一、前言
上一篇《Spring Boot 入门之基础篇(一)》介绍了 Spring Boot 的环境搭建以及项目启动打包等基础内容,本篇继续深入介绍 Spring Boot 与 Web 开发相关的知识。
二、整合模板引擎
由于 jsp 不被 SpringBoot 推荐使用,所以模板引擎主要介绍 Freemarker 和 Thymeleaf。
2.1 整合 Freemarker
2.1.1 添加 Freemarker 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarkerartifactId>
dependency>2.1.2 添加 Freemarker 模板配置
在 application.properties 中添加如下内容:
spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false
spring.freemarker.cache=true
spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true
spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8
spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html
spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false
spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false
spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=false
spring.freemarker.prefix=
spring.freemarker.suffix=.ftl上述配置都是默认值。
2.1.3 Freemarker 案例演示
在 controller 包中创建 FreemarkerController:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("freemarker")
public class FreemarkerController {
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello(Map map) {
map.put("msg", "Hello Freemarker");
return "hello";
}
}在 templates 目录中创建名为 hello.ftl 文件,内容如下:
html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<link href="/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>${msg}h2>
div>
body>
html>结果如下:
2.2 整合 Thymeleaf
2.2.1 添加 Thymeleaf 依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>2.2.2 添加 Thymeleaf 模板配置
在 application.properties 中添加如下内容:
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html上述配置都是默认值。
2.2.3 Thymeleaf 案例演示
在 controller 包中创建 ThymeleafController:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafController {
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello(Map map) {
map.put("msg", "Hello Thymeleaf");
return "hello";
}
}在 template 目录下创建名为 hello.html 的文件,内容如下:
html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Documenttitle>
<link href="/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2 th:text="${msg}">h2>
div>
body>
html>结果如下:
三、整合 Fastjson
3.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.35version>
dependency>3.2 整合 Fastjson
创建一个配置管理类 WebConfig ,如下:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat);
fastJsonHttpMessageConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
HttpMessageConverter converter = fastJsonHttpMessageConverter;
return new HttpMessageConverters(converter);
}
}3.3 演示案例:
创建一个实体类 User:
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
}getter 和 setter 此处省略。
创建控制器类 FastjsonController :
@Controller
@RequestMapping("fastjson")
public class FastJsonController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public User test() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("jack");
user.setPassword("jack123");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
return user;
}
}打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test,结果如下图:
此时,还不能看出 Fastjson 是否正常工作,我们在 User 类中使用 Fastjson 的注解,如下内容:
@JSONField(format="yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birthday;再次访问 http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test,结果如下图:
日期格式与我们修改的内容格式一致,说明 Fastjson 整合成功。
四、自定义 Servlet
4.1 编写 Servlet
public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
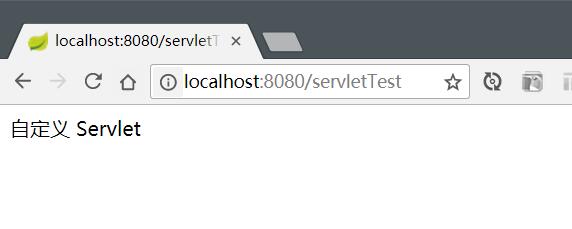
resp.getWriter().write("自定义 Servlet");
}
}4.2 注册 Servlet
将 Servelt 注册成 Bean。在上文创建的 WebConfig 类中添加如下代码:
