过hpa中配置的最大副本数
else if currentReplicas > hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas {
rescaleReason = "Current number of replicas above Spec.MaxReplicas"
desiredReplicas = hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas
}
// 期望副本数不能低于配置的最小副本数
else if hpa.Spec.MinReplicas != nil && currentReplicas < *hpa.Spec.MinReplicas {
rescaleReason = "Current number of replicas below Spec.MinReplicas"
desiredReplicas = *hpa.Spec.MinReplicas
}
// 期望副本数最少为1
else if currentReplicas == 0 {
rescaleReason = "Current number of replicas must be greater than 0"
desiredReplicas = 1
}
// 如果当前副本数在Min和Max之间,则需要根据cpu或者custom metrics(如果加了对应的Annotation)数据进行算法计算得到期望副本数。
else {
// All basic scenarios covered, the state should be sane, lets use metrics.
cmAnnotation, cmAnnotationFound := hpa.Annotations[HpaCustomMetricsTargetAnnotationName]
if hpa.Spec.TargetCPUUtilizationPercentage != nil || !cmAnnotationFound {
// 根据cpu利用率计算期望副本数
cpuDesiredReplicas, cpuCurrentUtilization, cpuTimestamp, err = a.computeReplicasForCPUUtilization(hpa, scale)
if err != nil {
// 更新hpa的当前副本数
a.updateCurrentReplicasInStatus(hpa, currentReplicas)
return fmt.Errorf("failed to compute desired number of replicas based on CPU utilization for %s: %v", reference, err)
}
}
if cmAnnotationFound {
// 根据custom metrics数据计算期望副本数
cmDesiredReplicas, cmMetric, cmStatus, cmTimestamp, err = a.computeReplicasForCustomMetrics(hpa, scale, cmAnnotation)
if err != nil {
// 更新hpa的当前副本数
a.updateCurrentReplicasInStatus(hpa, currentReplicas)
return fmt.Errorf("failed to compute desired number of replicas based on Custom Metrics for %s: %v", reference, err)
}
}
// 取cpu和custom metric得到的期望副本数的最大值作为最终的desired replicas,并且要在min和max范围内。
rescaleMetric := ""
if cpuDesiredReplicas > desiredReplicas {
desiredReplicas = cpuDesiredReplicas
timestamp = cpuTimestamp
rescaleMetric = "CPU utilization"
}
if cmDesiredReplicas > desiredReplicas {
desiredReplicas = cmDesiredReplicas
timestamp = cmTimestamp
rescaleMetric = cmMetric
}
if desiredReplicas > currentReplicas {
rescaleReason = fmt.Sprintf("%s above target", rescaleMetric)
}
if desiredReplicas < currentReplicas {
rescaleReason = "All metrics below target"
}
if hpa.Spec.MinReplicas != nil && desiredReplicas < *hpa.Spec.MinReplicas {
desiredReplicas = *hpa.Spec.MinReplicas
}
// never scale down to 0, reserved for disabling autoscaling
if desiredReplicas == 0 {
desiredReplicas = 1
}
if desiredReplicas > hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas {
desiredReplicas = hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas
}
// Do not upscale too much to prevent incorrect rapid increase of the number of master replicas caused by
// bogus CPU usage report from heapster/kubelet (like in issue #32304).
if desiredReplicas > calculateScaleUpLimit(currentReplicas) {
desiredReplicas = calculateScaleUpLimit(currentReplicas)
}
// 根据currentReplicas和desiredReplicas的对比,以及scale时间是否满足配置间隔要求,决定是否此时需要rescale
rescale = shouldScale(hpa, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas, timestamp)
}
if rescale {
scale.Spec.Replicas = desiredReplicas
// 执行ScaleInterface的Update接口,触发调用API Server的对应resource的scale subresource的数据更新。其实最终会去修改对应rc或者deployment的replicas,然后由rc或deployment Controller去最终扩容或者缩容,使得副本数达到新的期望值。
_, err = a.scaleNamespacer.Scales(hpa.Namespace).Update(hpa.Spec.ScaleTargetRef.Kind, scale)
if err != nil {
a.eventRecorder.Eventf(hpa, v1.EventTypeWarning, "FailedRescale", "New size: %d; reason: %s; error: %v", desiredReplicas, rescaleReason, err.Error())
return fmt.Errorf("failed to rescale %s: %v", reference, err)
}
a.eventRecorder.Eventf(hpa, v1.EventTypeNormal, "SuccessfulRescale", "New size: %d; reason: %s", desiredReplicas, rescaleReason)
glog.Infof("Successfull rescale of %s, old size: %d, new size: %d, reason: %s",
hpa.Name, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas, rescaleReason)
} else {
desiredReplicas = currentReplicas
}
// 更新hpa resource的status数据
return a.updateStatus(hpa, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas, cpuCurrentUtilization, cmStatus, rescale)
}上面reconcileAutoscaler的代码很重要,把想说的都写到对应的注释了。其中computeReplicasForCPUUtilization和computeReplicasForCustomMetrics需要单独提出来看看,因为这两个方法是HPA算法的体现,实际上最终算法是在pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go:45#GetResourceReplicas和pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go:153#GetMetricReplicas实现的:
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go:45#GetResourceReplicas负责根据heapster提供的cpu利用率数据计算得到desired replicas number。pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go:153#GetMetricReplicas负责根据heapster提供的custom raw metric数据计算得到desired replicas number。
具体关于HPA算法的源码分析,我后续会单独写一篇博客,有兴趣的可以关注(对于绝大部分同学来说没必要关注,除非需要定制HPA算法时,才会具体去分析)。
总而言之,根据cpu和custom metric数据分别计算得到desired replicas后,取两者最大的值,但不能超过配置的Max Replicas。
稍等稍等,计算出了desired replicas还还够,我们还要通过shouldScale看看现在距离上一次弹性伸缩的时间间隔是否满足条件:
- 两次缩容的间隔不得小于5min。
- 两次扩容的间隔不得小于3min。
shouldScale的代码如下:
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:387
...
