RocketMQ学习(四)——RocketMQ消息发送
RocketMQ 网络架构图
RocketMQ分布式消息队列的网络部署架构图如下图所示

于上图中几个角色的说明:
(1) NameServer: RocketMQ集群的命名服务器(也可以说是注册中心),它本身是无状态的(实际情况下可能存在每个NameServer实例上的数据有短暂的不一致现象,但是通过定时更新,在大部分情况下都是一致的),用于管理集群的元数据( 例如,KV配置、Topic、Broker的注册信息)。nameserver存有全量的路由信息,提供对等的读写服务,支持快速扩缩容。nameserver接收client(producer/consumer)的请求,根据消息的topic获取相应的broker路由信息。集群部署后,节点之间无任何信息同步。
(2)Broker(Master): RocketMQ消息代理服务器主节点,起到串联Producer的消息发送和Consumer的消息消费,和将消息的落盘存储的作用;
(3)Broker(Slave): RocketMQ消息代理服务器备份节点,主要是通过同步/异步的方式(同步复制:消息发给master的同时也会将消息发送给slave 异步双写:只发送到master,再由master异步同步到slave)将主节点的消息同步过来进行备份,为RocketMQ集群的高可用性提供保障;
(4)Producer(消息生产者): 在这里为普通消息的生产者,主要基于RocketMQ-Client模块将消息发送至RocketMQ的主节点(Broker Master)。一般由业务系统负责产生消息。消息有3种发送方式:同步、异步、单向。
(5)ProducerGroup(生产组): 通常具有同样作用(同样topic)的一些producer可以归为同一个group。在事务消息机制中,如果发送某条事务消息后的producer-A宕机,使得事务消息一直处于PREPARED状态并超时,则broker会回查同一个group的其他producer,确认这条消息应该commit还是rollback。
其他核心概念:
(1)topic(主题): 一种消息的逻辑分类(消息的类型),比如说你有订单类的消息,也有库存类的消息,那么就需要进行分类存储。生产者方面:发消息时需指定topic,可以有1-n个生产者发布1个topic的消息,也1个生产者可以发布不同topic的消息。消费者方面:收消息时需订阅topic,可以有1-n个消费者组订阅1个topic的消息,1个消费者组可以订阅不同topic的消息。1个消息必须指定1个topic,topic允许自动创建与手工创建,topic创建时需要指定broker,可以指定1个或多个,name server就是通过broker与topic的映射关系来做路由。producer和consumer在生产和消费消息时,都需要指定消息的 topic,当topic匹配时,consumer 才会消费到producer发送的消息。topic与broker是多对多的关系,一个topic分布在多个broker上,一个broker可以配置多个topic。
(2)message(消息): message是消息的载体。每个message必须指定一个topic,相当于寄信的地址。message还有一个可选的tag设置,以便消费端可以基于tag进行过滤消息。message还有扩展的kv结构,例如你可以设置一个业务key到你的消息中,在broker上查找消息并诊断问题。
(3)tag(标签): 标签可以被认为是对topic的进一步细化。一般在相同业务模块中通过引入标签来标记不同用途的消息。区分相同topic下不同种类的消息。生产到哪个topic的哪个tag下,消费者也是从topic的哪个tag进行消费,即实现消息的过滤。
(4)queue(队列): queue是消息的物理管理单位,而topic是逻辑管理单位。一个topic下可以有多个queue,默认自动创建是4个,手动创建是8个。queue的引入使得消息存储可以分布式集群化,具有了水平扩展的能力。1个message只能属于1个queue、1个topic。在rocketmq中,所有消息队列都是持久化,长度无限的数据结构,所谓长度无限是指队列中的每个存储单元都是定长,访问其中的存储单元使用offset来访问,offset 为 java long 类型,64 位,理论上在 100年内不会溢出,所以认为是长度无限,另外队列中只保存最近几天的数据,之前的数据会按照过期时间来删除。也可以认为 Message Queue是一个长度无限的数组,offset就是下标。
rocketmq中,producer将消息发送给broker时,需要指定发送到哪一个queue中,默认情况下,producer会轮询的将消息发送到每个queue中,顺序是随机的,但总体上每个queue的消息数量均分,所有broker下的queue合并成一个list去轮询,也可以由程序员通过MessageQueueSelector接口来指定具体发送到哪个queue中。
对于consumer而言,会为每个consumer分配固定的队列(如果队列总数没有发生变化),consumer从固定的队列中去拉取没有消费的消息进行处理。消费端会通过RebalanceService线程,10秒钟做一次基于topic下的所有队列负载,获取同一个Consumer Group下的所有Consumer实例数或Topic的queue的个数是否改变,通知所有Consumer实例重新做一次负载均衡算法。
(5) offset(消费进度): 理解成消费进度,可自增。
(6) commit log(存储文件): 虽然每个topic下面有很多message queue,但是message queue本身并不存储消息。真正的消息存储会写在CommitLog的文件,message queue只是存储CommitLog中对应的位置信息,方便通过message queue找到对应存储在CommitLog的消息。 不同的topic,message queue都是写到相同的CommitLog 文件,也就是说CommitLog完全的顺序写。
对于上面图中几条通信链路的关系:
(1)Broker和NamerServer: Broker(Master or Slave)均会和每一个NameServer实例来建立TCP连接,定时注册topic&broker的路由信息到所有name server中。Broker在启动的时候会注册自己配置的Topic信息到NameServer集群的每一台机器中。即每一个NameServer均有该broker的Topic路由配置信息。其中,Master与Master之间无连接,Master与Slave之间有连接;
(2)Producer与NamerServer: 每一个Producer会与NameServer集群中的一个实例建立TCP连接,从这个NameServer实例上拉取Topic路由信息;
(3)Producer和Broker: Producer会和它要发送的topic相关联的Master的Broker代理服务器建立TCP连接,用于发送消息以及定时的心跳信息;