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean() {
return new ServletRegistrationBean(new ServletTest(),"/servletTest");
}结果如下:
五、自定义过滤器/第三方过滤器
5.1 编写过滤器
public class TimeFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("=======初始化过滤器=========");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
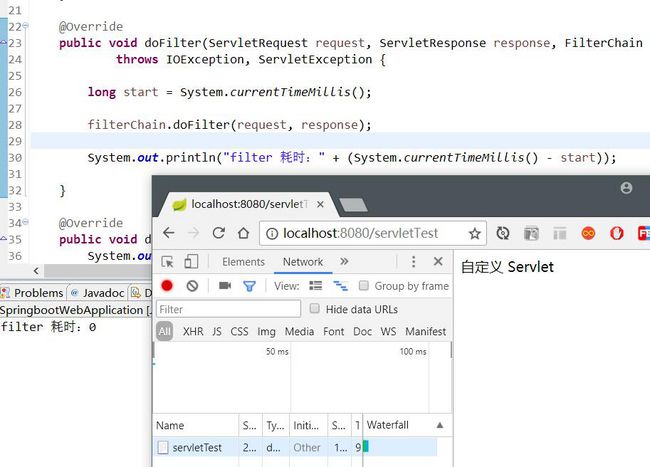
System.out.println("filter 耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("=======销毁过滤器=========");
}
}5.2 注册过滤器
要是该过滤器生效,有两种方式:
1) 使用 @Component 注解
2) 添加到过滤器链中,此方式适用于使用第三方的过滤器。将过滤器写到 WebConfig 类中,如下:
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean timeFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
TimeFilter timeFilter = new TimeFilter();
registrationBean.setFilter(timeFilter);
List urls = new ArrayList<>();
urls.add("/*");
registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(urls);
return registrationBean;
} 结果如下:
六、自定义监听器
6.1 编写监听器
public class ListenerTest implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
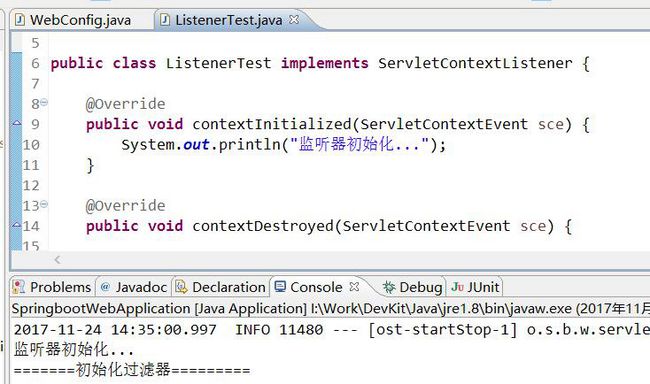
System.out.println("监听器初始化...");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}6.2 注册监听器
注册监听器为 Bean,在 WebConfig 配置类中添加如下代码:
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean servletListenerRegistrationBean() {
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(new ListenerTest());
} 当启动容器时,结果如下:
针对自定义 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener 的配置,还有另一种方式:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootWebApplication implements ServletContextInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// 配置 Servlet
servletContext.addServlet("servletTest",new ServletTest())
.addMapping("/servletTest");
// 配置过滤器
servletContext.addFilter("timeFilter",new TimeFilter())
.addMappingForUrlPatterns(EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST),true,"/*");
// 配置监听器
servletContext.addListener(new ListenerTest());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootWebApplication.class, args);
}
}七、自定义拦截器
7.1 编写拦截器
使用 @Component 让 Spring 管理其生命周期:
@Component
public class TimeInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("========preHandle=========");
System.out.println(((HandlerMethod)handler).getBean().getClass().getName());
System.out.println(((HandlerMethod)handler).getMethod().getName());
request.setAttribute("startTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
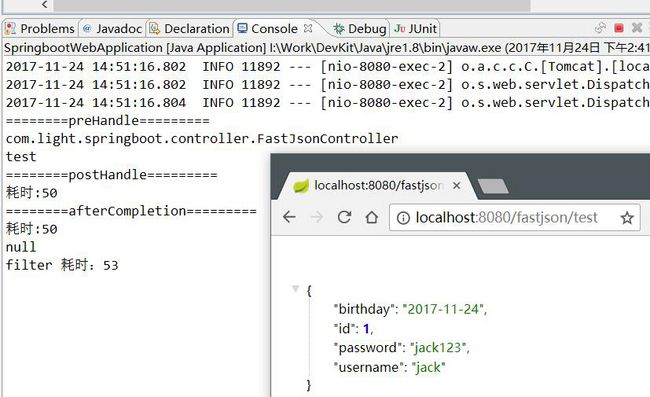
System.out.println("========postHandle=========");
Long start = (Long) request.getAttribute("startTime");
System.out.println("耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception exception)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("========afterCompletion=========");
Long start = (Long) request.getAttribute("startTime");
System.out.println("耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
System.out.println(exception);
}
}7.2 注册拦截器
编写拦截器后,我们还需要将其注册到拦截器链中,如下配置:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private TimeInterceptor timeInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(timeInterceptor);
}
}请求一个 controller ,结果如下:
八、配置 AOP 切面
8.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>8.2 编写切面类
使用 @Component,@Aspect 标记到切面类上:
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimeAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.light.springboot.controller.FastJsonController..*(..))")
