centos 7 编译安装mysql5.7.20支持systemd及报错事项
一、MYSQL的新特性及环境
1、性能更快3倍
2、新的优化器
3、原生的JSON支持
4、多源复制
5、GIS空间扩展
本次部署环境
Linux:CentOS Linux release 7.3.1611 (Core)
MYSQL版本:mysql-5.7.20
二、boost概述
boost是开源免费的第三方库,它是一个非常优秀的库,是C++标准的最好实践之一。
在这里讲使用boost库主要是在对mysql的数据备份时,将会使用的percona-xtrabackup需要用到boost库。
对mysql数据库的备份及其中的报错在我的另一篇文章记录。
三、编译安装
直接下载包
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz
tar -xf mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz解决依赖问题
yum install -y cmake gcc-c++ ncurses-devel perl-Data-Dumper boost boost-doc boost-develmkdir /usr/local/mysql
mkdir /usr/local/mysql/mydata
mkdir /usr/local/mysql/conf
useradd mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql /usr/local/mysql/cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql \
-DMYSQL_DATADIR=/usr/local/mysql/mydata \
-DSYSCONFDIR=/usr/local/mysql/conf \
-DMYSQL_USER=mysql -DWITH_MYISAM_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \
-DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/usr/local/mysql/mysql.sock \
-DMYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306 -DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all \
-DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci \
-DWITH_DEBUG=0 -DMYSQL_MAINTAINER_MODE=0 \
-DWITH_SSL:STRING=bundled -DWITH_ZLIB:STRING=bundled \
-DWITH_SYSTEMD=1 -DDOWNLOAD_BOOST=1 -DWITH_BOOST=./boost一定要使用boost,./boost表示是boost的存放路径
-DWITH_SYSTEMD=1 这是MySQL 5.7原生支持Systemd的选项,如果要是用systemctl启动,就必须开启。
在后面将对system的选项,进行解读,其他选项就不多解析。
make && make install配置my.cnf文件
mv /etc/my.cnf /usr/local/mysql/conf/
cd /usr/local/mysql/conf
vim my.cnf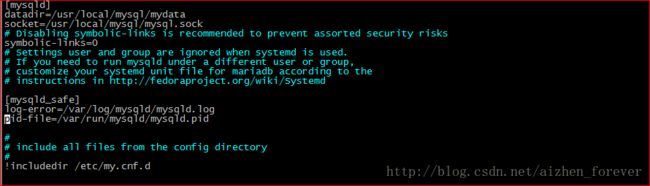
改完my.cnf文件, 一定要将文件属主改为mysql,否则启动不了。
chown mysql:mysql my.cnf根据my.cnf的配置,如上图,创建mysqld_safe所需的目录及授权。
mkdir /var/log/mysqld
mkdir /var/run/mysqld
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/log/mysqld
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld在 mysqld.service ,把默认的pid文件指定到了 /var/run/mysqld/ 目录,把默认的log文件指定到/var/log/mysql/目录(可自定义),而并没有事先建立该目录,因此要手动建立该目录并把权限赋给 mysql 用户。
对数据库的初始化。
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/mydata[root@localhost support-files]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/mydata
2017-11-10T17:27:54.190490Z 0 [Warning] TIMESTAMP with implicit DEFAULT value is deprecated. Please use --explicit_defaults_for_timestamp server option (see documentation for more details).
2017-11-10T17:27:56.972612Z 0 [Warning] InnoDB: New log files created, LSN=45790
2017-11-10T17:27:57.535329Z 0 [Warning] InnoDB: Creating foreign key constraint system tables.
2017-11-10T17:27:57.807244Z 0 [Warning] No existing UUID has been found, so we assume that this is the first time that this server has been started. Generating a new UUID: 7e5736cd-c63c-11e7-925d-000c29b8cbd5.
2017-11-10T17:27:57.849665Z 0 [Warning] Gtid table is not ready to be used. Table 'mysql.gtid_executed' cannot be opened.