客户端发送普通消息的demo方法
public class ProducerTest {
//nameserver地址
private String namesrvAddr = "192.168.152.129:9876;192.168.152.130:9876";
private final DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("ProducerTest");
private String TOPIC_TEST = "TOPIC_TEST";
private String TAG_TEST = "TAG_TEST";
/**
* 初始化
*/
public void start() {
try {
System.out.println("MQ:启动ProducerTest生产者");
producer.setNamesrvAddr(namesrvAddr);
producer.start();
//发送消息
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
sendMessage("hello mq" + i);
}
} catch (MQClientException e) {
System.out.println("MQ:启动ProducerTest生产者失败:" + e.getResponseCode() + e.getErrorMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
public void sendMessage(String data) {
System.out.println("MQ: 生产者发送消息 :{}" + data);
Message message = null;
try {
//转换成字符数组
byte[] messageBody = data.getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET);
//创建消息对象
message = new Message(TOPIC_TEST, TAG_TEST, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()), messageBody);
//同步发送消息
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(message);
//异步发送消息
/*producer.send(message, new SendCallback() {
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) {
System.out.println("MQ: CouponProducer生产者发送消息" + sendResult);
}
public void onException(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage() + throwable);
}
});*/
//单向发送 只发送消息,不等待服务器响应,只发送请求不等待应答。
//producer.sendOneway(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (message != null) {
System.out.println("producerGroup:ProducerTest,Message:{}" + JSON.toJSON(message));
}
System.out.println("MQ: CouponProducer error :" + e);
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void stop() {
if (producer != null) {
producer.shutdown();
System.out.println("MQ:关闭ProducerTest生产者");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProducerTest producerTest = new ProducerTest();
producerTest.start();
}
}
RocketMQ发送普通消息的全流程解读
消息生产者发送消息的demo代码还是较为简单的,核心就几行代码,但在深入研读RocketMQ的Client模块后,发现其发送消息的核心流程还是有一些复杂的。下面将主要从DefaultMQProducer的启动流程、send发送方法和Broker代理服务器的消息处理三方面分别进行分析和阐述。
DefaultMQProducer的启动流程
在客户端发送普通消息的demo代码部分,我们先是将DefaultMQProducer实例启动起来,里面调用了默认生成消息的实现类—DefaultMQProducerImpl的start()方法。
public class DefaultMQProducer extends ClientConfig implements MQProducer {
//处理发送消息的类内部类
protected final transient DefaultMQProducerImpl defaultMQProducerImpl;
public DefaultMQProducer(String producerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook) {
this.createTopicKey = "TBW102";
this.defaultTopicQueueNums = 4;
this.sendMsgTimeout = 3000;
this.compressMsgBodyOverHowmuch = 4096;
this.retryTimesWhenSendFailed = 2;
this.retryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed = 2;
this.retryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK = false;
this.maxMessageSize = 4194304;
this.producerGroup = producerGroup;
//将自己作为参数传入,实现了两个类相互引用
this.defaultMQProducerImpl = new DefaultMQProducerImpl(this, rpcHook);
}
public DefaultMQProducer(String producerGroup) {
this(producerGroup, (RPCHook)null);
}
...