public Object method(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
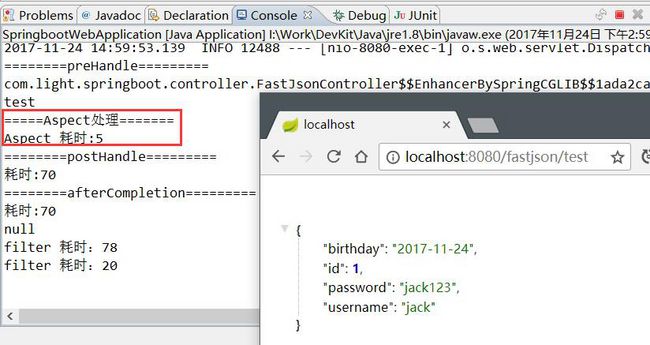
System.out.println("=====Aspect处理=======");
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
for (Object arg : args) {
System.out.println("参数为:" + arg);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object object = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("Aspect 耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
return object;
}
}请求 FastJsonController 控制器的方法,结果如下:
九、错误处理
9.1 友好页面
先演示非友好页面,修改 FastJsonController 类中的 test 方法:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("fastjson")
public class FastJsonController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public User test() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("jack");
user.setPassword("jack123");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
// 模拟异常
int i = 1/0;
return user;
}
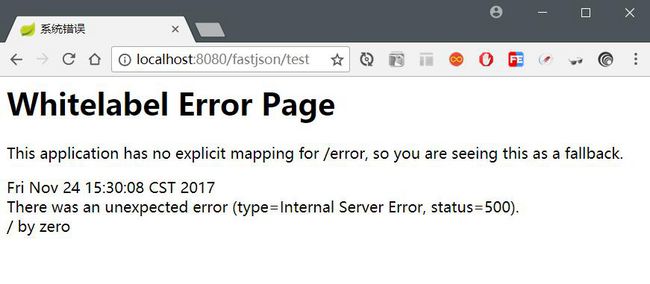
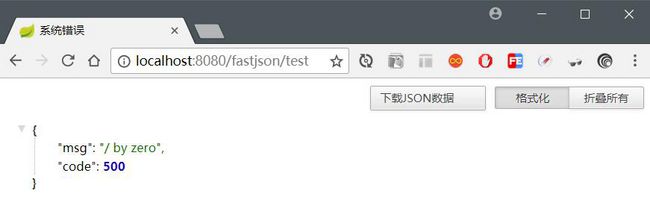
}浏览器请求:http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test,结果如下:
当系统报错时,返回到页面的内容通常是一些杂乱的代码段,这种显示对用户来说不友好,因此我们需要自定义一个友好的提示系统异常的页面。
在 src/main/resources 下创建 /public/error,在该目录下再创建一个名为 5xx.html 文件,该页面的内容就是当系统报错时返回给用户浏览的内容:
html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>系统错误title>
<link href="/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>系统内部错误h2>
div>
body>
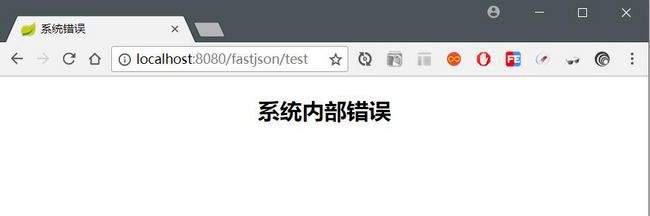
html>路径时固定的,Spring Boot 会在系统报错时将返回视图指向该目录下的文件。
如下图:
上边处理的 5xx 状态码的问题,接下来解决 404 状态码的问题。
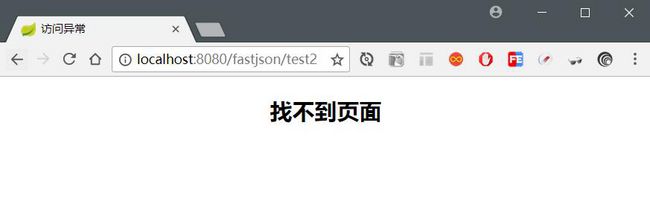
当出现 404 的情况时,用户浏览的页面也不够友好,因此我们也需要自定义一个友好的页面给用户展示。
在 /public/error 目录下再创建一个名为 404.html 的文件:
html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>访问异常title>
<link href="/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>找不到页面h2>
div>
body>
html>我们请求一个不存在的资源,如:http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test2,结果如下图:
9.2 全局异常捕获
如果项目前后端是通过 JSON 进行数据通信,则当出现异常时可以常用如下方式处理异常信息。
编写一个类充当全局异常的处理类,需要使用 @ControllerAdvice 和 @ExceptionHandler 注解:
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalDefaultExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理 Exception 类型的异常
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map defaultExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("code", 500);
map.put("msg", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
} 其中,方法名为任意名,入参一般使用 Exception 异常类,方法返回值可自定义。
启动项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test,结果如下图:
我们还可以自定义异常,在全局异常的处理类中捕获和判断,从而对不同的异常做出不同的处理。
十、文件上传和下载
10.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-iogroupId>
<artifactId>commons-ioartifactId>
<version>2.4version>
dependency>10.2 实现
编写一个实体类,用于封装返回信息:
public class FileInfo {
private String path;
public FileInfo(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
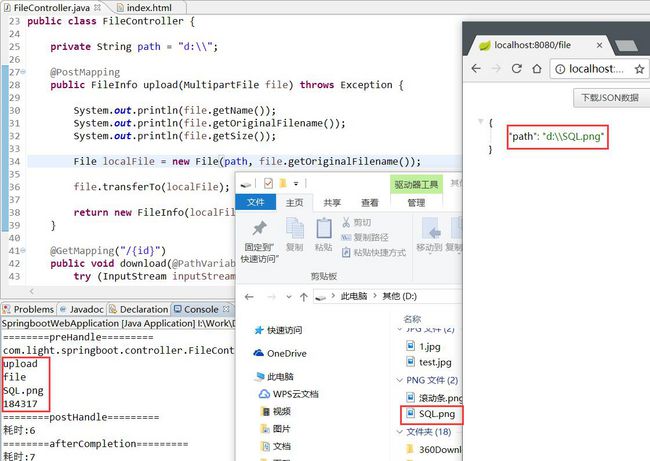
}编写 Controller,用于处理文件上传下载:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileController {
private String path = "d:\\";
@PostMapping
public FileInfo upload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println(file.getSize());
File localFile = new File(path, file.getOriginalFilename());
file.transferTo(localFile);
return new FileInfo(localFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public void download(@PathVariable String id, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(path, id + ".jpg"));
OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();) {
response.setContentType("application/x-download");
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + id + ".jpg");
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, outputStream);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}基本上都是在学习 javaweb 时用到的 API。
文件上传测试结果如下图:
十一、CORS 支持
前端页面:
html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>跨域测试title>
head>
<body>
<button id="test">测试button>
<script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.12.3.min.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
$("#test").on("click", function() {
$.ajax({
"url": "http://localhost:8080/fastjson/test",
"type": "get",
"dataType": "json",
"success": function(data) {
console.log(data);
}
})
});
});
</script>
body>
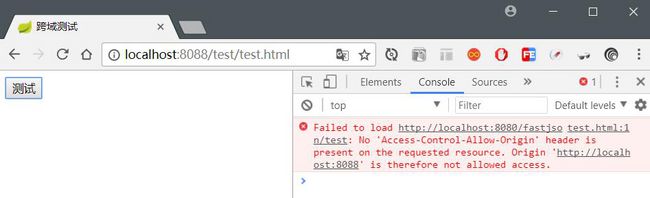
