SpringBoot 如何使用 MessageSource 实现国际化
使用 MessageSource 实现国际化
国际化,我理解的是根据用户的语言设置显示相应的语言、提示。对应于代码来说就是根据不同的语言环境返回对应语言的描述。比如默认环境为中文的 你好! ,当语言变更为英文时应当显示 Hello!,这就是国际化。
最早接触国际化是在现有项目中,有现成的国际化配置,专门有一个用于国际化的类:I18nService.java ,需要国际化就直接拿来使用就好了。如今被委派魔都新做一个项目,所有东西都需要自己配置,有幸自己独立完成国际化配置,虽然现在想想是挺简单的,但在成功完成那一刻还是超有成就感的!
1、I18nService 封装 MessageSource 类,按照需要新增方法或简化调用链
public class I18nService {
private final MessageSource messageSource;
public I18nService(MessageSource messageSource) {
this.messageSource = messageSource;
}
public String getMessage(String msgKey, Object[] args) {
return messageSource.getMessage(msgKey, args, LocaleUtils.getCurrentLocale());
}
public String getMessage(String msgKey) {
return messageSource.getMessage(msgKey, null, LocaleUtils.getCurrentLocale());
}
}
2、配置 I18nService 、MessageSource Bean,主要是配置资源文件的 baseNames ;当然,也可以通过 yml 属性(spring.messages.basename)配置
@Bean
public I18nService i18nService() {
return new I18nService(messageSource());
}
@Bean
public ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource() {
Locale.setDefault(Locale.CHINESE);
ResourceBundleMessageSource source = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
source.setBasenames("i18n/messages");// name of the resource bundle
source.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(true);
source.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return source;
}
3、多语言资源配置文件( basenames = i18n/messages ),即配置文件所在目录为 i18n,文件前缀为 messages
(1)messages.properties
message.key.test=测试!
message.key.hello=你好!{0}~
(2)messages_en.properties
message.key.test=test!
message.key.hello=hello!{0}~
4、用于测试用的 controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/api")
public class HelloJavaCoderController {
private final I18nService i18nService;
public HelloJavaCoderController(I18nService i18nService) {
this.i18nService = i18nService;
}
@GetMapping("/hello-coder")
public ResponseEntity greeting() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(i18nService.getMessage("message.key.hello", new Object[]{"JavaCoder"}));
}
@GetMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity test() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(i18nService.getMessage("message.key.test"));
}
}
5、使用 Postman 进行 restful API 测试(启动服务,server.port=8888)
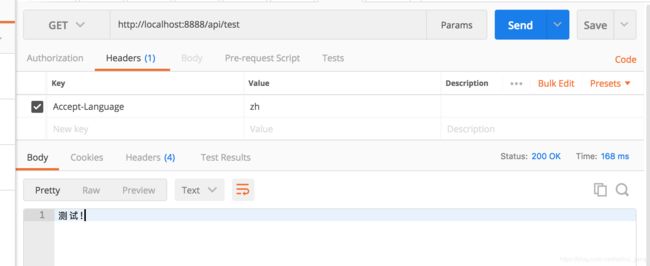
(1)请求 http://localhost:8888/api/test 并在 header 中设置 Accept-Languate=zh,结果如下:
(2)请求 http://localhost:8888/api/test 并在 header 中设置 Accept-Languate=en,结果如下:

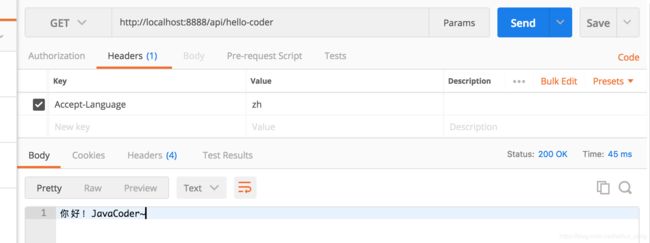
(3)请求 http://localhost:8888/hello-coder 并在 header 中设置 Accept-Languate=zh,结果如下:
(4)请求 http://localhost:8888/hello-coder 并在 header 中设置 Accept-Languate=en,结果如下:
(1)(2)是正常的国际化展示,(3)(4)展示了国际化中也可以使用占位符,在运行时绑定特定参数, 通过使用类似于 {0} 这种方式,在 getMessage 时传入一个 Object[] args 进行相应位置的参数替换
在将其跑通、验证之后,想了解了一下其内部实现(MessageSource 是如何从 properties 文件中读取国际化的值的?),大致看了一下源码并进行了调试,最终了解到它是将 properties 文件中的 msgKey、value 都 load 到了一个lookup 的 HashMap 中(第一次加载时会缓存起来,后面直接走的缓存,有兴趣的同学可以在 PropertyResourceBundle.java:157 中寻找答案),得到 msgKey -> value,外层还有一个 locale 做索引,即 locale -> (msgKey -> value),最后是通过 locale + msgKey 得到相应的 value 。
最终,一个 properties 文件对应于一个 PropertyResourceBundle 对象。
以上代码均可在 github 上找到:spring-i18n-support