public void start() throws MQClientException {
//调用内部类的start方法
this.defaultMQProducerImpl.start();
}
...
}
让我们看看内部类DefaultMQProducerImpl是如何做的
public class DefaultMQProducerImpl implements MQProducerInner {
//重载的方法,默认传入true
public void start() throws MQClientException {
this.start(true);
}
//启动方法
public void start(boolean startFactory) throws MQClientException {
switch(this.serviceState) {
//第一次调用进入这个case
case CREATE_JUST:
//更改状态防止多次启动
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
//验证groupname
this.checkConfig();
//获取了jvm进程id作为producer的intancename名。
if (!this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup().equals("CLIENT_INNER_PRODUCER")) {
this.defaultMQProducer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
//获取MQClientManager单例对象,调用getAndCreateMQClientInstance,获取MQClientInstance(mq客户端对象实例)
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getAndCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQProducer, this.rpcHook);
//查询groupname是否注册过,有就会false,没有就添加到map中,返回true
boolean registerOK = this.mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this);
//如果groupname创建过则报错
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
throw new MQClientException("The producer group[" + this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup() + "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo("http://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/faq/"), (Throwable)null);
} else {
//新建TopicPublishInfo放入本地缓存变量—topicPublishInfoTable,key是默认的Topic(“TBW102”)
this.topicPublishInfoTable.put(this.defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey(), new TopicPublishInfo());
//如果该方法入参是true,则会调用MQClientInstance的start方法
if (startFactory) {
this.mQClientFactory.start();
}
this.log.info("the producer [{}] start OK. sendMessageWithVIPChannel={}", this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this.defaultMQProducer.isSendMessageWithVIPChannel());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
}
default:
//向所有的broker master发送心跳
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
return;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
throw new MQClientException("The producer service state not OK, maybe started once, " + this.serviceState + FAQUrl.suggestTodo("http://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/faq/"), (Throwable)null);
}
}
private void checkConfig() throws MQClientException {
//首先验证ProducerGroup名称的 有效性。包括,非空,正则是否合法,最长字符不能超过255
Validators.checkGroup(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup());
//组名不能为空且不能是生产组名“DEFAULT_PRODUCER”
if (null == this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup()) {
throw new MQClientException("producerGroup is null", (Throwable)null);
} else if (this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup().equals("DEFAULT_PRODUCER")) {
throw new MQClientException("producerGroup can not equal DEFAULT_PRODUCER, please specify another one.", (Throwable)null);
}
}
}
public class MQClientManager {
private static MQClientManager instance = new MQClientManager();
//保存MQClientInstance实例
private ConcurrentMap<String, MQClientInstance> factoryTable = new ConcurrentHashMap();
//获取MQClientManager实例,这里的实例是单例模式
public static MQClientManager getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public MQClientInstance getAndCreateMQClientInstance(ClientConfig clientConfig, RPCHook rpcHook) {
//client分配id,规则:客户端外网ip@jvm进程id。
String clientId = clientConfig.buildMQClientId();
//根据clientId获取虚拟机中的MQClientInstance的实例
MQClientInstance instance = (MQClientInstance)this.factoryTable.get(clientId);
//如果没有重新创建
if (null == instance) {
instance = new MQClientInstance(clientConfig.cloneClientConfig(), this.factoryIndexGenerator.getAndIncrement(), clientId, rpcHook);
MQClientInstance prev = (MQClientInstance)this.factoryTable.putIfAbsent(clientId, instance);
if (prev != null) {
instance = prev;
log.warn("Returned Previous MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
} else {
log.info("Created new MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
}
}
return instance;
}
}
public class MQClientInstance {
...