</html>通过 http 容器启动前端页面代码,笔者使用 Sublime Text 的插件启动的,测试结果如下:
从图中可知,前端服务器启动端口为 8088 与后端服务器 8080 不同源,因此出现跨域的问题。
现在开始解决跨域问题,可以两种维度控制客户端请求。
粗粒度控制:
方式一
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/fastjson/**")
.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:8088");// 允许 8088 端口访问
}
};
}
}方式二
@Configuration
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/fastjson/**")
.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:8088");// 允许 8088 端口访问
}
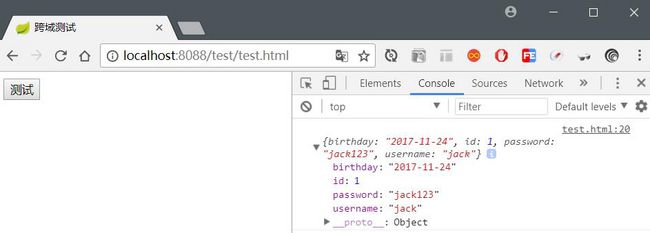
}配置后,重新发送请求,结果如下:
细粒度控制:
在 FastJsonController 类中的方法上添加 @CrossOrigin(origins="xx") 注解:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@CrossOrigin(origins="http://localhost:8088")
public User test() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("jack");
user.setPassword("jack123");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
return user;
}在使用该注解时,需要注意 @RequestMapping 使用的请求方式类型,即 GET 或 POST。
十二、整合 WebSocket
12.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocketartifactId>
dependency>12.2 实现方式
方式一:
该方式只适用于通过 jar 包直接运行项目的情况。
WebSocket 配置类:
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}WebSocket 处理类:
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/webSocketServer/{userName}")
@Component
public class WebSocketServer {
private static final Set connections = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
private String nickname;
private Session session;
private static String getDatetime(Date date) {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return format.format(date);
}
@OnOpen
public void start(@PathParam("userName") String userName, Session session) {
this.nickname = userName;
this.session = session;
connections.add(this);
String message = String.format("* %s %s", nickname, "加入聊天!");
broadcast(message);
}
@OnClose
public void end() {
connections.remove(this);
String message = String.format("* %s %s", nickname, "退出聊天!");
broadcast(message);
}
@OnMessage
public void pushMsg(String message) {
broadcast("【" + this.nickname + "】" + getDatetime(new Date()) + " : " + message);
}
@OnError
public void onError(Throwable t) throws Throwable {
}
private static void broadcast(String msg) {
// 广播形式发送消息
for (WebSocketServer client : connections) {
try {
synchronized (client) {
client.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
connections.remove(client);
try {
client.session.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String message = String.format("* %s %s", client.nickname, "断开连接");
broadcast(message);
}
}
}
} 前端页面:
html>
<html>
<head lang="zh">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap-theme.min.css">
<script src="js/jquery-1.12.3.min.js">script>
<script src="js/bootstrap.js">script>
<style type="text/css">
#msg {
height: 400px;
overflow-y: auto;
}
#userName {
width: 200px;
}
#logout {
display: none;
}
style>
<title>webSocket测试title>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="page-header" id="tou">webSocket及时聊天Demo程序div>
<p class="text-right" id="logout">
<button class="btn btn-danger" id="logout-btn">退出button>
p>
<div class="well" id="msg">div>
<div class="col-lg">
<div class="input-group">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="发送信息..." id="message"> <span class="input-group-btn">
<button class="btn btn-default" type="button" id="send"
disabled="disabled">发送button>
span>
div>
<div class="input-group">
<input id="userName" type="text" class="form-control" name="userName" placeholder="输入您的用户名" />
<button class="btn btn-default" type="button" id="connection-btn">建立连接button>
div>
div>
div>
div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
var websocket;
$("#connection-btn").bind("click", function() {
var userName = $("#userName").val();
if (userName == null || userName == "") {
alert("请输入您的用户名");
return;
}
connection(userName);
});
function connection(userName) {
var host = window.location.host;
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
websocket = new WebSocket("ws://" + host +
"/webSocketServer/" + userName);
} else if ('MozWebSocket' in window) {
websocket = new MozWebSocket("ws://" + host +
"/webSocketServer/" + userName);
}
websocket.onopen = function(evnt) {
$("#tou").html("链接服务器成功!")