var downscaleForbiddenWindow = 5 * time.Minute
var upscaleForbiddenWindow = 3 * time.Minute
...
func shouldScale(hpa *autoscaling.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas int32, timestamp time.Time) bool {
if desiredReplicas == currentReplicas {
return false
}
if hpa.Status.LastScaleTime == nil {
return true
}
// Going down only if the usageRatio dropped significantly below the target
// and there was no rescaling in the last downscaleForbiddenWindow.
if desiredReplicas < currentReplicas && hpa.Status.LastScaleTime.Add(downscaleForbiddenWindow).Before(timestamp) {
return true
}
// Going up only if the usage ratio increased significantly above the target
// and there was no rescaling in the last upscaleForbiddenWindow.
if desiredReplicas > currentReplicas && hpa.Status.LastScaleTime.Add(upscaleForbiddenWindow).Before(timestamp) {
return true
}
return false
}只有满足这个条件后,接着才会调用Scales.Update接口与API Server交互,完成Scale对应的RC的replicas的设置。以rc Controller为例(deployment Controller的雷同),API Server对应的Scales.Update接口的实现逻辑如下:
pkg/registry/core/rest/storage_core.go:91
func (c LegacyRESTStorageProvider) NewLegacyRESTStorage(restOptionsGetter generic.RESTOptionsGetter) (LegacyRESTStorage, genericapiserver.APIGroupInfo, error) {
...
if autoscalingGroupVersion := (schema.GroupVersion{Group: "autoscaling", Version: "v1"}); registered.IsEnabledVersion(autoscalingGroupVersion) {
apiGroupInfo.SubresourceGroupVersionKind["replicationcontrollers/scale"] = autoscalingGroupVersion.WithKind("Scale")
}
...
restStorageMap := map[string]rest.Storage{
...
"replicationControllers": controllerStorage.Controller,
"replicationControllers/status": controllerStorage.Status,
...
}
return restStorage, apiGroupInfo, nil
}
pkg/registry/core/controller/etcd/etcd.go:124
func (r *ScaleREST) Update(ctx api.Context, name string, objInfo rest.UpdatedObjectInfo) (runtime.Object, bool, error) {
rc, err := r.registry.GetController(ctx, name, &metav1.GetOptions{})
if err != nil {
return nil, false, errors.NewNotFound(autoscaling.Resource("replicationcontrollers/scale"), name)
}
oldScale := scaleFromRC(rc)
obj, err := objInfo.UpdatedObject(ctx, oldScale)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, err
}
if obj == nil {
return nil, false, errors.NewBadRequest("nil update passed to Scale")
}
scale, ok := obj.(*autoscaling.Scale)
if !ok {
return nil, false, errors.NewBadRequest(fmt.Sprintf("wrong object passed to Scale update: %v", obj))
}
if errs := validation.ValidateScale(scale); len(errs) > 0 {
return nil, false, errors.NewInvalid(autoscaling.Kind("Scale"), scale.Name, errs)
}
// 设置rc对应spec.replicas为Scale中的期望副本数
rc.Spec.Replicas = scale.Spec.Replicas
rc.ResourceVersion = scale.ResourceVersion
// 更新到etcd
rc, err = r.registry.UpdateController(ctx, rc)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, err
}
return scaleFromRC(rc), false, nil
}了解kubernetes rc Controller的同学很清楚,修改rc的replicas后,会被rc Controller watch到,然后触发rc Controller去执行创建或者销毁对应差额数量的replicas,最终使得其副本数达到HPA计算得到的期望值。也就是说,最终由rc controller去执行具体的扩容或缩容动作。
最后,来看看HorizontalController的Run方法:
pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go:130
func (a *HorizontalController) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
glog.Infof("Starting HPA Controller")
go a.controller.Run(stopCh)
<-stopCh
glog.Infof("Shutting down HPA Controller")
}很简单,就是负责 HPA Resource的ListWatch,将change更新到对应的store(cache)。
HPA Resource的同步周期通过
--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-sync-period设置,默认值为30s。