private final ConcurrentMap<String, MQProducerInner> producerTable;
//通过groupname保存内部类到map中,注意这里如果一个ip的虚拟机里只能有一个groupname,否则会报错
public boolean registerProducer(String group, DefaultMQProducerImpl producer) {
if (null != group && null != producer) {
MQProducerInner prev = (MQProducerInner)this.producerTable.putIfAbsent(group, producer);
if (prev != null) {
this.log.warn("the producer group[{}] exist already.", group);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
//启动方法
public void start() throws MQClientException {
synchronized(this) {
switch(this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
}
//启动remotingClient
this.mQClientAPIImpl.start();
//启动若干定时任务(更新路由/清理下线broker/发送心跳/持久化consumerOffset/调整线程池)
this.startScheduledTask();
//启动拉取消息的线程
this.pullMessageService.start();
//启动负载均衡服务线程
this.rebalanceService.start();
//重新做一次start,但是参数是false
this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultMQProducerImpl().start(false);
this.log.info("the client factory [{}] start OK", this.clientId);
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
case RUNNING:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
default:
return;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", (Throwable)null);
}
}
}
...
}
总结起来,DefaultMQProducer的主要启动流程如下:
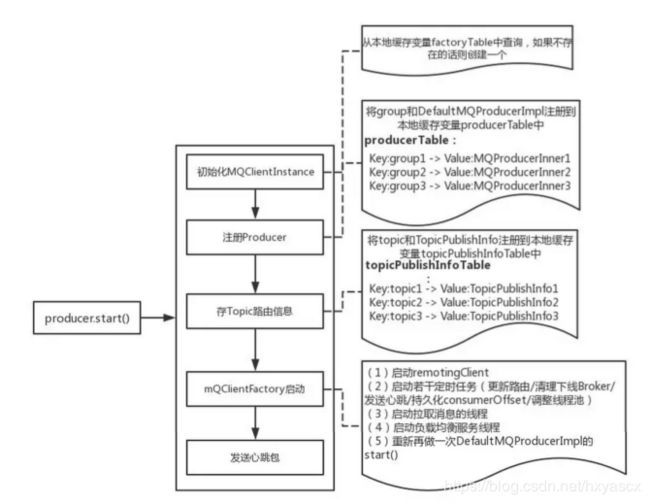
这里有以下几点需要说明:
(1)在一个客户端中,一个producerGroup只能有一个实例;
(2)根据不同的clientId,MQClientManager将给出不同的MQClientInstance;
(3)根据不同的producerGroup,MQClientInstance将给出不同的MQProducer和MQConsumer(保存在本地缓存变量——producerTable和consumerTable中);
send发送方法的核心流程
(1) 同步方式
//同步发送消息
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(message);
(2)异步方式
//异步发送消息
producer.send(message, new SendCallback() {
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) {
System.out.println("MQ: CouponProducer生产者发送消息" + sendResult);
}
public void onException(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage() + throwable);
}
});
(3)Oneway方式
//单向发送 只发送消息,不等待服务器响应,只发送请求不等待应答。
producer.sendOneway(message);
其中,使用(1)、(2)种方式来发送消息比较常见,具体使用哪一种方式需要根据业务情况来判断。使用同步方式发送消息核心流程的入口如下:
private SendResult sendDefaultImpl(Message msg, CommunicationMode communicationMode, SendCallback sendCallback, long timeout) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
//判断生产者是否正常运行
this.makeSureStateOK();
//验证topic和body没有问题
Validators.checkMessage(msg, this.defaultMQProducer);
//调用编号:用于下面打印日志,标记为同一次发消息
long invokeID = this.random.nextLong();
//开始发消息时间
long beginTimestampFirst = System.currentTimeMillis();
long beginTimestampPrev = beginTimestampFirst;
//从nameserver更新topic的路由信息,这里比较复杂
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());
//已经获取到了topic路由信息
if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
// 最后选择消息要发送到的队列
MessageQueue mq = null;
Exception exception = null;
// 最后一次发送结果
SendResult sendResult = null;
//设置失败重试次数 同步1次+重试次数 其他都是1次
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC ? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
// 第几次发送
int times = 0;
// 存储每次发送消息选择的broker名
String[] brokersSent = new String[timesTotal];
while(true) {
String info;
//还在重试次数内
if (times < timesTotal) {
info = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
//选择其中一个queue
MessageQueue mqSelected = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, info);
//已经有了选中的queue
if (mqSelected != null) {
mq = mqSelected;
brokersSent[times] = mqSelected.getBrokerName();
long endTimestamp;
try {
beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis();
//发送消息到选中的队列
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout);
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
//更新Broker可用性信息<容错> 上面到准备工作(获取topic和queue相关)时间过长,那么会让该broker休息一段时间(不可用)
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
switch(communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
return null;
case ONEWAY:
return null;
case SYNC:
if (sendResult.getSendStatus() == SendStatus.SEND_OK || !this.defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) {
return sendResult;
}
}
} catch (RemotingException var24) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mqSelected.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);
this.log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mqSelected), var24);
this.log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = var24;
