JUC线程框架深度解析 — 06、DelayQueue延迟队列
所谓的延迟队列最大的特征是它可以自动通过队列进行脱离,例如:现在有一些对象被临时保存着,但是有可能该集合对象是一个公共对象,那么里面的某些数据如果不再使用的时候就希望其可以在指定的时间到达后自动的消失。
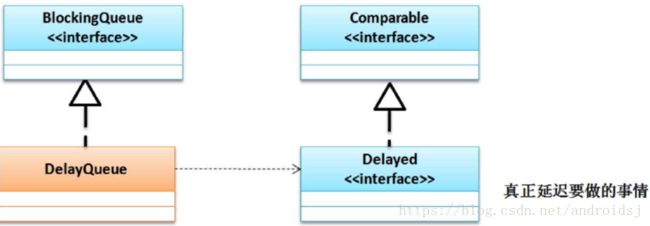
DelayQueue是延迟队列主要的使用类,所谓的延迟队列=BlockingQueue + PriorityQueue + Delayed。
【 延迟队列的基本使用 】
下面编写一个简单的延时队列,延时队列的本质就是到点后自动离开。那么一定要为其设置一个离开的时间点。
范例:使用DelayedQueue进行延迟队列的定义
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MLDNTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("准备聚会。。。。。。");
// 设置延迟队列
DelayQueue queue = new DelayQueue() ;
queue.add(new Member("张三", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
queue.add(new Member("李四", 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// 如果聚会还有人在呢
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 从里面取出数据内容
Delayed dyd = queue.poll() ;
// 如果通过队列里面可以获取数据,就表示当前的用户已经离开了,满足了延迟的条件了
System.out.println("【poll = {" + dyd + "}】"
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
// 延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}
}
}
// 如果成员要想离开一定要实现Delayed接口
class Member implements Delayed {
// 聚会人员的名单
private String name ;
// 失效时间,人员离开的时间,毫秒单位
private long expire ;
// 设置的延迟时间,毫秒单位
private long delay ;
/**
* 设置参与到队列之中的用户信息
* @param name 用户的姓名
* @param delay 延迟时间
* @param unit 时间处理单位
*/
public Member(String name,long delay,TimeUnit unit) {
this.name = name ;
// 保存延迟的时间
this.delay = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(delay, unit) ;
// 当前时间加上延迟时间
this.expire = System.currentTimeMillis() + this.delay ;
}
@Override // 决定了你优先级队列的弹出操作
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int) (this.delay – this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
@Override // 计算延迟时间是否到达
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(this.expire-System.currentTimeMillis(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name + "预计"
+ this.delay + "离开,现在已经到点了。";
}
} 使用这种延迟队列最大的特征就像吃自助餐一样,给你一个固定的时间限制,只要到达这个限制或者说你自己定义好了离开时间了,那么你就可以离开。就可以使用poll()从队列里面把你拽出来,如果不到时间不能拽。
【 延迟队列案例 】
案例:现在学生考试里面可以有许多的学生参加考试,且老师需要进行学生考试的监督,
每一个学生的考试时间都是不同的,但是不管你多不同,一旦到点之后一定要结束考试。
范例:实现本次模型
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MLDNTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 利用这个类来模拟一个不同的交卷时间
Random rand = new Random() ;
DelayQueue students =
new DelayQueue() ;
for (int x = 0 ; x < 45 ; x ++) {
int time = rand.nextInt(10) ;
while(time < 3) {
// 必须保证考试的时间大于3秒
time = rand.nextInt(10) ;
}
students.put(new Student("学生 - "
+ x , time, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
new Thread(new Teacher(students,45)).start();
}
}
class Teacher implements Runnable { // 老师也设置一个多线程
private int studentCount = 0 ; // 参与考试的学生数量
private int submitCount = 0 ; // 保存交卷的学生个数
private DelayQueue students = null ;
public Teacher(DelayQueue students,
int studentCount) {
// 保存所有的学生信息
this.students = students ;
// 保存学生数量
this.studentCount = studentCount ;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("********** 同学们开始答题 ************");
try {
// 还有未交卷
while (this.submitCount < this.studentCount) {
Student stu = this.students.poll() ;
// 有人出队列了,就表示有人交卷了
if (stu != null) {
stu.exam(); // 交卷处理
this.submitCount ++ ; // 交卷的学生个数加1
}
}
} catch (Exception e) { }
System.out.println("********** 同学们结束考试 ************");
}
}
class Student implements Delayed {
private String name ;
// 学生交卷时间,使用毫秒单位
private long submitTime ;
// 实际的考试时间
private long workTime ;
public Student(String name,long workTime,TimeUnit unit) {
