死锁的成因、场景以及死锁的避免
目录
1、死锁概念
2、死锁成因
3、死锁场景
4、死锁的避免
前言
关于多线程死锁的问题,其实很多人在实际的项目开发中并没有真正的遇到过,当别的同事提起的时候只能知其然,但并不知其所以然(其实那很多人中也包括我 惭愧 哈哈),所以为了日后避免此种尴尬场景的重现,安排它(死锁)!
1、死锁概念
在Java中使用多线程,就会有可能导致死锁问题(并不是每次都会导致死锁,但往往实在高负载下发生)。死锁会让程序一直卡住,不再程序往下执行。我们只能通过中止并重启的方式来让程序重新执行。所以我们能做的就是尽可能避免死锁的发生;
2、死锁成因
造成死锁的原因可以概括成三句话:
- 当前线程拥有其他线程需要的资源
- 当前线程等待其他线程已拥有的资源
- 都不放弃自己拥有的资源
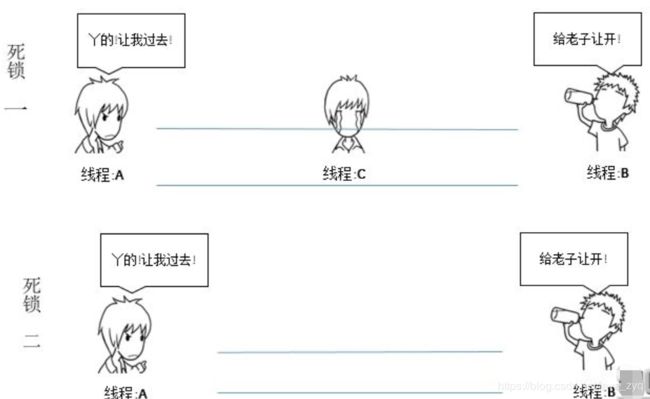
下面引入一张图片来巩固下理解:
3、死锁场景
3.1锁顺序死锁
首先我们来看一下最简单的死锁(锁顺序死锁)是怎么样发生的:
测试类:
@Test
public void test() {
Object o1 = new Object();
Object o2 = new Object();
MyThread thread = new MyThread(o1,o2);
MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2(o1,o2);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(thread);
Thread thread22 = new Thread(thread2);
thread1.start();
thread22.start();
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
private Object o1;
private Object o2;
public MyThread(Object o1,Object o2) {
this.o1=o1;
this.o2=o2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("我已经持有锁o1");
try{
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("我已经持有锁o2");
}
}
}
}
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
private Object o1;
private Object o2;
public MyThread2(Object o1,Object o2) {
this.o1=o1;
this.o2=o2;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("我已经持有锁o2");
try{
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("我已经持有锁o1");
}
}
}
}
我们的线程是交错执行的,那么就很有可能出现以下的情况:
- 线程A调用
MyThread ()方法,得到o1锁 - 同时线程B调用
MyThread2 ()方法,得到o2锁 - 线程A和线程B都继续执行,此时线程A需要o1锁才能继续往下执行。此时线程B需要o2锁才能继续往下执行。
- 但是:线程A的o1锁并没有释放,线程B的o2锁也没有释放。
- 所以他们都只能等待,而这种等待是无期限的-->永久等待-->死锁
3.2 动态锁顺序死锁
经典场景引入:银行转账问题:线程 A 从 X 账户向 Y 账户转账,线程 B 从账户 Y 向账户 X 转账,那么就会发生死锁。
下面这段代码乍一看是没有问题的:锁定两个账户来判断余额是否充足才进行转账!
// 转账
public static void transferMoney(Account fromAccount,
Account toAccount,
DollarAmount amount)
throws InsufficientFundsException {
// 锁定汇账账户
synchronized (fromAccount) {
// 锁定来账账户
synchronized (toAccount) {
// 判余额是否大于0
if (fromAccount.getBalance().compareTo(amount) < 0) {
throw new InsufficientFundsException();
} else {
// 汇账账户减钱
fromAccount.debit(amount);
// 来账账户增钱
toAccount.credit(amount);
}
}
}
}但是,同样有可能会发生死锁:
- 如果两个线程同时调用
transferMoney() - 线程A从X账户向Y账户转账
- 线程B从账户Y向账户X转账
- 那么就会发生死锁。
A:transferMoney(myAccount,yourAccount,10);
B:transferMoney(yourAccount,myAccount,20);3.3、协作对象之间发生死锁
我们来看一下下面的例子:
public class CooperatingDeadlock {
// Warning: deadlock-prone!
class Taxi {
@GuardedBy("this") private Point location, destination;
private final Dispatcher dispatcher;
public Taxi(Dispatcher dispatcher) {
this.dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public synchronized Point getLocation() {
return location;
}
// setLocation 需要Taxi内置锁
public synchronized void setLocation(Point location) {
this.location = location;
if (location.equals(destination))
// 调用notifyAvailable()需要Dispatcher内置锁
dispatcher.notifyAvailable(this);
}
public synchronized Point getDestination() {
return destination;
}
public synchronized void setDestination(Point destination) {
this.destination = destination;
}
}
class Dispatcher {
@GuardedBy("this") private final Set taxis;
@GuardedBy("this") private final Set availableTaxis;
public Dispatcher() {
taxis = new HashSet();
availableTaxis = new HashSet();
}
public synchronized void notifyAvailable(Taxi taxi) {
availableTaxis.add(taxi);
}
// 调用getImage()需要Dispatcher内置锁
public synchronized Image getImage() {
Image image = new Image();
for (Taxi t : taxis)
// 调用getLocation()需要Taxi内置锁
image.drawMarker(t.getLocation());
return image;
}
}
class Image {
public void drawMarker(Point p) {
}
}
}
上面的getImage()和setLocation(Point location)都需要获取两个锁的
- 并且在操作途中是没有释放锁的
这就是隐式获取两个锁(对象之间协作)..