} catch (MQClientException var25) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mqSelected.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);
this.log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mqSelected), var25);
this.log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = var25;
} catch (MQBrokerException var26) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mqSelected.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);
this.log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mqSelected), var26);
this.log.warn(msg.toString());
exception = var26;
switch(var26.getResponseCode()) {
case 1:
case 14:
case 16:
case 17:
case 204:
case 205:
break;
default:
if (sendResult != null) {
return sendResult;
}
throw var26;
}
} catch (InterruptedException var27) {
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.updateFaultItem(mqSelected.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
this.log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, throw exception, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s", invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mqSelected), var27);
this.log.warn(msg.toString());
this.log.warn("sendKernelImpl exception", var27);
this.log.warn(msg.toString());
throw var27;
}
++times;
continue;
}
}
if (sendResult != null) {
return sendResult;
}
info = String.format("Send [%d] times, still failed, cost [%d]ms, Topic: %s, BrokersSent: %s", times, System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestampFirst, msg.getTopic(), Arrays.toString(brokersSent));
info = info + FAQUrl.suggestTodo("http://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/faq/");
MQClientException mqClientException = new MQClientException(info, (Throwable)exception);
if (exception instanceof MQBrokerException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(((MQBrokerException)exception).getResponseCode());
} else if (exception instanceof RemotingConnectException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(10001);
} else if (exception instanceof RemotingTimeoutException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(10002);
} else if (exception instanceof MQClientException) {
mqClientException.setResponseCode(10003);
}
throw mqClientException;
}
} else {
List<String> nsList = this.getmQClientFactory().getMQClientAPIImpl().getNameServerAddressList();
if (null != nsList && !nsList.isEmpty()) {
throw (new MQClientException("No route info of this topic, " + msg.getTopic() + FAQUrl.suggestTodo("http://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/faq/"), (Throwable)null)).setResponseCode(10005);
} else {
throw (new MQClientException("No name server address, please set it." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo("http://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/faq/"), (Throwable)null)).setResponseCode(10004);
}
}
}
从上面的核心流程来看主要几个重要的步骤,让我们来分别分析一下。
尝试获取TopicPublishInfo的路由信息
我们一步步debug进去后会发现在sendDefaultImpl()方法中先对待发送的消息进行前置的验证。如果消息的Topic和Body均没有问题的话,那么会调用—tryToFindTopicPublishInfo()方法。
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(String topic) {
//先从本地缓存里取
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = (TopicPublishInfo)this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
//如果缓存没有先根据要发送的topic从nameserver上获取路由信息
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
topicPublishInfo = (TopicPublishInfo)this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
//如果还是没有使用默认的topic获取路由信息,并在broker上创建
if (!topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() && !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer);
topicPublishInfo = (TopicPublishInfo)this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
return topicPublishInfo;
}
}
主要的逻辑是这样的:根据待发送消息的中包含的Topic尝试从Client端的本地缓存变量—topicPublishInfoTable中查找,如果没有则会从NameServer上更新Topic的路由信息(其中,调用了MQClientInstance实例的updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer方法,最终执行的是MQClientAPIImpl实例的getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer方法),这里分别会存在以下两种场景:
1、生产者第一次发送消息(此时,Topic在NameServer中并不存在): 因为第一次获取时候并不能从远端的NameServer上拉取下来并更新本地缓存变量—topicPublishInfoTable成功。因此,第二次需要通过默认Topic—TBW102的TopicRouteData变量来构造TopicPublishInfo对象,并更新DefaultMQProducerImpl实例的本地缓存变量——topicPublishInfoTable。
