深入理解MyBatis-Spring中间件
Mybatis-Spring
1.应用
mybatis是比较常用的数据库中间件,我们都知道我们来看看怎么在spring中使用mybatis,假设有用户表User,包含四个字段(id,name,sex,mobile),在Spring中使用mybatis操作User表非常简单,这里使用的是mybatis-spring 1.3.0,首先定义接口,
public interface UserMapper {
int createUser(@Param("user") User user);
}
INSERT INTO
User
(name,sex,mobile)
VALUES
(#{user.name},#{user.sex},#{user.mobile})
定义服务UserService接口和实现类,此处没给出UserService接口定义,
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
UserMapper userMapper;
public int createUser(UserDTO userDTO) {
User user = new User();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDTO,user,new String[]{"id"});
int row = userMapper.createUser(user);//插入返回值为作用的记录数;生成的主键已经被赋值到user对象上
if(row >= 1)
return user.getId();
return -1;
}
public UserDTO getUserById(Integer id) {
return null;
}
}@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath*:spring/spring-*.xml"})
public class TestUser{
private static UserService userService;
@BeforeClass
public static void beforeClass(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml");
userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
}
@Test
public void testCreatUser(){
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.setName("your name");
userDTO.setSex(true);
userDTO.setMobile("12134232211");
Integer userId = userService.createUser(userDTO);
System.out.println(userId);
System.out.println(userDTO.getId());
}
}2. 原理
从UserServiceImpl实现类中可以看出,服务类直接使用的UserMapper接口来操作数据库,而UserMapper接口没有对应的实现类,这一切都是由spring-mybatis库通过动态代理实现的,接下来分析下它的实现原理,先由SqlSessionFactoryBean生成SQLSessionFactory和并扫描接口,为接口生成动态代理1. SqlSessionFactoryBean配置
它的主要作用是扫描sql xml文件,查看源码,
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean, InitializingBean if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public boolean hasMapper(Class type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
} public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
} 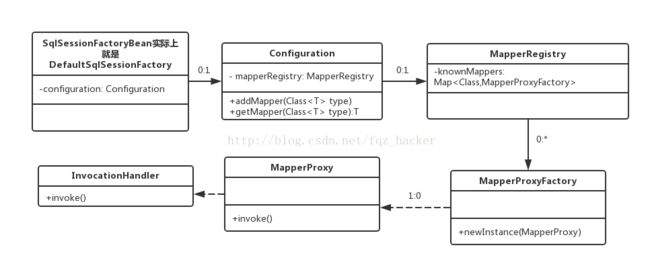
总结,SqlSessionFactoryBean实际上对应的是SqlSessionFactory类,它会扫描sql xml文件,并对接口创建动态代理,将接口类的Class和动态代理关系保存在SqlSessionFactory中,这仅仅是完成了动态代理的生成,而动态代理在哪里被使用到,怎么使用,这些都是由MapperScannerConfigurer完成,接下来看看MapperScannerConfigurer都做了些什么?
2. MapperScannerConfigurer
从开始的配置文件可以看出,MapperScannerConfigurer依赖于SqlSessionFactoryBean和Mapper接口所在package,之前也说过SqlSessionFactoryBean实际上对应的是SqlSessionFactory,它可以提供Mapper接口的动态代理类,而Mapper所在package提供了扫描的路径,在扫描过程中,会把每个Mapper接口对应到一个MapperFactoryBean,MapperFactoryBean实际上对应的是动态代理类,这一切也就说通了,下面来看看源码,
MapperScannerConfigurer实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,因此会在bean factory初始化的时候,被调用到,调用的方法为postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,因此看看postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry的源码,
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}public Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName()
+ "' and '" + definition.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface");
}
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); // issue #59
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());//将其bean Class类型设置为mapperFactoryBean,放入BeanDefinitions
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
}
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
}
} MapperFactoryBean extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean @Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}