// 保存名字
this.name = name ;
// 毫秒是存储单位
this.workTime = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(
workTime, unit) ;
// 交卷时间
this.submitTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
+ this.workTime ;
}
public void exam() { // 考试处理
System.out.println("【"+this.name+"交卷
-{"+this.submitTime+"}】交卷时间:"
+ System.currentTimeMillis() + "、花费时间:"
+ this.workTime);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int) (this.workTime –
this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(this.submitTime
- System.currentTimeMillis(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} 到达指定时间点之后根据优先级进行队列的弹出处理。
【 延迟队列实现数据缓存 】
在延迟队列之中有一个最大的特征就是到点后进行清除处理,那么在实际的开发之中,可以利用此机制来实现一个缓存的处理操作。正规的开发之中,往往都会利用数据层通过数据库进行数据的获得,并且将这些数据变为VO的形式。
范例:实现一个缓存的基础模型
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MLDNTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Cache cache = new Cache() ;
cache.put("小岳岳",new News("小岳岳","跑路了
"),3,TimeUnit.SECONDS) ;
cache.put("小疯冯",new News("小疯冯","吃屎了
"),3,TimeUnit.SECONDS) ;
System.out.println(cache.get("小岳岳"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(cache.get("小岳岳"));
System.out.println(cache.get("小疯冯"));
}
}
// // 定义缓存的操作类,该类之中需要用户设置保存的key类型与value类型
class Cache {
// 如果要想实现多个线程的并发访问操作,必须要考虑使用ConcurrentHashMap子类
private ConcurrentMap cacheObjectMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private DelayQueue> delayQueue = new DelayQueue>() ;
private class Pair { // 定义一个内部类,该类可以保存队列之中的K与V类型
private K key ;
private V value ;
public Pair(K key,V value) {
this.key = key ;
this.value = value ;
}
}
// 如果要想清空不需要的缓冲数据,则需要守护线程
public Cache() {
Runnable daemonTask = () -> {
// 守护线程要一直进行执行,当已经超时之后可以取出数据
while(true) {
// 通过延迟队列获取数据
DelayItem item =
Cache.this.delayQueue.poll() ;
// 已经有数据超时了
if (item != null) {
Pair pair = item.getItem() ;
Cache.this.cacheObjectMap.remove(
pair.key, pair.value) ;
}
}
} ;
Thread thread = new Thread(daemonTask,"缓存守护线程") ;
// 设置守护线程
thread.setDaemon(true);
// 启动守护线程
thread.start();
}
/**
* 表示将要保存的数据写入到缓存之中,如果一个对象重复被保存了,则应该重置它的超时时间
* @param key 要写入的K的内容
* @param value 要写入的对象
* @param time 保存的时间
* @param unit 保存的时间单位
*/
public void put(K key, V value, long time, TimeUnit unit) {
// put()方法如果发现原本的key存在,
则会用新的value替换掉旧的内容,同时返回旧的内容
// 将数据保存进去
V oldValue = this.cacheObjectMap.put(key, value) ;
// 原本已经存储过此内容了
if (oldValue != null) {
this.delayQueue.remove(key) ;
}
this.delayQueue.put(new DelayItem(
new Pair(key,value), time, unit));
}
// 根据key获取内容
public V get(K key) {
// Map负责查询
return this.cacheObjectMap.get(key) ;
}
}
class DelayItem implements Delayed {
private T item ; // 设置要保存的数据内容
private long delay ; // 保存缓存的时间
private long expire ; // 设置缓存数据的失效时间
public DelayItem(T item,long delay,TimeUnit unit) {
this.item = item ;
this.delay = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(delay, unit) ;
this.expire = System.currentTimeMillis() + this.delay ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int) (this.delay –
this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(this.expire
- System.currentTimeMillis(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public T getItem() {
return item;
}
}
class News { // 定义一个新闻类
private String title ;
private String note ;
public News(String title,String note) {
this.title = title ;
this.note = note ;
}
public String toString() {
return "【新闻数据】title = " + this.title
+ "、note = " + this.note ;
}
}