另外,在该种类型的场景下,当消息发送至Broker代理服务器时,在SendMessageProcessor业务处理器的sendBatchMessage/sendMessage方法里面的super.msgCheck(ctx, requestHeader, response)消息前置校验中,会调用TopicConfigManager的createTopicInSendMessageMethod方法,在Broker端完成新Topic的创建并持久化至配置文件中(配置文件路径:{rocketmq.home.dir}/store/config/topics.json)。因此需要注意的是需要broker设置允许topic自动创建。
2、生产者发送Topic已存在的消息: 由于在NameServer中已经存在了该Topic,因此在第一次获取时候就能够取到并且更新至本地缓存变量中topicPublishInfoTable,随后tryToFindTopicPublishInfo方法直接可以return。
选择消息发送的队列
在获取了TopicPublishInfo路由信息后,RocketMQ的客户端在默认方式下,selectOneMessageQueuef()方法会从TopicPublishInfo中的messageQueueList中选择一个队列(MessageQueue)进行发送消息。这里通过一个sendLatencyFaultEnable开关来进行选择采用下面哪种方式:
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, String lastBrokerName) {
//若开启了延迟容错机制,默认未开启
if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) {
try {
//
int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement();
int i = 0;
while(true) {
int writeQueueNums;
MessageQueue mq;
if (i >= tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size()) {
String notBestBroker = (String)this.latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast();
writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker);
if (writeQueueNums > 0) {
mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
if (notBestBroker != null) {
mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker);
mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement() % writeQueueNums);
}
return mq;
}
this.latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker);
break;
}
writeQueueNums = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size();
if (writeQueueNums < 0) {
writeQueueNums = 0;
}
mq = (MessageQueue)tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(writeQueueNums);
if (this.latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName()) && (null == lastBrokerName || mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName))) {
return mq;
}
++i;
}
} catch (Exception var7) {
log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue", var7);
}
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
} else {
//容错开关关闭
//采用随机递增取模的方式选择一个队列(MessageQueue)来发送消息
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName);
}
}
sendLatencyFaultEnable开关关闭(默认关闭): 采用随机递增取模的方式选择一个队列(MessageQueue)来发送消息。
第一次发送,会按顺序获取所有MessageQueue里上次发送队列的的下一位;若第一次发送失败了,按顺序隔位筛选,直到找到一个不是上个Broker的MessageQueue,也就是不要再向发送失败的Broker发送消息了。
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(String lastBrokerName) {
//上一个broker,这个值只有在上次发送失败的时候才会有值
if (lastBrokerName == null) {
return this.selectOneMessageQueue();
} else {
//有值证明上次发送失败那么不会再选择上次发送失败的broker发送
int index = this.sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement();
for(int i = 0; i < this.messageQueueList.size(); ++i) {
int pos = Math.abs(index++) % this.messageQueueList.size();
if (pos < 0) {
pos = 0;
}
MessageQueue mq = (MessageQueue)this.messageQueueList.get(pos);
if (!mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) {
return mq;
}
}
return this.selectOneMessageQueue();
}
}
//取模操作
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue() {
int index = this.sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement();
int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size();
if (pos < 0) {
pos = 0;
}
return (MessageQueue)this.messageQueueList.get(pos);
}
//获取一个随机int值并放到threadlocal中
public int getAndIncrement() {
Integer index = (Integer)this.threadLocalIndex.get();
if (null == index) {
index = Math.abs(this.random.nextInt());
if (index.intValue() < 0) {
index = Integer.valueOf(0);
}
this.threadLocalIndex.set(index);
}
//每次都获取上次保存的+1值,这样取模就会轮训发送
index = Math.abs(index.intValue() + 1);
if (index.intValue() < 0) {
index = Integer.valueOf(0);
}
this.threadLocalIndex.set(index);
return index.intValue();
}
sendLatencyFaultEnable开关打开: 在随机递增取模的基础上,再过滤掉not available的Broker代理。所谓的"latencyFaultTolerance",是指对之前失败的,按一定的时间做退避。例如,如果上次请求的latency超过550Lms,就退避3000Lms;超过1000L,就退避60000L。
public class MQFaultStrategy {
//维护每个Broker发送消息的延迟
private final LatencyFaultTolerance<String> latencyFaultTolerance = new LatencyFaultToleranceImpl();
//发送消息延迟容错开关
private boolean sendLatencyFaultEnable = false;
//延迟级别数组
private long[] latencyMax = new long[]{50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L};
//不可用时长数组
private long[] notAvailableDuration = new long[]{0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L};
...