2017-11-10T17:27:57.853497Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: oldLEIN+P6Xi[Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: oldLEIN+P6Xi此处的oldLEIN+P6Xi是数据库root的密码(请注意自己的密码,可以在日志中找到,或者使用跳过数据库授权,然后重置密码),第一次进入mysq将使用到。
测试是否能正常启动:
[root@localhost support-files]# pwd
/usr/local/mysql/support-files
[root@localhost support-files]# ./mysql.server start
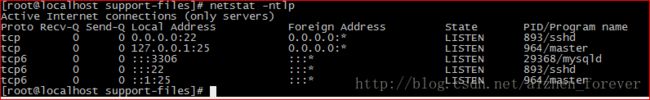
查看端口是否在监听:
开始进入数据库:
刚才提到的oldLEIN+P6Xi要使用啦。
![]()
提示已经告知我们要先修改root密码
mysql> set password = password('000000');四、mysql5.7支持原生的systemd
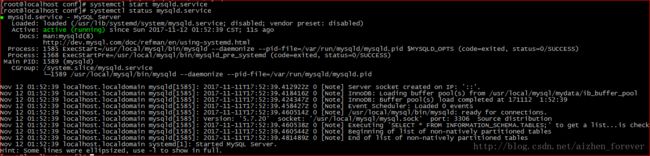
我是比较喜欢systemctl的启动方式,排错方便,简单明了。
1、systemd是所有主要Linux发行版中可用的管理和配置平台。它提供了服务启动,停止,重新启动和其他一些新功能来管理服务的基础设施。
2、systemd是不是在init守护的不仅仅是名字,但也指它周围的整个软件包,其中,除了systemd的init守护进程,包括守护进程journald,logind和networkd,以及许多其他低级别的组件。
3、systemd的核心组件包括以下内容:
(1)systemd是Linux操作系统的系统和服务管理器。
(2)systemctl可用于反思和控制系统和服务管理器的状态。
(3)systemd-analysis可用于确定系统启动性能统计信息,并从系统和服务管理器中检索其他状态和跟踪信息。
4、systemd提供的主要功能之一是集成过程监控,并在发生服务故障/终止时自动重启。从MySQL 5.7开始,进程监视和自动重启现在由systemd在有系统的系统上处理。如果mysqld由于崩溃等可重启故障而失败,则systemd会自动重新启动mysqld。这就棒棒棒的。
5、mysqld.service:这是systemd服务定义文件,告诉它什么服务启动,指定自动重新启动设置,服务类型和所有各个单位之间的依赖关系,等等。这里是mysqld的内容。现在已经安装在Fedora 21的/ usr / lib / systemd / system下的服务文件:
6、mysql.conf:该文件描述配置设置,如tmp文件的位置,权限模式和所有权,与mysqld服务相关的tmpfiles的时代等等。例如,这个文件安装在Fedora 21上的/usr/lib/tmpfiles.d中
7、mysqld_pre_systemd:这是一个bash脚本文件,当mysqld第一次通过systemctl启动时,生成数据目录。这个脚本在启动mysqld之前由systemd运行,以检查指定的数据目录位置内是否存在正确的data / mysql目录。如果data / mysql目录不存在,那么systemd将运行mysqld并--initialize创建数据目录(这个文件通常安装在/ usr / bin中)。
查看是否存在mysqld.service,这是systemd的原生支持文件。
[root@localhost mysql-5.7.20]# find / -name mysqld.service
/usr/local/src/mysql-5.7.20/scripts/mysqld.service
/usr/local/mysql/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service[root@localhost mysql]# pwd
/usr/local/mysql
[root@localhost mysql]# cd usr/lib/systemd/system/
[root@localhost system]# ls
mysqld.service [email protected]查看mysqld.service
[root@localhost system]# cat mysqld.service
# Copyright (c) 2015, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; version 2 of the License.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
# Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
#
# systemd service file for MySQL forking server
#
[Unit]
Description=MySQL Server
Documentation=man:mysqld(8)
Documentation=http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html
After=network.target
After=syslog.target
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Service]
User=mysql
Group=mysql
Type=forking
PIDFile=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
# Disable service start and stop timeout logic of systemd for mysqld service.
TimeoutSec=0
# Execute pre and post scripts as root
PermissionsStartOnly=true
# Needed to create system tables
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_pre_systemd
# Start main service
ExecStart=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid $MYSQLD_OPTS
# Use this to switch malloc implementation
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/mysql
# Sets open_files_limit
LimitNOFILE = 5000
Restart=on-failure
RestartPreventExitStatus=1
PrivateTmp=false[root@localhost system]# cp mysqld.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/
[root@localhost system]# chown 775 /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service 五、编译遇到的报错
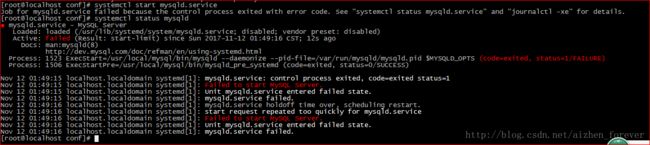
1、启动mysql失败
[root@localhost support-files]# ./mysql.server start
Starting MySQL.Logging to '/usr/local/mysql/mydata/node4.err'.
...... ERROR! The server quit without updating PID file (/usr/local/mysql/mydata/node4.pid).如果直接将这个问题贴google或者百度,是没用的,最实在的还是查看日志。
[root@localhost backup]# cat /var/log/mysqld/mysqld.log
171108 22:18:39 mysqld_safe Starting mysqld daemon with databases from /usr/local/mysql/mydata
171108 22:18:40 [Note] /usr/libexec/mysqld (mysqld 5.7.20.) starting as process 2413 ...
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: The InnoDB memory heap is disabled
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Mutexes and rw_locks use GCC atomic builtins
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.7
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Using Linux native AIO
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Initializing buffer pool, size = 128.0M
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Completed initialization of buffer pool
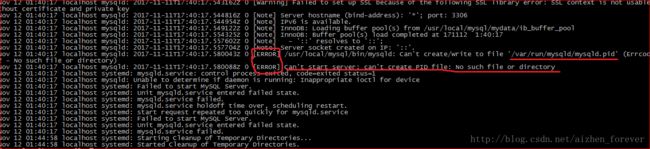
171108 22:18:40 InnoDB: Operating system error number 13 in a file operation.
InnoDB: The error means mysqld does not have the access rights to
InnoDB: the directory.
InnoDB: File name ./ibdata1
InnoDB: File operation call: 'open'.
InnoDB: Cannot continue operation.
171108 22:18:41 mysqld_safe mysqld from pid file /var/run/mysql/mysql.pid ended重点来了:
InnoDB: The error means mysqld does not have the access rights to
InnoDB: the directory.
InnoDB: File name ./ibdata1
InnoDB: File operation call: 'open'.
InnoDB: Cannot continue operation.
解决方法:
将mysql的dasedir、datadir、conf等目录检查一遍,查看里面的文件是否都授权给mysql用户。
2、使用systemctl启动失败
忘记创建目录了。所以查看系统日志,找ERROR就行啦。
解决方法:
mkdir /var/run/mysqld
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld