PostGIS 爆管分析之找出上游阀门
环境:
Win10
ArcMap10.4(用于数据处理)
postgresql9.4
postgis2.2.3
pgRouting2.3(postgresql插件)
说明:
继上一篇文章做了爆管分析找出周围所有影响阀门后(参见:https://www.cnblogs.com/giser-s/p/11662932.html),发现在业务上使用有局限性,因为通常爆管以后我并不需要关闭所有周围阀门,而是只要关闭上游阀门即可。
下面的方法,是在查找到周围所有阀门的基础上继续的,在周围阀门中找出与他相接的上游阀门
步骤:
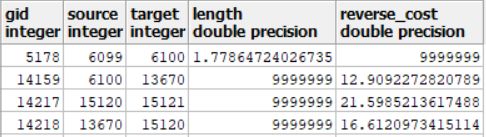
1、在PostGIS中,建立方向模型,模拟气体流向。原理就是新增length或者reverse_cost(关键字),与source/target方向一致的,则length为值,reverse_cost为设一个大点的值9999999;如source/target方向不一致,则给reverse_cost赋值,length为设一个大点的值9999999。
这里在查询时,pgr_dijkstraCost会识别关键词cost和reverse_cost
双向查询时不用关注reverse_cost(注意cost字段一定要有,或可以如下例子将length命名cost的别名)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra( 'SELECT gid AS id, source, target, length as cost FROM zy', 15139, 13670, directed := false);
单向查询时需要加上reverse_cost一起查(注意cost字段一定要有,或可以如下例子将length命名cost的别名)
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra( 'SELECT gid AS id, source, target, length as cost,reverse_cost as reverse_cost FROM zy', 15139, 13670, directed := true);
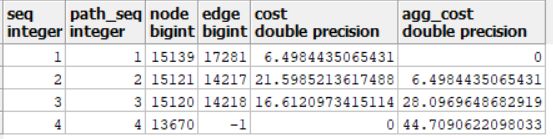
#正向结果:
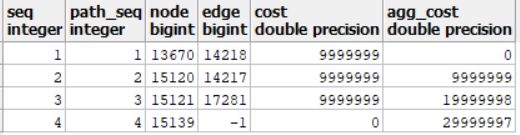
#逆向结果:
2、这里查询到爆点周围所有影响阀门后,需要进行记录,这里采用拼接成字符串记录在数组中(这里略复杂,不同于上一博文直接返回输出了)
格式:[{v_uptap_gid||','||cast(v_uptap_geom as text)||','||up_temprow.source]}]
说明:[{阀门gid,转成字符串的geom,管段的头source}]
raise notice '%' , up_temprow.source;
--记录阀门所在管段source
IF (v_cost @> ARRAY[up_temprow.source::integer]) THEN
ELSE
SELECT array_append(v_cost,up_temprow.source) into v_cost;
SELECT array_append(v_cost,up_temprow.target) into v_cost;
END IF;
IF (res_tap_pipe is not null) THEN
select res_tap_pipe || ARRAY[v_uptap_gid||','||cast(v_uptap_geom as text)||','||up_temprow.source] into res_tap_pipe;
ELSE
select ARRAY[v_uptap_gid||','||cast(v_uptap_geom as text)||','||up_temprow.source] into res_tap_pipe;
END IF;
3、v_cost是周围所有阀门,利用pgRouting的pgr_dijkstraCost函数,逆向找出与爆点管段相接的阀门。
--查找上游阀门
FOREACH m_cost IN ARRAY v_cost
LOOP
SELECT count(*) FROM pgr_dijkstraCost('select gid as id, source, target, length as cost, reverse_cost from zy',m_cost, ARRAY[v_startSource,v_startTarget], true) where agg_cost >= 9999999 into m_cost_value;
raise notice '%' , 'm_cost---'||cast(m_cost as text);
----如果没有消耗大于9999999的(阈值),则认为是上游阀门
IF(m_cost_value = 0) THEN
FOREACH m_tap_pipe IN ARRAY res_tap_pipe
LOOP
raise notice '%' , 'm_cost---'||cast(m_cost as text) ;
raise notice '%' , 'm_tap_pipe---'||cast(m_tap_pipe as text) ;
IF (split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 3)::integer = m_cost) THEN
--阀门id,阀门图形要素,阀门类型(上游/下游)
return query
select split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 1)::integer as res_uptap_gid,split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 2)::geometry as res_uptap_geom ,split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 3)::integer as res_source;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END IF;
END LOOP;
4、附上全部存储过程
declare
v_startLine geometry;--离起点最近的线
v_startTarget integer;--距离起点最近线的终点
v_startSource integer;
v_statpoint geometry;--在v_startLine上距离起点最近的点
v_endpoint geometry;--在v_endLine上距离终点最近的点
v_up_source integer;--游标,记录是否有记录
v_up_idx integer;--记录遍历到多少层级
v_uptap_gid integer;--上游阀门gid
v_uptap_geom geometry;--上游阀门要素
v_all_where integer[];--记录所有查询过的管段
v_up_where integer[];--where条件,将遍历到阀门的管段gid排除
v_down_where integer[];--where条件,将遍历到阀门的管段gid排除
up_temprow record ;
--v_cost record;--记录阀门管段source(用于计算消耗,判断方向)
m_cost integer;
m_cost_value integer;
temprow record;
v_cost integer[];
res_source integer;
res_tap_pipe text[];
m_tap_pipe text;
idx_tap_pipe integer; --遍历结果游标
m_up_cost integer;--上游阀门
v_up_cost integer[];--上游阀门集合
res_main_pipe integer[];--总阀门集合
m_main_pipe integer;--总阀门
begin
--查询离起点最近的线
--3857坐标系
--找起点15米范围内的最近线
execute 'select geom, source, target, ST_StartPoint(geom) as startpoint,ST_EndPoint(geom) as endpoint from ' ||tbl||
' where ST_DWithin(geom,ST_Geometryfromtext(''point('|| startx ||' ' || starty ||')'',3857),15)
order by ST_Distance(geom,ST_GeometryFromText(''point('|| startx ||' '|| starty ||')'',3857)) limit 1'
into v_startLine, v_startSource ,v_startTarget, v_statpoint ,v_endpoint;
raise notice '%' , 'v_startSource---'||cast(v_startSource as text);
--查找上游阀门
v_up_idx = 0;
v_up_source = 1;
--寻找上游阀门
SELECT array_append(v_up_where, v_startSource) into v_up_where;
--如果没有下级节点需要遍历
WHILE array_length(v_up_where,1) > 0
LOOP
--游标归零
v_up_source = 0;
--记录层级
--v_up_idx = v_up_idx + 1;
--获取当前层级节点
FOR up_temprow IN
select zy1.gid,zy1.source,zy1.target from zy zy1 where source = any(v_up_where) or target = any(v_up_where)
--select zy1.gid,zy1.source,zy1.target from zy zy1 where target = any(v_up_where)--找上游
LOOP
--清空需要查的点
IF(v_up_source = 0) THEN
v_up_where = null;
END IF;
--清空初始执行节点
--v_startSource = 0;
--标志执行有数据
v_up_source = 1;
--查询管网上的点
select t.gid,t.geom from fm t where t.gid in (
select a.gid from fm a,(select c.* from zy c where c.gid = up_temprow.gid) b where ST_intersects(a.geom,b.geom)
) into v_uptap_gid, v_uptap_geom;
raise notice '%' , 'UP---'||up_temprow.gid;
--如果没查找到阀门,则继续往下查
IF(v_uptap_gid is null) then
--source去重,判断如果数组中已有,则不添加
IF (v_up_where @> ARRAY[up_temprow.source::integer] OR v_all_where @> ARRAY[up_temprow.source::integer]) THEN
ELSE
SELECT array_append(v_up_where,up_temprow.source) into v_up_where;
SELECT array_append(v_all_where,up_temprow.source) into v_all_where;
END IF;
--target去重,判断如果数组中已有,则不添加
IF (v_up_where @> ARRAY[up_temprow.target::integer] OR v_all_where @> ARRAY[up_temprow.target::integer]) THEN
ELSE
SELECT array_append(v_up_where,up_temprow.target) into v_up_where;
SELECT array_append(v_all_where,up_temprow.target) into v_all_where;
END IF;
ELSE
raise notice '%' , up_temprow.source;
--记录阀门所在管段source
IF (v_cost @> ARRAY[up_temprow.source::integer]) THEN
ELSE
SELECT array_append(v_cost,up_temprow.source) into v_cost;
SELECT array_append(v_cost,up_temprow.target) into v_cost;
END IF;
IF (res_tap_pipe is not null) THEN
select res_tap_pipe || ARRAY[v_uptap_gid||','||cast(v_uptap_geom as text)||','||up_temprow.source] into res_tap_pipe;
ELSE
select ARRAY[v_uptap_gid||','||cast(v_uptap_geom as text)||','||up_temprow.source] into res_tap_pipe;
END IF;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
--raise notice '%' , v_cost;
raise notice '%' , 'res_tap_pipe---'||cast(res_tap_pipe as text);
--return query select * from v_cost;
raise notice '%' , 'v_cost---'||cast(v_cost as text);
--查找上游阀门
FOREACH m_cost IN ARRAY v_cost
LOOP
SELECT count(*) FROM pgr_dijkstraCost('select gid as id, source, target, length as cost, reverse_cost from zy',m_cost, ARRAY[v_startSource,v_startTarget], true) where agg_cost >= 9999999 into m_cost_value;
raise notice '%' , 'm_cost---'||cast(m_cost as text);
----如果没有消耗大于9999999的(阈值),则认为是上游阀门
--IF(m_cost_value = 0) THEN
-- --判断上游阀门间是否有上下游关系
-- SELECT array_append(v_up_cost,m_cost) into v_up_cost;
--END IF;
IF(m_cost_value = 0) THEN
FOREACH m_tap_pipe IN ARRAY res_tap_pipe
LOOP
raise notice '%' , 'm_cost---'||cast(m_cost as text) ;
raise notice '%' , 'm_tap_pipe---'||cast(m_tap_pipe as text) ;
IF (split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 3)::integer = m_cost) THEN
--阀门id,阀门图形要素,阀门类型(上游/下游)
return query
select split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 1)::integer as res_uptap_gid,split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 2)::geometry as res_uptap_geom ,split_part(m_tap_pipe, ',', 3)::integer as res_source;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END IF;
END LOOP;
raise notice '%' , '上游阀门---'||cast(v_up_cost as text);
end;
结尾:
此文算是半成品文章,代码很乱也没有进行优化,很多没有用到的变量没有删掉,这里暂且当作思路的记录。
算法上还有很多需要改进,这里只是在找到所有周边阀门的基础上继续往下写的,其实可以不用分两块,直接上来就开始找上游阀门(算法留待后面继续优化)