}
发送封装后的RemotingCommand数据包
在选择完发送消息的队列后,RocketMQ就会调用sendKernelImpl()方法发送消息(该方法为,通过RocketMQ的Remoting通信模块真正发送消息的核心)。在该方法内总共完成以下几个步流程:
(1)根据前面获取到的MessageQueue中的brokerName,调用MQClientInstance实例的findBrokerAddressInPublish()方法,得到待发送消息中存放的Broker代理服务器地址,如果没有找到则跟新路由信息;
(2)如果没有禁用,则发送消息前后会有钩子函数的执行(executeSendMessageHookBefore()/executeSendMessageHookAfter()方法);
(3)将与该消息相关信息封装成RemotingCommand数据包,其中请求码RequestCode为以下几种之一:
a.SENDMESSAGE(普通发送消息)
b.SENDMESSAGEV2(优化网络数据包发送)
c.SENDBATCH_MESSAGE(消息批量发送)
(4)根据获取到的Broke代理服务器地址,将封装好的RemotingCommand数据包发送对应的Broker上,默认发送超时间为3s;
(5)这里,真正调用RocketMQ的Remoting通信模块完成消息发送是在MQClientAPIImpl实例sendMessageSync()方法中。
(6)processSendResponse方法对发送正常和异常情况分别进行不同的处理并返回sendResult对象;
(7)发送返回后,调用updateFaultItem更新Broker代理服务器的可用时间;
(8)对于异常情况,且标志位—retryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK,设置为true时,在发送失败的时候,会选择换一个Broker;
Broker代理服务器的消息处理简析
Broker代理服务器中存在很多Processor业务处理器,用于处理不同类型的请求,其中一个或者多个Processor会共用一个业务处理器线程池。对于接收到消息,Broker会使用SendMessageProcessor这个业务处理器来处理。SendMessageProcessor会依次做以下处理:
(1)消息前置校验,包括broker是否可写、校验queueId是否超过指定大小、消息中的Topic路由信息是否存在,如果不存在就新建一个。
(2)构建MessageExtBrokerInner;
(3)调用“brokerController.getMessageStore().putMessage”将MessageExtBrokerInner做落盘持久化处理;
(4)根据消息落盘结果(正常/异常情况),BrokerStatsManager做一些统计数据的更新,最后设置Response并返回;
同步发送消息返回参数
同步发送消息会返回SendResult。SendStatus代表着发送的结果状态。
SendResult send = producer.send(message);
SendStatus sendStatus = send.getSendStatus();
SendStatus 包含4个类型,除了SEND_OK之外,要保证消息100%投递,要处理其他类型的消息,进行消息到补偿。
public enum SendStatus {
SEND_OK,
FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT,
FLUSH_SLAVE_TIMEOUT,
SLAVE_NOT_AVAILABLE;
private SendStatus() {
}
}
发送消息选择队列
这个发送消息的方法会传入一个MessageQueueSelector对象,根据自定义规则发送到指定队列。如根据订单号取模,List list代表topic下的queue。
producer.send(message, new MessageQueueSelector() {
@Override
public MessageQueue select(List<MessageQueue> list, Message message, Object arg) {
//这里会将send中到第三个参数注入进来
Integer num = (Integer) arg;
return list.get(num);
}
}, 2);