Linux文件编程--系统调用
linux文件编程可以使用两种方法,
1)linux系统调用 2)C语言库函数
1)依赖linux操作系统,2)与操作系统对立。
linux系统调用:
1.文件创建
int creat(const char *filename,mode_t mode)
mode: S_IRUSR(可读,4) S_IWUSR(可写,2) S_IXUSR(可执行,1) S_IRWXU(可读写执行,7)
返回值:creat()会返回新的文件描述符,若有错误发生则会返回-1,并把错误代码设给errno。
2.文件打开
int open(const char *pathname,int flags)
int open(const char *pathname,int flags,mode_t mode)
flags: O_RDONLY(只读打开),O_WRONLY(只写打开),O_RDWR(读写打开),O_CREAT(创建打开),
O_APPEND(追加打开),O_NOBLOCK(非阻塞打开)
返回值:若所有欲核查的权限都通过了检查则返回0 值,表示成功,只要有一个权限被禁止则返回-1。
3.文件关闭
int close(int fd)
fd:文件描述符
返回值:若文件顺利关闭则返回0,发生错误时返回-1。
4.文件读
int read(int fd,const void *buf,size_t length)
返回值:读取字节数。
5.文件写
int write(int fd,const void *buf,size_t length)
返回值:写入字节数。
6.文件定位
int lseek(int fd,offset_t offset,int whence)
wherece:SEEK_SET(文件头),SEEK_CUR(文件当前位置),SEEK_END(文件尾)
返回值:指针相对头文件长度。
7.访问判断
int access(const char *pathname,int mode)
mode:R_OK(文件可读) W_OK(文件可写) X_OK(文件可执行)F_OK(文件存在)
返回值:成功,返回0;失败返回-1。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
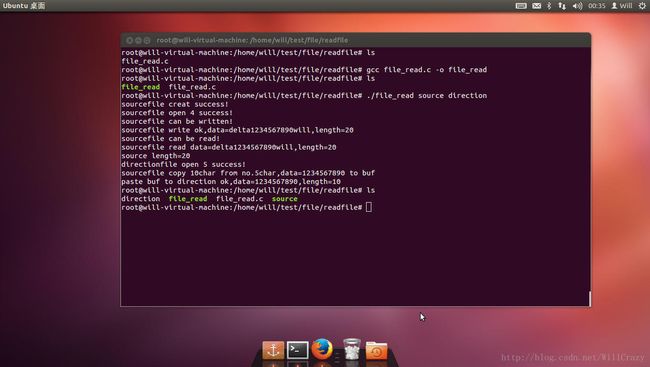
//拷贝source文件内容 到 direction
int main(int argc,char *argv[1])
{
int fd_source,fd_direction;
int read_length,write_length,source_length;
char source_data[20]={"delta1234567890will"};
char source_readout[20];
char buf[10];
if(argc<3)
{
puts("please input the sourcefile & direction pathname!\n");
exit(1);
}
//创建sourcefile
if(creat(argv[1],0777)<0)
printf("sourcefile creat failurei\n");
else
printf("sourcefile creat success!\n");
//打开创建好的sourcefile
if((fd_source=open(argv[1],O_RDWR))<0)
{
perror("sourcefile open failure!\n");
exit(1);
}
else
{
printf("sourcefile open %d success!\n",fd_source);
}
//往sourcefile写入内容
if(access(argv[1],W_OK)==0)//判断sourcefile是否可写?
printf("sourcefile can be written!\n");
write_length=write(fd_source,source_data,20);//把从sourcefile内容写到direction里面;
if(write_length!=-1)
printf("sourcefile write ok,data=%s,length=%d\n",source_data,write_length);//写入字节数
//读出刚写入sourcefile内容
if(access(argv[1],R_OK)==0)//判断sourcefile是否可读?
printf("sourcefile can be read!\n");
source_length=lseek(fd_source,0,SEEK_SET);
read_length=read(fd_source,source_readout,20);//读sourcefile内容
if(read_length!=-1)
printf("sourcefile read data=%s,length=%d\n",source_readout,read_length);//输出读出内容;
//计算sourcefile长度
source_length=lseek(fd_source,0,SEEK_END);
printf("source length=%d\n",source_length);//lseek计算文件长度
//打开directionfile
if((fd_direction=open(argv[2],O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0666))<0)
{
perror("directionfile open failure!\n");
exit(1);
}
else
{
printf("directionfile open %d success!\n",fd_direction);
}
//从sourcefile第5个字符开始,连续拷贝10个字符到buf
lseek(fd_source,5,SEEK_SET);//lseek定位到sourcefile第五个字符
read_length=read(fd_source,buf,10);//读sourcefile内容
if(read_length!=-1)
printf("sourcefile copy 10char from no.5char,data=%s to buf\n",buf);//输出读出内容;
//把从sourcefile里面读取出来的内容放到direction里面
write_length=write(fd_direction,buf,10);//把从sourcefile内容写到direction里面;
if(write_length!=-1)
printf("paste buf to direction ok,data=%s,length=%d\n",buf,write_length);//写入字节数
close(fd_source);
close(fd_direction);
exit(0);
}