Centos7下的systemctl命令与service和chkconfig
博主使用的操作系统是最新的CentOS 7,所以可能和网上一些老的博文有一定出入,那是因为版本更新的原因。
1 service
service命令用于对系统服务进行管理,比如启动(start)、停止(stop)、重启(restart)、重新加载配置(reload)、查看状态(status)等。
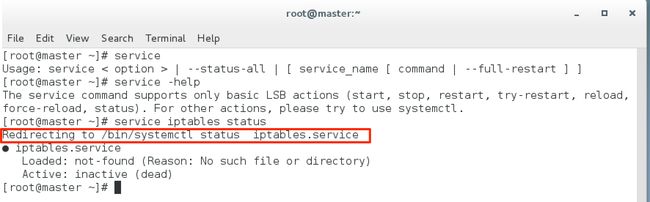
下面我们来看看在Centos 7上service命令的使用情况。
相信看到这里,大家已经发现问题了。那就是service命令的使用情况已经和以前的老版本不一样了。(作为一个初学Linux的人,我也是通过看网上的资料,发现把网友贴出的命令执行时,发现的问题。)同样的情况对于 chkconfig 命令也是一样。
2 chkconfig
老版本的使用说明:
chkconfig
提供了一个维护/etc/rc[0~6] d 文件夹的命令行工具,它减轻了系统直接管理这些文件夹中的符号连接的负担。chkconfig主要包括5个原始功能:为系统管理增加新的服务、为系统管理移除服务、列出单签服务的启动信息、改变服务的启动信息和检查特殊服务的启动状态。当单独运行chkconfig命令而不加任何参数时,他将显示服务的使用信息。
必要参数
–add 开启指定的服务程序
–del 关闭指定的服务程序
–list 列出chkconfig所知道的所有服务
选择参数
–level<代号> 设置服务程序的等级代号,它是一串0~7的数字,如“-level35”代表指定运行等级3和5
–help 显示帮助信息
–version 显示版本信息
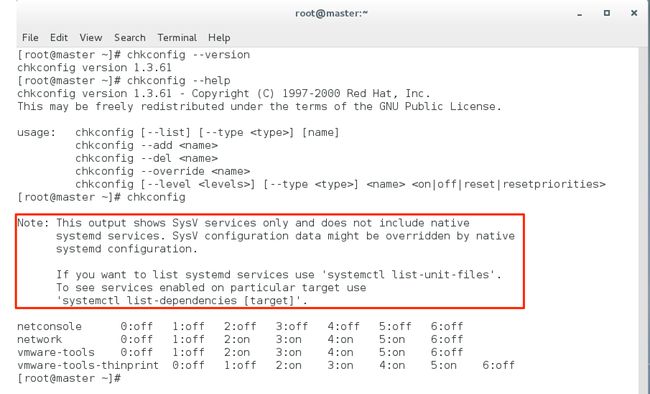
我们在Centos7中试一试嘛。
所以问题已经很明显了,service和chkconfig命令的功能好像都被阉割了,而且好像已经被systemctl命令取代了。是这样吗?我们来看一看systemctl命令的介绍。
3 systemctl
文档中是这么介绍它的:
systemctl may be used to introspect and control the state of the “systemd” system and service manager.
再结合上面两个命令的执行结果,我们已经可以大致猜出systemctl的作用了,那就是:主要负责控制systemd系统和服务管理器。
什么是systemd系统?
CentOS 7 使用systemd替换了SysV。Systemd目的是要取代Unix时代以来一直在使用的init系统,兼容SysV和LSB的启动脚本,而且够在进程启动过程中更有效地引导加载服务。
systemd的特性有:
- 支持并行化任务;
- 同时采用socket式与D-Bus总线式激活服务;
- 按需启动守护进程(daemon);
- 利用 Linux 的 cgroups 监视进程;
- 支持快照和系统恢复;
- 维护挂载点和自动挂载点;
- 各服务间基于依赖关系进行精密控制。
我们再来看看维基百科对它的介绍:
systemd is an init system used by some Linux distributions to bootstrap the user space and manage all processes subsequently, instead of the UNIX System V or Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) init systems. The name systemd adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter d.[6] It is published as free and open-source software under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) version 2.1 or later.[5] One of systemd’s main goals is to unify basic Linux configurations and service behaviors across all distributions.[7]
As of 2015, many Linux distributions have adopted systemd as their default init system.[8] The increasing adoption of systemd has been controversial, with critics arguing the software has violated the Unix philosophy by becoming increasingly complex, and that distributions have been forced to adopt it due to the dependency of various other software upon it, including, most notably, the GNOME 3 desktop environment.
