pytorch利用rnn通过sin预测cos 利用lstm预测手写数字
一.利用rnn通过sin预测cos
1.首先可视化一下数据
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def show(sin_np,cos_np):
plt.figure()
plt.title('Sin and Cos', fontsize='18')
plt.plot(steps, sin_np, 'r-', label='sin')
plt.plot(steps, cos_np, 'b-', label='cos')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi*2, 256, dtype=np.float32)
sin_np = np.sin(steps)
cos_np = np.cos(steps)
#debug to show
show(sin_np, cos_np)2.构建rnn模型,其中输入数据可以看成是一个batch,步长自定义,维度为1的数据
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch import optim
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# import matplotlib.animation
import math, random
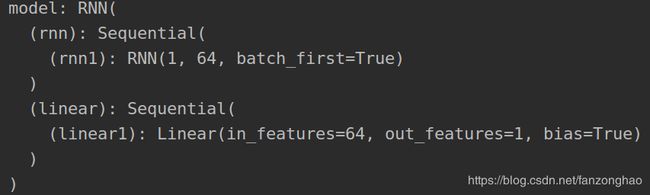
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN,self).__init__()
self.rnn=nn.Sequential() #batch,sequence,input_size
self.rnn.add_module('rnn1',nn.RNN(input_size=1,hidden_size=64,num_layers=1,batch_first=True))
self.linear=nn.Sequential()
self.linear.add_module('linear1', nn.Linear(64,1))
def forward(self, x):
y,_=self.rnn(x)
# print('y.shape:',y.shape)
outs=[]
for time_step in range(y.size(1)):
outs.append(self.linear(y[:,time_step,:]))
return torch.stack(outs,dim=1)
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model=RNN().to(DEVICE)
print('model:',model)
optimzer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.0001,weight_decay=0.00001)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_params.pth',map_location='cpu'))
def train():
# model=model.cuda()
model.train()
for epoch in range(10000):
start, end = epoch*np.pi, (epoch+2)*np.pi
steps = np.linspace(start,end,Times_step,dtype=np.float32)
sin_x = np.sin(steps)
cos_x = np.cos(steps)
# print('sin_x.shape',sin_x.shape)
#batch,sequence,input_size (1,256,1)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
sinx_input = torch.from_numpy(sin_x[np.newaxis,:,np.newaxis]).cuda()
# print('sinx_input.shape:',sinx_input.shape)
cosx_lable = torch.from_numpy(cos_x[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis]).cuda()
else:
sinx_input = torch.from_numpy(sin_x[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
# print('sinx_input.shape:',sinx_input.shape)
cosx_lable = torch.from_numpy(cos_x[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
y_pre = model(sinx_input)
# print('y_pre.shape:',y_pre.shape)
loss = criterion(y_pre,cosx_lable)
optimzer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimzer.step()
if epoch%100==0:
print('epoch,loss',epoch,loss)
# plt.plot(steps, sinx_lable.cpu().data.numpy().flatten(),color='r')
# plt.plot(steps, sinx_input.cpu().data.numpy().flatten(), color='b')
# plt.show()
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_params.pth') # save only the parameters
def eval():
model.eval()
start, end =0 * np.pi, (0+2) * np.pi
steps = np.linspace(start, end, Times_step, dtype=np.float32)
sin_x = np.sin(steps)
print('sin_x:', sin_x)
cos_x = np.cos(steps)
# print('sin_x.shape',sin_x.shape)
# batch,sequence,input_size (1,256,1)
sinx_input = torch.from_numpy(sin_x[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_params.pth',map_location='cpu'))
with torch.no_grad():
y_pre=model(sinx_input)
# print('sinx_input.shape:',sinx_input.shape)
cosx_lable = torch.from_numpy(cos_x[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
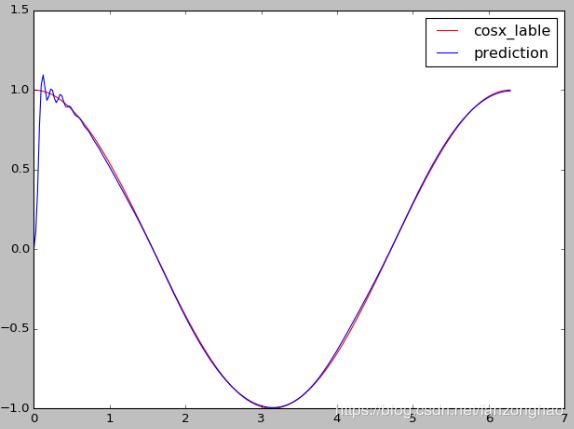
plt.plot(steps, cosx_lable.data.numpy().flatten(), color='r',label='cosx_lable')
plt.plot(steps, y_pre.data.numpy().flatten(), color='b',label='prediction')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# train()
eval()
最后一个epoch的结果
二.利用lstm预测手写数字
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torch.utils.data as Data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision
torch.manual_seed(1)
epochs = 5
BATCH_SIZE = 8
TIME_STEP = 28
INPUT_SIZE = 28
LR = 0.01
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
train_data = dsets.MNIST(
root='./mnist',
train=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist', train=False)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# print(test_data.data.size())
test_x = Variable(test_data.data).type(torch.FloatTensor) / 255.
test_y = test_data.targets
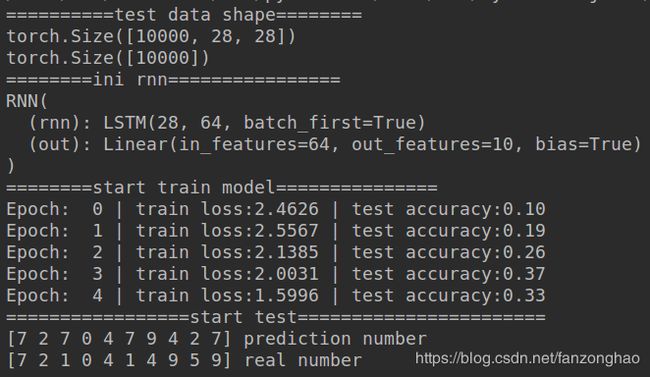
print('==========test data shape========')
print(test_x.size())
print(test_y.size())
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(
input_size=INPUT_SIZE,
hidden_size=64,
num_layers=1,
batch_first=True,
)
self.out = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.rnn(x)
# print('r_out',r_out.size())
# 取出最后一次循环的r_out传递到全连接层
out = self.out(r_out[:, -1, :])
return out
rnn = RNN()
print('========ini rnn================')
print(rnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print('========start train model===============')
for epoch in range(epochs):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader):
if step < 10:
# print(x.size())
#[batch,28,28]
input = Variable(x.squeeze())
#[batch]
label = Variable(y)
# print('============train data input shape=========')
# print(input.size())
# print(label.size())
output = rnn(input)
loss = loss_func(output, label)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
else:
break
test_output = rnn(test_x.squeeze())
# print(test_output.size())
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze()
# print(pred_y.shape)
accuracy = sum(pred_y == test_y.numpy()) / float(test_y.size(0))
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss:%.4f' % loss.item(), '| test accuracy:%.2f' % accuracy)
print('=================start test=======================')
test_output = rnn(test_x[:10].squeeze())
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10].numpy(), 'real number')