这种方式也很容易就造成死锁..... 其实,这个跟经典的:三个人 三根筷子:每个人需要拿到身边的两根筷子才能开始吃饭 相仿;
4、避免死锁
避免死锁可以概括成三种方法:
- 固定加锁的顺序(针对锁顺序死锁)
- 开放调用(针对对象之间协作造成的死锁)
- 使用定时锁-->
tryLock()- 如果等待获取锁时间超时,则抛出异常而不是一直等待!
- 如果等待获取锁时间超时,则抛出异常而不是一直等待!
4.1固定锁顺序避免死锁
上面transferMoney()发生死锁的原因是因为加锁顺序不一致而出现的~
- 正如书上所说的:如果所有线程以固定的顺序来获得锁,那么程序中就不会出现锁顺序死锁问题!
那么上面的例子我们就可以改造成这样子:
public class InduceLockOrder {
// 额外的锁、避免两个对象hash值相等的情况(即使很少)
private static final Object tieLock = new Object();
public void transferMoney(final Account fromAcct,
final Account toAcct,
final DollarAmount amount)
throws InsufficientFundsException {
class Helper {
public void transfer() throws InsufficientFundsException {
if (fromAcct.getBalance().compareTo(amount) < 0)
throw new InsufficientFundsException();
else {
fromAcct.debit(amount);
toAcct.credit(amount);
}
}
}
// 得到锁的hash值
int fromHash = System.identityHashCode(fromAcct);
int toHash = System.identityHashCode(toAcct);
// 根据hash值来上锁
if (fromHash < toHash) {
synchronized (fromAcct) {
synchronized (toAcct) {
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
} else if (fromHash > toHash) {// 根据hash值来上锁
synchronized (toAcct) {
synchronized (fromAcct) {
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
} else {// 额外的锁、避免两个对象hash值相等的情况(即使很少)
synchronized (tieLock) {
synchronized (fromAcct) {
synchronized (toAcct) {
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
}
}
}
}
得到对应的hash值来固定加锁的顺序,这样我们就不会发生死锁的问题了!
4.2开放调用避免死锁
在协作对象之间发生死锁的例子中,主要是因为在调用某个方法时就需要持有锁,并且在方法内部也调用了其他带锁的方法!
- 如果在调用某个方法时不需要持有锁,那么这种调用被称为开放调用!
我们可以这样来改造:
- 同步代码块最好仅被用于保护那些涉及共享状态的操作!
class CooperatingNoDeadlock {
@ThreadSafe
class Taxi {
@GuardedBy("this") private Point location, destination;
private final Dispatcher dispatcher;
public Taxi(Dispatcher dispatcher) {
this.dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public synchronized Point getLocation() {
return location;
}
public synchronized void setLocation(Point location) {
boolean reachedDestination;
// 加Taxi内置锁
synchronized (this) {
this.location = location;
reachedDestination = location.equals(destination);
}
// 执行同步代码块后完毕,释放锁
if (reachedDestination)
// 加Dispatcher内置锁
dispatcher.notifyAvailable(this);
}
public synchronized Point getDestination() {
return destination;
}
public synchronized void setDestination(Point destination) {
this.destination = destination;
}
}
@ThreadSafe
class Dispatcher {
@GuardedBy("this") private final Set taxis;
@GuardedBy("this") private final Set availableTaxis;
public Dispatcher() {
taxis = new HashSet();
availableTaxis = new HashSet();
}
public synchronized void notifyAvailable(Taxi taxi) {
availableTaxis.add(taxi);
}
public Image getImage() {
Set copy;
// Dispatcher内置锁
synchronized (this) {
copy = new HashSet(taxis);
}
// 执行同步代码块后完毕,释放锁
Image image = new Image();
for (Taxi t : copy)
// 加Taix内置锁
image.drawMarker(t.getLocation());
return image;
}
}
class Image {
public void drawMarker(Point p) {
}
}
}
使用开放调用是非常好的一种方式,应该尽量使用它~
4.3使用定时锁
使用显式Lock锁,在获取锁时使用tryLock()方法。当等待超过时限的时候,tryLock()不会一直等待,而是返回错误信息。
使用tryLock()能够有效避免死锁问题~~
4.4死锁检测
虽然造成死锁的原因是因为我们设计得不够好,但是可能写代码的时候不知道哪里发生了死锁。
JDK提供了两种方式来给我们检测:
- JconsoleJDK自带的图形化界面工具,使用JDK给我们的的工具JConsole
- Jstack是JDK自带的命令行工具,主要用于线程Dump分析。
具体可参考:
- https://www.cnblogs.com/flyingeagle/articles/6853167.html
总结
发生死锁的原因主要由于:
- 线程之间交错执行
- 解决:以固定的顺序加锁
- 执行某方法时就需要持有锁,且不释放
- 解决:缩减同步代码块范围,最好仅操作共享变量时才加锁
- 永久等待
- 解决:使用
tryLock()定时锁,超过时限则返回错误信息
- 解决:使用
参考文章地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/68c0fef7b63e