Spring源码:bean创建(四)属性注入
一、populateBean
在创建了bean的实例后,Spring的下一步工作就是为bean注入其依赖的属性:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
//传入的beanWrapper为空,如果属性不为空就抛出异常,否则返回null
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// 应用后处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,调用其postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
// 在注入属性前修改bean状态,如果方法中发挥false的话,可以终止后面代码运行,直接返回
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
//为bean注入PropertyValues中包含的属性
//这种注入方式适用的是配置文件中通过配置的属性并且显示在配置文件中配置了autowireMode属性
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// 根据名称自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// 根据类型自动注入
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
//如果存在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器 || 需要进行依赖检查
//一般情况下,Spring会提前注册几种存在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
//应用后处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,调用其postProcessPropertyValues方法
//作用是对需要进行依赖检查的属性进行处理
//Autowired等注解的属性就是在这里完成注入的
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
//注入配置文件中配置的属性
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
} 处理流程:
- 应用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor处理器的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法。该方法可以控制是否继续进行属性填充
- 获取配置文件中配置的property属性
- 应用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor处理器的postProcessPropertyValues方法,完成对注入属性的验证、处理。值得注意的是,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor会负责注入标注有@Autowired等注解的属性.
- 将配置的
属性注入到bean中
二、配置属性的注入
对于通过配置文件中给
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs == null || pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List original;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
if (bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
}
//BeanDefinition中定义的PropertyValues的类型就是MutablePropertyValues,所以为true
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
//属性是否已经转换过类型了
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// 如果属性已经转换为对应的类型,则直接设置到BeanWrapper中
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
//catch
}
//获取配置文件中配置的原始值
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
//获取类型转换器,如果没有配置的话为null
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
//如果类型转换器为null,则使用BeanWrapper作为类型转换器,因为BeanWrapper实现了TypeConverter接口
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// 遍历属性,并将配置的值转换为对应的类型
List deepCopy = new ArrayList(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
//解析原始值,例如RuntimeBeanReference类型,会获取BeanFactory中其真正的bean;String或TypedStringValue类型会视为一个表达式进行求值等
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
//是否能进行类型转换 = 可以写入 && 没有'.'或者'[' 符号
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
//将value转换为对应的类型
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
//为了避免每次创建bean的时候都重复转换类型,Spring会尽可能地将转换好的值放入对应的BeanDefinition中
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
//如果原始值并未进行解析
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
//需要进行解析的情况
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
//无法被缓存
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// 将解析、转换好的属性设置到BeanWrapper中
//之所以bean需要BeanWrapper包装一次,也是为了方便给bean填充属性
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
} 最终是通过BeanWrapper的setPropertyValues来完成属性的注入,而前面的工作主要是解析配置文件配置的原始值,因为原始值可能是最终注入的值(String类型),也可能需要被解析后才能被应用,所以Spring花费大量工作来解析原始值。解析完成后,如果有必要还得转换值的类型,最终将解析、转换好的值注入到bean中。
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs) throws BeansException {
setPropertyValues(pvs, false, false);
}
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
//保存注入时抛出的PropertyAccessException
List propertyAccessExceptions = null;
//获取需要注入的propertyValue列表
List propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// 注入属性
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException|NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
} catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new LinkedList();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// 如果注入时抛出的PropertyAccessException不为空,Spring会收集起来,在这里统一抛出
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray =
propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[propertyAccessExceptions.size()]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
} 在上面的代码中主要是进行统一的异常处理和遍历属性列表,真正的属性注入还需要继续向下调用设置单个属性的方法setPropertyValue:
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
setPropertyValue(pv.getName(), pv.getValue());
}
public void setPropertyValue(String propertyName, Object value) throws BeansException {
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor nestedPa;
try {
//将属性访问的工作交给AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor完成
//当配置的属性名propertyName中包含'.'或者'['这样字符时,代表需要设置嵌套属性
//如果存在嵌套属性,Spring会递归向下获取最终设置的属性,比如:a.b.c,Spring会递归调用获取到b,c是需要设置的属性
//如果没有嵌套属性的话。会返回BeanWrapper自身
nestedPa = getPropertyAccessorForPropertyPath(propertyName);
}
catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) {
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Nested property in path '" + propertyName + "' does not exist", ex);
}
PropertyTokenHolder tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedPa, propertyName));
//设置属性
nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, new PropertyValue(propertyName, value));
}上面主要是解析propertyName,处理嵌套的属性,确定最终需要设置的属性
protected void setPropertyValue(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
//如果propertyName中存在'['的情况,即存在数组下标
if (tokens.keys != null) {
processKeyedProperty(tokens, pv);
}
else {
//非数组、容器类型的属性设置
processLocalProperty(tokens, pv);
}
}属性设置分为了数组类型设置和非数组类型设置,我们分析更为普遍的非数组类型:
private void processLocalProperty(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) {
//属性设置交由PropertyHandler完成
//Spring会使用反射获取属性的getter和setter方法
PropertyHandler ph = getLocalPropertyHandler(tokens.actualName);
//如果不存在属性或者属性不是可写的
if (ph == null || !ph.isWritable()) {
//如果属性是Optional类型,则直接返回
if (pv.isOptional()) {
//日志,略
return;
} else {
//其他情况会抛出异常
throw createNotWritablePropertyException(tokens.canonicalName);
}
}
Object oldValue = null;
try {
//获取属性值
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object valueToApply = originalValue;
//需要转换值的类型
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(pv.conversionNecessary)) {
//如果已经完成了类型转换,直接使用就可以了
if (pv.isConverted()) {
valueToApply = pv.getConvertedValue();
}
else {
//如果需要读取旧值(默认为false) && 值是可读的
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && ph.isReadable()) {
try {
oldValue = ph.getValue();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//无法读取旧值
}
}
//类型装换
valueToApply = convertForProperty(
tokens.canonicalName, oldValue, originalValue, ph.toTypeDescriptor());
}
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().conversionNecessary = (valueToApply != originalValue);
}
//使用PropertyHandler完成属性的注入
ph.setValue(this.wrappedObject, valueToApply);
}
//catch略
}下面就是注入属性的代码:
public void setValue(final Object object, Object valueToApply) throws Exception {
//获取解析好的setter方法
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
//设置Method的访问权限
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()) && !writeMethod.isAccessible()) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction至此,配置文件中的peoperty已经注入到了bean中
三、Autowired注解的属性注入
在属性填充populateBean代码中,除了调用applyPropertyValues注入配置文件中配置的属性,在它前面有一段代码会应用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器的postProcessPropertyValues方法:
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
//应用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
//返回值为null时会属性的填充,直接返回
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
//配置文件的属性注入
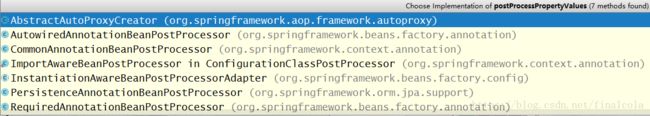
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的子类中,就包含了注解属性注入的实现方法,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的子类有:
重点需要关注的有以下几个实现类:
- RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:检查属性的setter方法上是否标注有@Required注解,如果带有此注解,但是未配置属性(配置文件中的
元素),那么就会抛出异常 - AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:遍历bean的Field属性,寻找标注有@Autowired和@Value注解的字段,并完成属性注入(如果能加载到javax.inject.Inject注解的话,也会扫描该注解)
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:遍历bean的字段,寻找通用的依赖(javax中规定的)注解,完成属性注入。通用注解包括有:javax.annotation.Resource,javax.xml.ws.WebServiceRef,javax.ejb.EJB。
重点讲解AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的实现:
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeanCreationException {
//遍历获取带有自动注入注解的字段和方法,并且将字段信息、注解信息
//注解包括:@Value、@Autowired、@Inject(javax.inject.Inject,如果能加载到这个类的话)
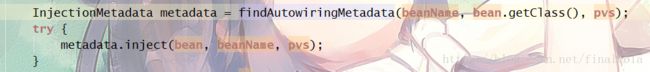
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//属性注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
上面代码的步骤为:
- 寻找带有@Value、@Autowired、@Inject(javax.inject.Inject,如果能加载到这个类的话)注解的字段或方法,并且将字段或方法、bean名、bean类型封装起来
- 完成属性注入
1、寻找注解标记的属性
寻找注解过的属性在findAutowiringMetadata中实现:
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class clazz, PropertyValues pvs) {
// 先尝试从缓存中查找,cacheKey为beanName或类名
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
//如果缓存未空 或者 需要解析的类与缓冲的类不同,则需要刷新缓存
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
//双重判断,避免多线程问题,与单例模式实现类似
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
try {
//解析后放入缓存
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
//catch略
}
}
}
return metadata;
}因为对类的解析需要大量用到反射,所以为了尽力提高性能,Spring会将解析好的字段、方法信息保存到缓存中,上面的代码也在主要是对缓存进行管理,具体的解析工作在buildAutowiringMetadata方法中完成:
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class clazz) {
//存放解析好的属性信息
LinkedList elements = new LinkedList();
Class targetClass = clazz;
//Spring会一直递归向上遍历bean的父类
do {
//存放当前解析的类中带有注解的属性
final LinkedList currElements =
new LinkedList();
//doWithLocalFields方法中,其实就是获取class的所有字段,对每个字段调用FieldCallback方法
//
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.FieldCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Field field) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
return;
}
//如果注解中存在required属性,获取属性的值,并保存起来
//如果不存在required属性则默认为true
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//使用AutowiredFieldElement类型,将字段信息封装起来
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
}
});
//与Field逻辑相同,都是遍历所有声明的方法,判断是否带有特定的注解
//如果存在注解标注的方法,并使用AutowiredMethodElement封装起来
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
//log...
return;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
//log...
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//与field不同的一点就是,AutowiredMethodElement会获取属性描述符,一起封装
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
//Spring会一直递归向上遍历bean的父类
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
//将封装有注入属性的列表一起封装到InjectionMetadata中
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
} 上面代码中,Spring先从当前类开始解析其字段和方法,并且会一直递归向上解析父类,把解析到的字段或方法信息封装到AutowiredFieldElement或AutowiredMethodElement中。
2、属性注入
回顾下先前的代码:
显示查找带有特定注解的属性,已经完成了,下一步就是属性注入,inject:
public void inject(Object target, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection elementsToIterate =
(this.checkedElements != null ? this.checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
} 代码较短,主要内容就是遍历先前解析好的AutowiredFieldElement或AutowiredMethodElement,调用其inject方法:
//AutowiredFieldElement
protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
//AutowiredFieldElement中保存的是Field对象,如果是AutowiredMethodElement则会保存Method对象
Field field = (Field) this.member;
//最终需要注入的值
Object value;
//如果已经被缓存过,就可以从缓存中获取
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
//使用DependencyDescriptor封装Field
//其属性包括:field:Field对象,declaringClass:Field所在类,fieldName:字段名
//required:是否允许为空,eager:是否懒加载(注解标注的字段都为false)
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet(1);
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
//通过BeanFactory根据DependencyDescriptor信息解决依赖
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
//将解析结果放入缓存
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
//在BeanFactory中注册依赖关系
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
//如果与属性类型相同的注入bean只有一个,那么就可以设置到缓存中
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
//通过Field对象的反射,将值设置到bean中
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
} 上面代码步骤为:
- 先尝试从缓存中获取属性值
- 如果没有被缓存,则通过beanFactory.resolveDependency方法,从BeanFactory中获取属性值
- 如果属性值满足条件(符合注入条件的bean只有一个、BeanFactory包含该bean、与属性类型相同),就缓存起来
- 通过反射,将属性值设置到bean中
beanFactory.resolveDependenc会将BeanFactory中,所有与传入参数的类型匹配的bean找出来,有autowiredBeanName保存这些匹配的beanName