总结一下关键信息:
- systemd是一个取代了SysV和LSB的初始化系统;
- 现在的大多数Linux发行版本都进行了这个更新;
- systemd不仅仅只是个初始化系统,它还包括了还包括了管理系统各种的方面的 daemon;
- systemd是大势所趋又存在争议。
所以,我们可以把systemctl理解为systemd的一个工具。也可以认为systemctl命令将service和chkconfig命令结合在了一起。总之,需要的时候会用就行。下面我们来看一些常见用法。
查看systemctl的相关信息
[root@master ~]# systemctl --version
systemd 219
+PAM +AUDIT +SELINUX +IMA -APPARMOR +SMACK +SYSVINIT +UTMP +LIBCRYPTSETUP +GCRYPT +GNUTLS +ACL +XZ -LZ4 -SECCOMP +BLKID +ELFUTILS +KMOD +IDN
[root@master ~]# whereis systemctl
systemctl: /usr/bin/systemctl /usr/share/man/man1/systemctl.1.gz
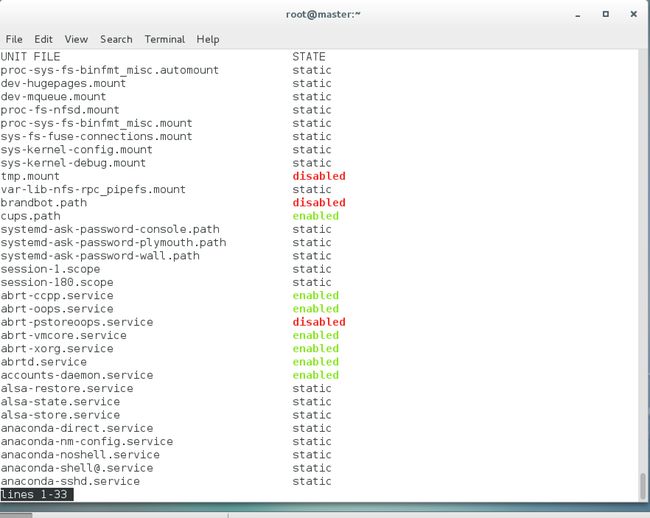
[root@master ~]# 列出所有可用单元
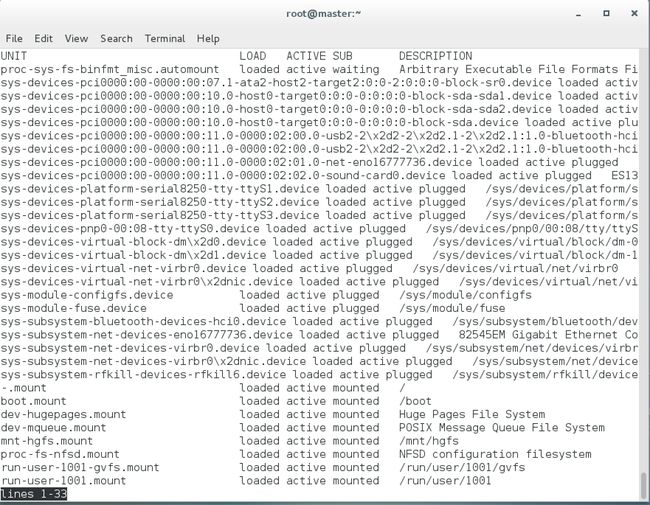
# systemctl list-unit-files列出所有运行中单元
# systemctl list-units列出所有失败的单元
[root@master ~]# systemctl --failed
0 loaded units listed. Pass --all to see loaded but inactive units, too.
To show all installed unit files use 'systemctl list-unit-files'.
[root@master ~]# 检查某个单元是否启用
[root@master ~]# systemctl is-enabled mysqld.service
disabled
[root@master ~]# 查看某个服务(单元)的状态
[root@master ~]# systemctl status firewalld.service
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)*启动、重启、停止、重载服务
# systemctl start httpd.service
# systemctl restart httpd.service
# systemctl stop httpd.service
# systemctl reload httpd.service
# systemctl status httpd.service*激活/禁止自动启动
# systemctl enable httpd.service
# systemctl disable httpd.service*杀死服务
# systemctl kill httpd以上就是我目前需要用的和想要和大家分享的功能,下面的只是补充,也没有详细的示例,所以有兴趣的朋友可以再简单看一看说明文档就好了。
附录
使用Systemctl控制并管理挂载点:
systemctl list-unit-files --type=mount
# systemctl start tmp.mount
# systemctl stop tmp.mount
# systemctl restart tmp.mount
# systemctl reload tmp.mount
# systemctl status tmp.mount
# systemctl is-active tmp.mount
# systemctl enable tmp.mount
# systemctl disable tmp.mount
# systemctl mask tmp.mount使用Systemctl控制并管理套接口
# systemctl list-unit-files --type=socket
# systemctl start cups.socket
# systemctl restart cups.socket
# systemctl stop cups.socket
# systemctl reload cups.socket
# systemctl status cups.socket
# systemctl is-active cups.socket
# systemctl enable cups.socket
# systemctl disable cups.socket
# systemctl mask cups.socket使用Systemctl管理服务的CPU利用率
# systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
# systemctl set-property httpd.service CPUShares=2000
# systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
# systemctl show httpd其他
# systemd-analyze critical-chain httpd.service
# systemctl list-dependencies httpd.service
# systemd-cgls
# systemd-cgtop
# systemctl emergency
# systemctl reboot
# systemctl halt
# systemctl suspend
# systemctl hibernate
# systemctl hybrid-sleep