gradle.properties的使用教程
一般我们都把全局属性都编写在一个工具类中,如果是有环境的切换的话,那么我们还会定义一个标志来进行相应的变换。对于项目而言,有时候需要配置某些敏感信息。比如密码,帐号等。而这些信息需要被很多类共同使用,所以必须有一个全局的配置。当需要把项目push到git上时,我们不希望别人看到我们项目的key,token等。我们可以将这些信息设置在gradle.properties中。
下面就讲解如何使用gradle.properties。
1,在gradle.properties文件中进行变量初始化。
如图: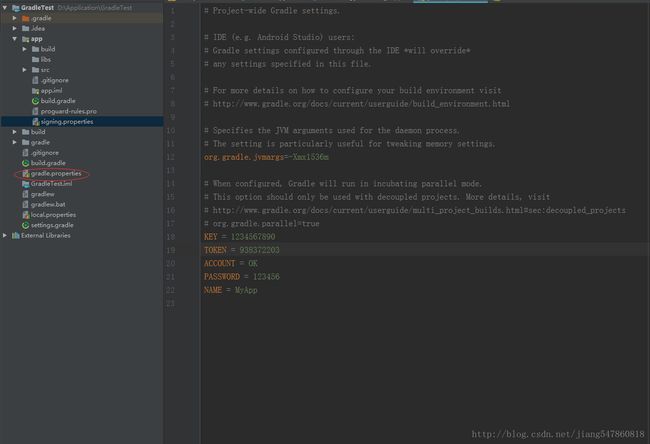
这里我们定义了5个属性。
KEY = 1234567890
TOKEN = 938372203
ACCOUNT = OK
PASSWORD = 123456
NAME = MyApp2,在build.gradle(module app)中进行变量的重定义,即将配置内容转化成java能够使用的形式
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
buildConfigField "String","APPNAME","\"${NAME}\""
resValue "string","app_key","${KEY}"
resValue "string","app_token","${TOKEN}"
resValue "string","account","${ACCOUNT}"
resValue "string","password","${PASSWORD}"
}
debug{
buildConfigField "String","APPNAME","\"${NAME}\""
resValue "string","app_key","${KEY}"
resValue "string","app_token","${TOKEN}"
resValue "string","account","${ACCOUNT}"
resValue "string","password","${PASSWORD}"
}
}其中,buildConfigField定义的方式是(这里定义出来的属性主要是在java代码中使用)
buildConfigField 类型,变量名,值
resValue定义的方式是(这里定义出来的主要是在xml文件中使用)
resValue XML中的类型,变量名,值
3.在Java中使用。
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.text);
textView.setText(BuildConfig.APPNAME);
}
}定义了buildConfigField 类型,那么Android studio会自动的在BuildConfig文件下生成对应的全局属性参数
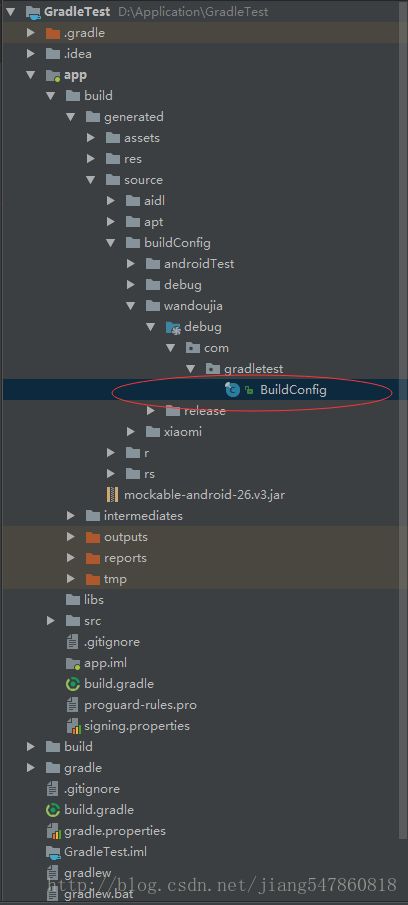
例如我们这里定义了之后生成的代码如下:
package com.gradletest;
public final class BuildConfig {
public static final boolean DEBUG = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
public static final String APPLICATION_ID = "com.gradletest";
public static final String BUILD_TYPE = "debug";
public static final String FLAVOR = "wandoujia";
public static final int VERSION_CODE = 1;
public static final String VERSION_NAME = "1.0";
// Fields from build type: debug
public static final String APPNAME = "MyApp";
}
其中APPNAME就是我们自定义的全局属性参数。
4.在xml文件中使用。
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.gradletest.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/password"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/account"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/app_key"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/app_token"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
通过build.gradle中的配置,可以直接使用@string 访问、
上面就是gradle.properties的使用教程,通过gradle.properties的参数设置,项目开发中不同的服务器环境,我们也可以定义在这个文件下。