C++拾取——stl标准库中集合交集、并集、差集、对称差方法
STL库中有丰富的集合运算方法,我们可以使用它们快速完成交集、并集、差集、对称差集的运算。(转载请指明出于breaksoftware的csdn博客)
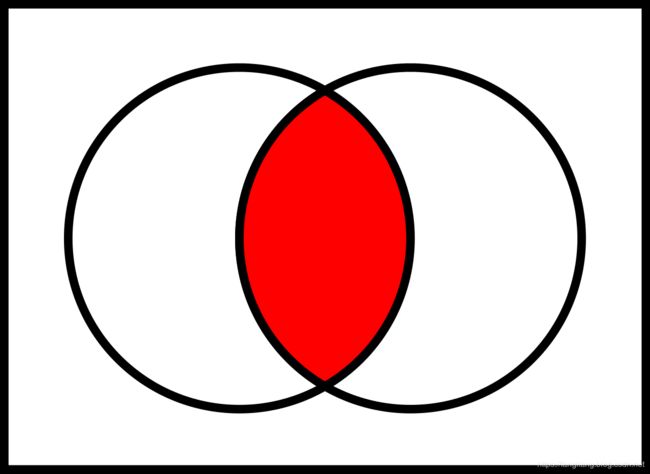
交集(intersection)
交集是集合运算中经常会用到的计算,其表达是两个集合共有的部分(图中红色区域)
STL中有set_intersection方法可以实现该功能。它是C++17开始支持的方法,声明于
template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt1, class ForwardIt2, class ForwardIt3 >
ForwardIt3 set_intersection( ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt1 first1, ForwardIt1 last1,
ForwardIt2 first2, ForwardIt2 last2,
ForwardIt3 d_first );
第一二个参数是某个集合的起止迭代器,第二三个参数是另一个集合的起止迭代器。这两个待比较集合要求是有序的。最终得到的交集保存在第五个参数所指向的集合的起始迭代器位置。
我们看个例子
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector a{1, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6};
std::vector b{2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7};
std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
std::sort(b.begin(), b.end());
std::vector result;
std::set_intersection(a.begin(), a.end(),
b.begin(), b.end(),
std::back_inserter(result));
std::copy(result.begin(), result.end(),
std::ostream_iterator(std::cout, " "));
return 0;
} 第7~10行保证了待比较的两个集合是有序的。第14行是将a、b两个集合的交集保存到result集合中。最终输出的是
3 4 4 5 并集(union)
并集是指两个集合组合在一起集合(图中红色区域)。
set_union
STL中有set_union方法可以实现该功能。它是C++17开始支持的方法,声明于
template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt1, class ForwardIt2, class ForwardIt3 >
ForwardIt3 set_union( ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt1 first1, ForwardIt1 last1,
ForwardIt2 first2, ForwardIt2 last2,
ForwardIt3 d_first );它的第一二个参数是某个集合的起止迭代器,第二三个参数是另一个集合的起止迭代器。这两个待合并集合要求是有序的。最终得到的并集保存在第五个参数所指向的集合的起始迭代器位置。
我们看个例子
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector a{ 1, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6 };
std::vector b{ 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7 };
std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
std::sort(b.begin(), b.end());
std::vector result;
std::set_union(a.begin(), a.end(),
b.begin(), b.end(),
std::back_inserter(result));
std::copy(result.begin(), result.end(),
std::ostream_iterator(std::cout, " "));
return 0;
} 其结果是
1 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 7a集合有2个3,b集合有1个3。理论上应该有3个3,但是set_union方法只从取max(countof(a, 3), countof(b, 3))个元素,所以只有2个3。如果希望取到3个3的并集,可以使用merge方法
merge
C++17开始支持该方法,其定义于
template< class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt >
constexpr OutputIt merge( InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first );它的第一二个参数是某个集合的起止迭代器,第二三个参数是另一个集合的起止迭代器。这两个待合并集合要求是有序的。最终得到的并集保存在第五个参数所指向的集合的起始迭代器位置。
将上例中set_union改成merge方法后,输出结果是
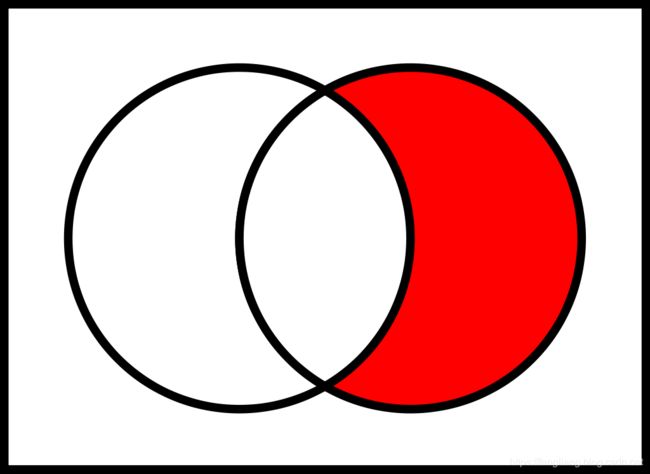
1 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 6 7差集(difference)
差集是指在一个集合中,不再另外一个集合中的部分(图中红色区域)
可以见得,两个集合的差集存在两个可能性:一种是在左侧集合不在右侧集合中的部分;一种是在右侧集合不在左侧集合中的部分。
STL中有set_difference方法可以实现该功能。它是C++17开始支持的方法,声明于
template< class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt >
OutputIt set_difference( InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first );它的第一二个参数是左侧集合的起止迭代器,第二三个参数是右侧集合的起止迭代器。这两个待比较集合要求是有序的。最终得到的差集保存在第五个参数所指向的集合的起始迭代器位置。
我们看个例子
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector a{ 1, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6 };
std::vector b{ 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7 };
std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
std::sort(b.begin(), b.end());
std::vector result;
std::set_difference(a.begin(), a.end(),
b.begin(), b.end(),
std::back_inserter(result));
std::copy(result.begin(), result.end(),
std::ostream_iterator(std::cout, " "));
return 0;
} 这个例子中,我们将算出在a集合中,不在b集合中的元素,并保存到result中。其结果是
1 3 6由于a集合中有两个3,所以结果中有一个3。
如果求在集合b中,不在集合a中的集合,只需要把std::set_difference中a、b替换位置
std::set_difference(b.begin(), b.end(),
a.begin(), a.end(),
std::back_inserter(result));得出的结果是
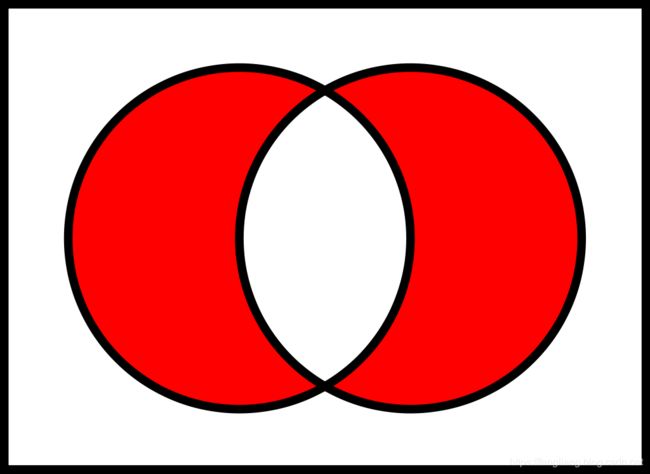
2 5 7对称差(symmetric difference)
对称差是指并集中,去除交集之外的部分(图中红色区域)
STL中有set_symmetric_difference方法可以实现该功能。它是C++17开始支持的方法,声明于
template< class InputIt1, class InputIt2, class OutputIt >
OutputIt set_symmetric_difference( InputIt1 first1, InputIt1 last1,
InputIt2 first2, InputIt2 last2,
OutputIt d_first );它的第一二个参数是某个集合的起止迭代器,第二三个参数是另一个集合的起止迭代器。这两个待比较集合要求是有序的。最终得到的等差分集保存在第五个参数所指向的集合的起始迭代器位置。
我们看个例子
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector a{ 1, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6 };
std::vector b{ 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7 };
std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
std::sort(b.begin(), b.end());
std::vector result;
std::set_symmetric_difference(a.begin(), a.end(),
b.begin(), b.end(),
std::back_inserter(result));
std::copy(result.begin(), result.end(),
std::ostream_iterator(std::cout, " "));
return 0;
} 得到的结果是
1 2 3 5 6 7 在项目中,我们使用上述集合操作方法,将使代码变的简洁。