$("#send").prop("disabled", "");
$("#connection-btn").prop("disabled", "disabled");
$("#logout").show();
};
websocket.onmessage = function(evnt) {
$("#msg").html($("#msg").html() + "
" + evnt.data);
};
websocket.onerror = function(evnt) {
$("#tou").html("报错!")
};
websocket.onclose = function(evnt) {
$("#tou").html("与服务器断开了链接!");
$("#send").prop("disabled", "disabled");
$("#connection-btn").prop("disabled", "");
$("#logout").hide();
}
}
function send() {
if (websocket != null) {
var $message = $("#message");
var data = $message.val();
if (data == null || data == "") {
return;
}
websocket.send(data);
$message.val("");
} else {
alert('未与服务器链接.');
}
}
$('#send').bind('click', function() {
send();
});
$(document).on("keypress", function(event) {
if (event.keyCode == "13") {
send();
}
});
$("#logout-btn").on("click", function() {
websocket.close(); //关闭TCP连接
});
});
</script>
body>
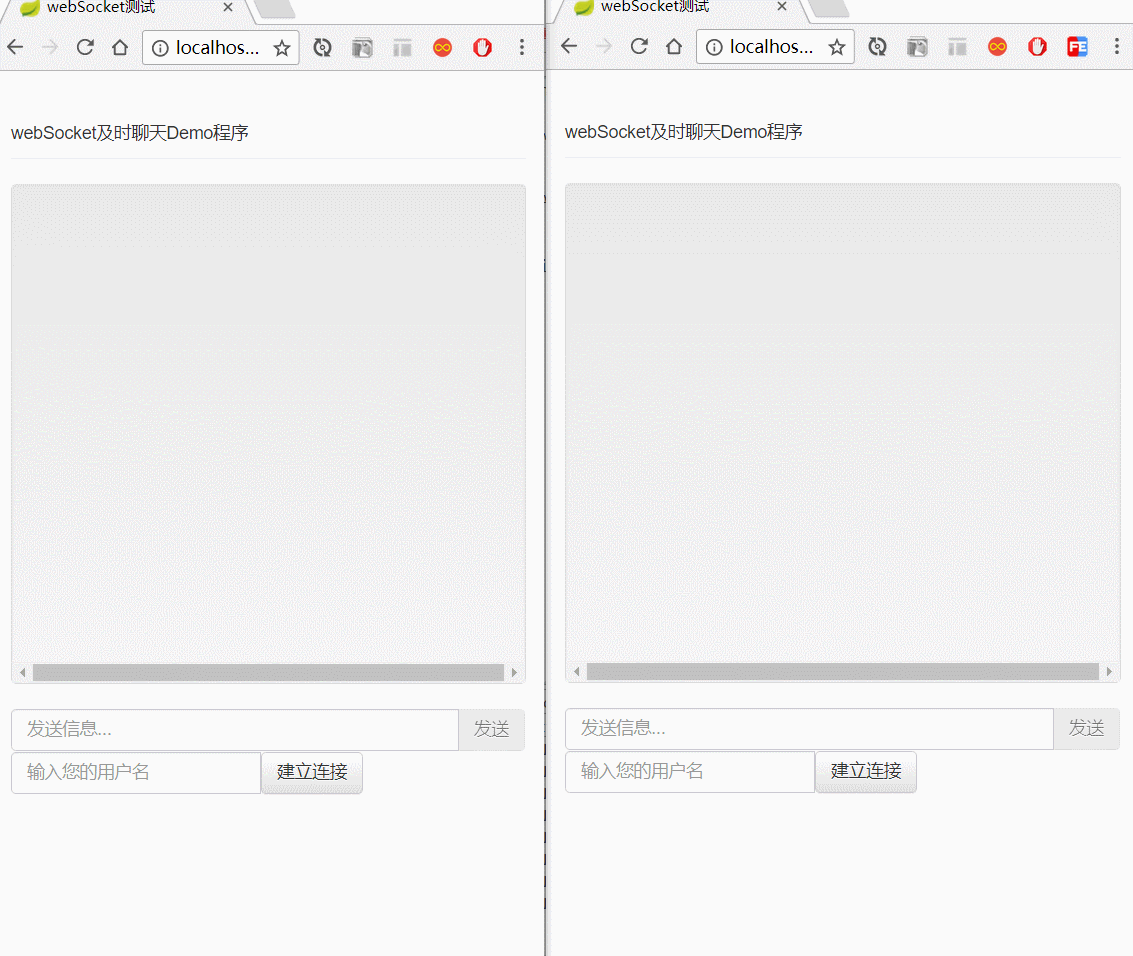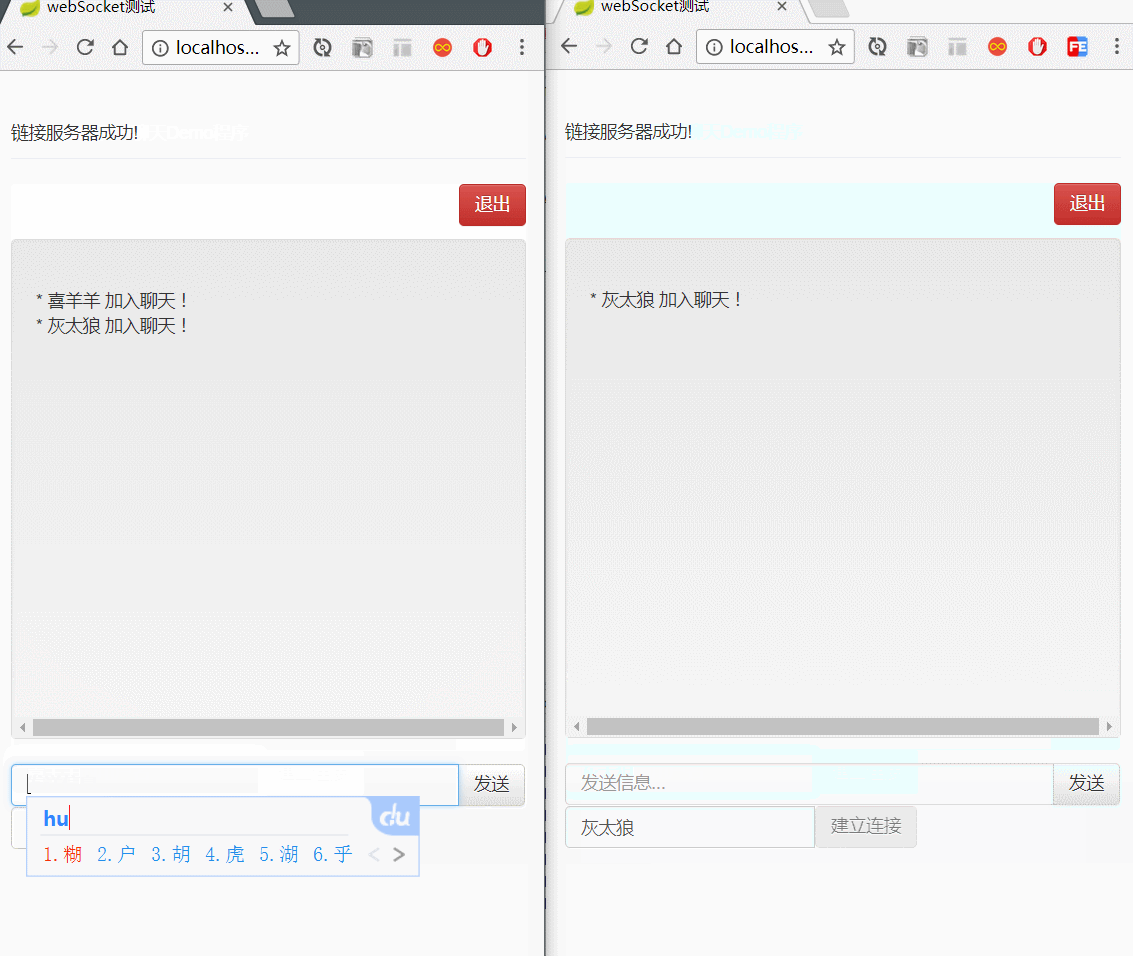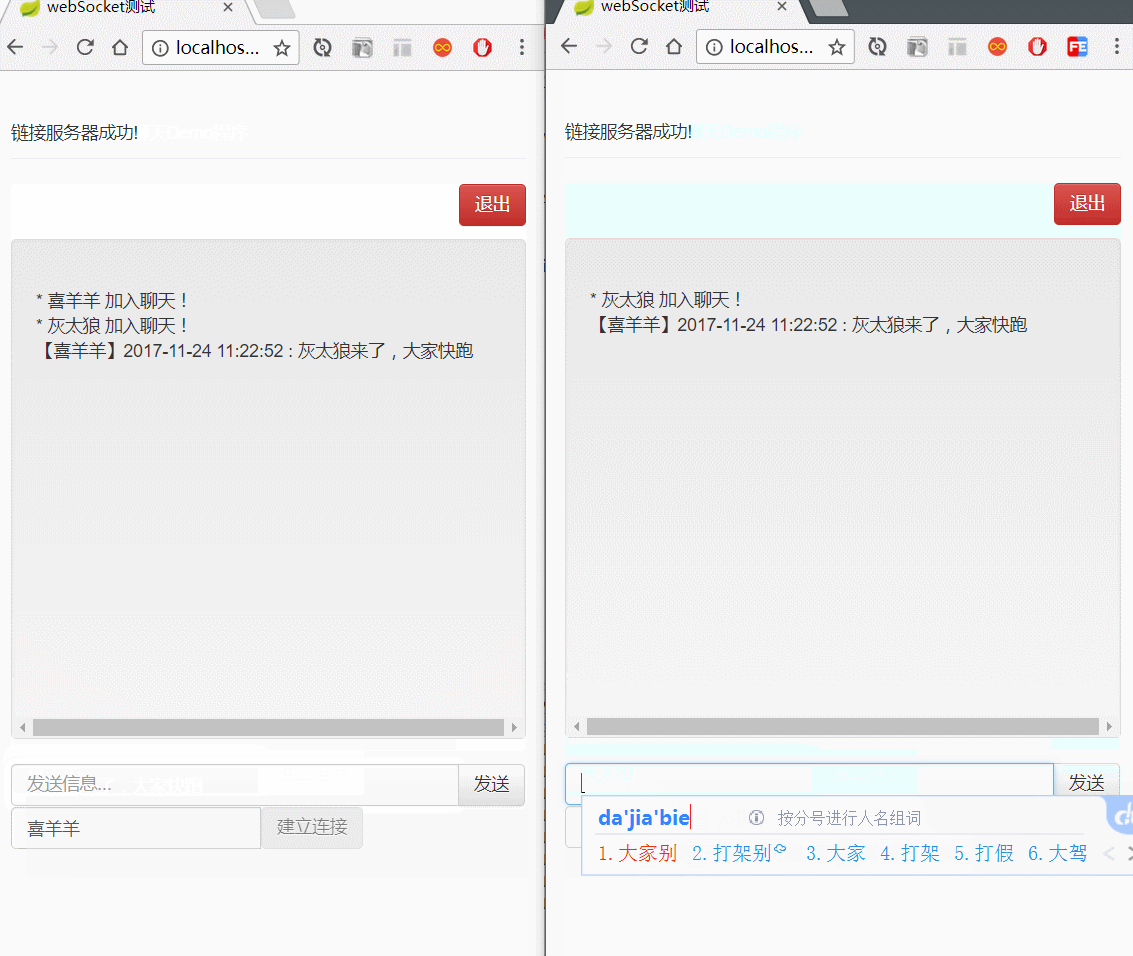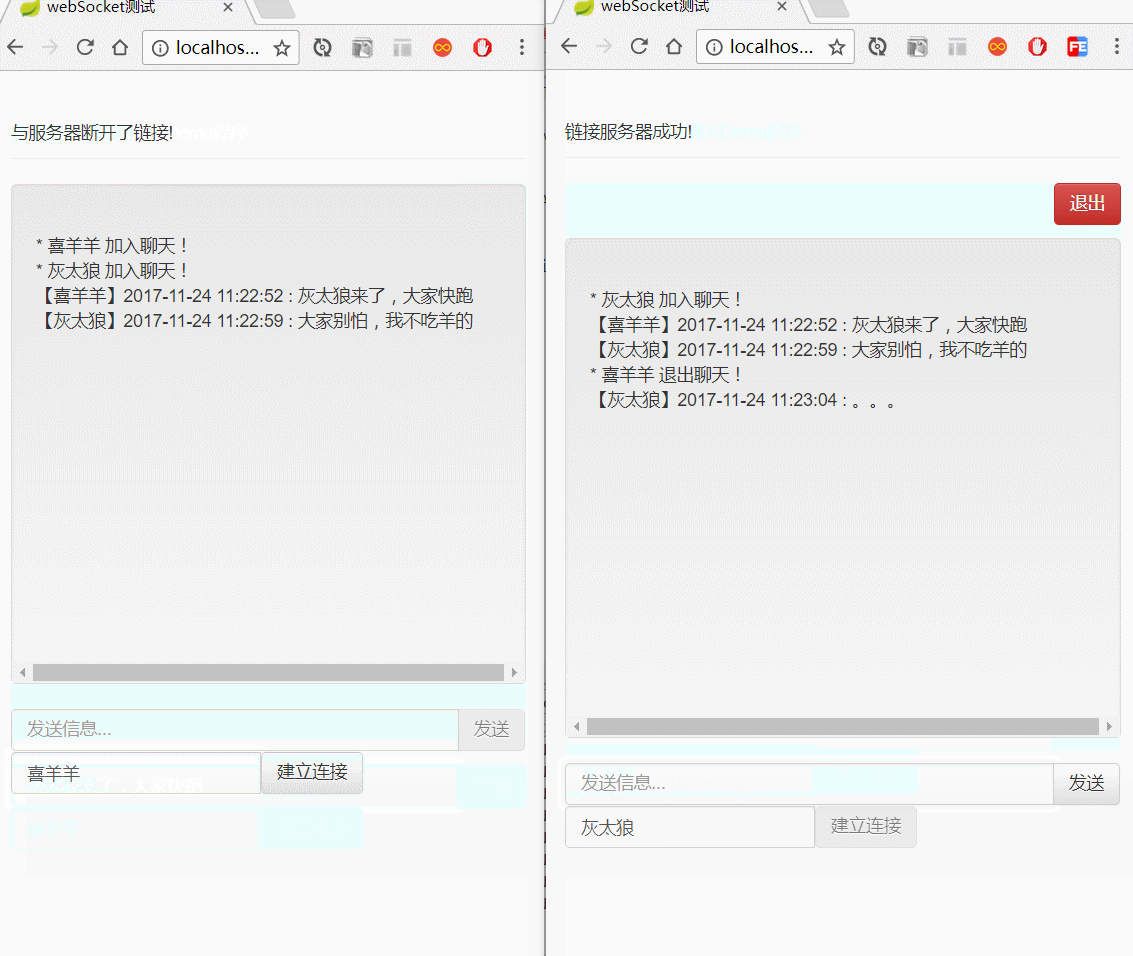
</html>演示图如下:
如果使用该方式实现 WebSocket 功能并打包成 war 运行会报错:
javax.websocket.DeploymentException: Multiple Endpoints may not be deployed to the same path 方式二:
该方式适用于 jar 包方式运行和 war 方式运行。
WebSocket 配置类:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(webSocketServer(), "/webSocketServer/*");
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler webSocketServer() {
return new WebSocketServer();
}
} WebSocket 处理类:
public class WebSocketServer extends TextWebSocketHandler {
private static final Map connections = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static String getDatetime(Date date) {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return format.format(date);
}
/**
* 建立连接
*/
@Override
public void afterConnectionEstablished(WebSocketSession session) throws Exception {
String uri = session.getUri().toString();
String userName = uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
String nickname = URLDecoder.decode(userName, "utf-8");
connections.put(session, nickname);
String message = String.format("* %s %s", nickname, "加入聊天!");
broadcast(new TextMessage(message));
}
/**
* 断开连接
*/
@Override
public void afterConnectionClosed(WebSocketSession session, CloseStatus status) throws Exception {
String nickname = connections.remove(session);
String message = String.format("* %s %s", nickname, "退出聊天!");
broadcast(new TextMessage(message));
}
/**
* 处理消息
*/
@Override
protected void handleTextMessage(WebSocketSession session, TextMessage message) throws Exception {
String msg = "【" + connections.get(session) + "】" + getDatetime(new Date()) + " : " + message.getPayload();
broadcast(new TextMessage(msg));
}
private static void broadcast(TextMessage msg) {
// 广播形式发送消息
for (WebSocketSession session : connections.keySet()) {
try {
synchronized (session) {
session.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
connections.remove(session);
try {
session.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
String message = String.format("* %s %s", connections.get(session), "断开连接");
broadcast(new TextMessage(message));
}
}
}
} 运行结果与上图一致。
十三、整合 Swagger2
13.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>13.2 配置
重新创建一个配置类,如下:
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Configuration {
@Bean
public Docket accessToken() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("api")// 定义组
.select() // 选择那些路径和 api 会生成 document
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.light.springboot.controller")) // 拦截的包路径
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/*/.*"))// 拦截的接口路径
.build() // 创建
.apiInfo(apiInfo()); // 配置说明
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()//
.title("Spring Boot 之 Web 篇")// 标题
.description("spring boot Web 相关内容")// 描述
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.extlight.com")//
.contact(new Contact("moonlightL", "http://www.extlight.com", "[email protected]"))// 联系
.version("1.0")// 版本
.build();
}
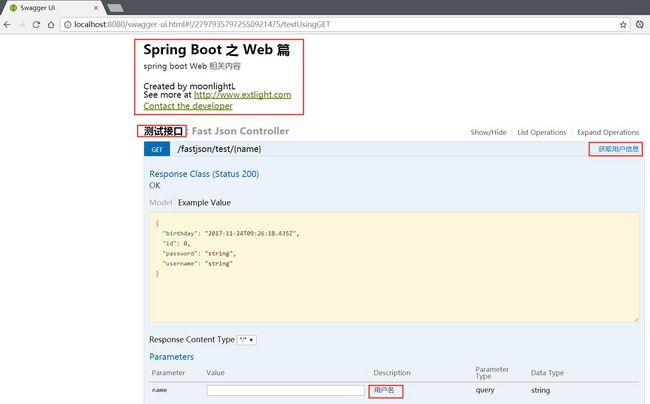
}为了能更好的说明接口信息,我们还可以在 Controller 类上使用 Swagger2 相关注解说明信息。
我们以 FastJsonController 为例:
@Api(value = "FastJson测试", tags = { "测试接口" })
@RestController
@RequestMapping("fastjson")
public class FastJsonController {
@ApiOperation("获取用户信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "name", value = "用户名", dataType = "string", paramType = "query")
@GetMapping("/test/{name}")
public User test(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername(name);
user.setPassword("jack123");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
return user;
}
}注意,上边的方法是用 @GetMapping 注解,如果只是使用 @RequestMapping 注解,不配置 method 属性,那么 API 文档会生成 7 种请求方式。
启动项目,打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html。结果如下图: