javaday09-面向对象3-多态的概述及其代码体现
09.01_面向对象(多态的概述及其代码体现)
- A:多态(polymorphic [,pɒlɪ’mɔːfɪk])概述
- 事物存在的多种形态
- B:多态前提
- a:要有继承关系。
- b:要有方法重写。
- c:要有父类引用指向子类对象。
- C:案例演示
- 代码体现多态
案例:
- 代码体现多态
class Demo1_Polymorphic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat();//猫是一只猫
c.eat();
Animal a = new Cat(); //父类引用指向子类对象,猫是一只动物
a.eat();
}
}
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("动物吃饭");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
09.02_面向对象(多态中的成员访问特点之成员变量)
- 成员变量
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)。
/*
成员变量
编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)
成员方法
编译看左边(父类),运行看右边(子类)。动态绑定
静态方法
编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)。
(静态和类相关,算不上重写,所以,访问还是左边的)
只有非静态的成员方法,编译看左边,运行看右边
*/
案例:
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)。
class Demo2_Polymorphic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Son(); //父类引用指向子类对象
System.out.println(f.num); //相当于是Father.method()
Son s = new Son();
System.out.println(s.num);
}
}
class Father {
int num = 10;
}
class Son extends Father {
int num = 20;
09.03_面向对象(多态中的成员访问特点之成员方法)
- 成员方法
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看右边(子类)。
案例:
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看右边(子类)。
class Demo2_Polymorphic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Son();
f.print(); //相当于是Father.method()
}
}
class Father {
int num = 10;
public void print() {
System.out.println("father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
int num = 20;
public void print() {
System.out.println("son");
}
}
09.04_面向对象(多态中的成员访问特点之静态成员方法)
- 静态方法
- 编译看左边(父类),运行看左边(父类)。
- (静态和类相关,算不上重写,所以,访问还是左边的)
- 只有非静态的成员方法,编译看左边,运行看右边
案例:
class Demo2_Polymorphic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Son();
f.method(); //相当于是Father.method()
}
}
class Father {
int num = 10;
public static void method() {
System.out.println("father static method");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
int num = 20;
public static void method() {
System.out.println("son static method");
}
}
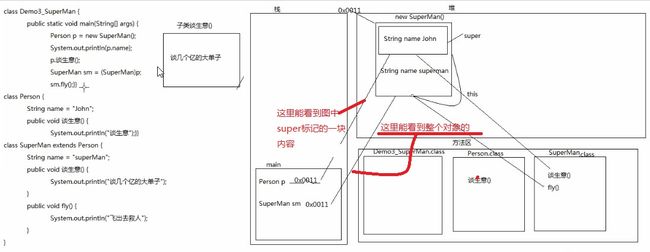
09.05_面向对象(超人的故事)
- A:案例分析
- 通过该案例帮助学生理解多态的现象(talkTrade:谈生意)
案例:
- 通过该案例帮助学生理解多态的现象(talkTrade:谈生意)
class Demo3_SuperMan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new SuperMan(); //父类引用指向子类对象,超人提升为了人
//父类引用指向子类对象就是向上转型
System.out.println(p.name);
p.talkTrade();
}
}
class Person {
String name = "John";
public void talkTrade() {
System.out.println("谈生意");
}
}
class SuperMan extends Person {
String name = "superMan";
public void talkTrade() {
System.out.println("谈几个亿的大单子");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("飞出去救人");
}
09.06_面向对象(多态中向上转型和向下转型)
- A:案例演示
- 详细讲解多态中向上转型和向下转型
Person p = new SuperMan();向上转型
SuperMan sm = (SuperMan)p;向下转型
案例:
- 详细讲解多态中向上转型和向下转型
class Demo3_SuperMan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new SuperMan(); //父类引用指向子类对象,超人提升为了人
//父类引用指向子类对象就是向上转型
System.out.println(p.name);
p.talkTrade();
SuperMan sm = (SuperMan)p; //向下转型
sm.fly();
/*
基本数据类型自动类型提升和强制类型转换
*/
int i = 10;
byte b = 20;
//i = b; //自动类型提升
//b = (byte)i; //强制类型转换
}
}
class Person {
String name = "John";
public void talkTrade() {
System.out.println("谈生意");
}
}
lass SuperMan extends Person {
String name = "superMan";
public void talkTrade() {
System.out.println("谈几个亿的大单子");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("飞出去救人");
}
}
09.07_面向对象(多态的好处和弊端)
- A:多态的好处
- a:提高了代码的维护性(继承保证)
- b:提高了代码的扩展性(由多态保证)
- B:案例演示
- 多态的好处
- 可以当作形式参数,可以接收任意子类对象
- C:多态的弊端
- 不能使用子类的特有属性和行为。
- D:案例演示
案例:
class Demo4_Animal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Cat c1 = new Cat();
//c1.eat();
method(new Cat());
method(new Dog());
//Animal a = new Cat(); 开发的是很少在创建对象的时候用父类引用指向子类对象,直接创建子类对象更方便,可以使用子类中的特有属性和行为
}
//Cat c = new Dog();狗是一只猫,这是错误的
/*public static void method(Cat c) {
c.eat();
}
public static void method(Dog d) {
d.eat();
}*/
//如果把狗强转成猫就会出现类型转换异常,ClassCastException
public static void method(Animal a) { //当作参数的时候用多态最好,因为扩展性强
//关键字 instanceof 判断前边的引用是否是后边的数据类型
if (a instanceof Cat) {
Cat c = (Cat)a;
c.eat();
c.catchMouse();
}else if (a instanceof Dog) {
Dog d = (Dog)a;
d.eat();
d.lookHome();
}else {
a.eat();
}
}
}
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("动物吃饭");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void catchMouse() {
System.out.println("抓老鼠");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狗吃肉");
}
public void lookHome() {
System.out.println("看家");
}
}
09.08_面向对象(多态中的题目分析题)
- A:看下面程序是否有问题,如果没有,说出结果 *
class Fu {
public void show() {
System.out.println("fu show");
}
}
class Zi extends Fu {
public void show() {
System.out.println("zi show");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("zi method");
}
}
class Test1Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fu f = new Zi();
f.method();
f.show();
}
}错误 多态中父类无法子类的特有方法
- B:看下面程序是否有问题,如果没有,说出结果
class A {
public void show() { show2(); } public void show2() { System.out.println("我"); } } class B extends A { public void show2() { System.out.println("爱"); } } class C extends B { public void show() { super.show(); } public void show2() { System.out.println("你"); } } public class Test2DuoTai { public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new B(); a.show();//爱 B b = new C(); b.show();//你 } }
09.09_面向对象(抽象类的概述及其特点)
- A:抽象类概述
- 抽象就是看不懂的
- B:抽象类特点
- a:抽象类和抽象方法必须用abstract关键字修饰
- abstract class 类名 {}
- public abstract void eat();//当不知道该方法具体是怎么实现的
//比如动物吃,你知道它吃什么吗?怎么吃?都不知道
- b:抽象类不一定有抽象方法,有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类或者是接口
- c:抽象类不能实例化那么,抽象类如何实例化呢?
- 按照多态的方式,由具体的子类实例化。其实这也是多态的一种,抽象类多态。
- d:抽象类的子类
- 要么是抽象类
- 要么重写抽象类中的所有抽象方法
- a:抽象类和抽象方法必须用abstract关键字修饰
- C:案例演示
- 抽象类特点
案例:
- 抽象类特点
class Demo1_Abstract {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Animal a = new Animal(); //错误: Animal是抽象的; 无法实例化
Animal a = new Cat(); //父类引用指向子类对象
a.eat();
}
}
abstract class Animal { //抽象类
public abstract void eat(); //抽象方法
public Animal() {
System.out.println("父类空参构造");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public Cat() {
super();
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
09.10_面向对象(抽象类的成员特点)
- A:抽象类的成员特点
- a:成员变量:既可以是变量,也可以是常量。abstract是否可以修饰成员变量?不能修饰成员变量
- b:构造方法:有。
- 用于子类访问父类数据的初始化。
- c:成员方法:既可以是抽象的,也可以是非抽象的。
- B:案例演示
- 抽象类的成员特点
- C:抽象类的成员方法特性:
- a:抽象方法 强制要求子类做的事情。
- b:非抽象方法 子类继承的事情,提高代码复用性。
案例:
class Demo2_Abstract {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
abstract class Demo {
int num1 = 10;//变量
final int num2 = 20;//常量
public Demo(){}//构造方法
public void print() {//非抽象方法,子类可以直接使用
System.out.println("111");
}
public abstract void method();//抽象方法,子类必须实现
}
class Test extends Demo {
public void method() {
System.out.println("111");
}
}
09.11_面向对象(葵花宝典)
- 案例演示
- 抽象类的作用
class Demo3_葵花宝典 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
岳不群 小岳子 = new 岳不群();
小岳子.自宫();
}
}
abstract class 葵花宝典 {
public abstract void 自宫();
}
class 岳不群 extends 葵花宝典 {
public void 自宫() {
System.out.println("用牙签");
}
}
class 林平之 extends 葵花宝典 {
public void 自宫() {
System.out.println("用指甲刀");
}
}
class 东方不败 extends 葵花宝典 {
public void 自宫() {
System.out.println("用锤子,不忍直视");
}
}
09.12_面向对象(抽象类练习猫狗案例)
- A:案例演示
- 具体事物:猫,狗
- 共性:姓名,年龄,吃饭
- 猫的特性:抓老鼠
- 狗的特性:看家
案例:
class Test1_Animal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat("加菲",8);
System.out.println(c.getName() + "..." + c.getAge());
c.eat();
c.catchMouse();
Dog d = new Dog("八公",30);
System.out.println(d.getName() + "..." + d.getAge());
d.eat();
d.lookHome();
}
}
abstract class Animal {
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
public Animal(){} //空参
public Animal(String name,int age) {//有参
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) { //设置姓名
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { //获取姓名
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) { //设置年龄
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() { //获取年龄
return age;
}
public abstract void eat(); //吃饭
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public Cat(){} //空参
public Cat(String name,int age) {//有参
super(name,age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void catchMouse() {
System.out.println("抓老鼠");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public Dog(){} //空参
public Dog(String name,int age) {//有参
super(name,age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狗吃肉");
}
public void lookHome() {
System.out.println("看家");
}
}
09.13_面向对象(抽象类练习老师案例)
- A:案例演示
- 具体事物:基础班老师,就业班老师
- 共性:姓名,年龄,讲课。
- 具体事物:基础班学生,就业班学生
- 共性:姓名,年龄,学习
案例:
class Test2_Teacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BaseTeacher bt = new BaseTeacher("冯佳",18);
bt.teach();
}
}
abstract class Teacher {
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
public Teacher(){} //空参
public Teacher(String name,int age) {//有参
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) { //设置姓名
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { //获取姓名
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) { //设置年龄
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() { //获取年龄
return age;
}
public abstract void teach();
}
class BaseTeacher extends Teacher {
public BaseTeacher(){} //空参
public BaseTeacher(String name,int age) {//有参
super(name,age);
}
public void teach() {
System.out.println("我的姓名是:" + this.getName() + ",我的年龄是:" + this.getAge() + ",讲的内容是java基础");
}
}
09.14_面向对象(抽象类练习员工案例)
- A:案例演示
- 假如我们在开发一个系统时需要对程序员类进行设计,程序员包含3个属性:姓名、工号以及工资。
- 经理,除了含有程序员的属性外,另为还有一个奖金属性。
- 请使用继承的思想设计出程序员类和经理类。要求类中提供必要的方法进行属性访问。
案例:
class Test3_Employee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coder c = new Coder("德玛西亚","007",8000);
c.work();
Manager m = new Manager("苍老师","9527",3000,20000);
m.work();
}
}
abstract class Employee {
private String name; //姓名
private String id; //工号
private double salary; //工资
public Employee() {} //空参构造
public Employee(String name,String id,double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.salary = salary;
}
public void setName(String name) { //设置姓名
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { //获取姓名
return name;
}
public void setId(String id) { //设置id
this.id = id;
}
public String getId() { //获取id
return id;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) { //设置工资
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() { //获取工资
return salary;
}
public abstract void work();
}
//程序员
class Coder extends Employee {
public Coder() {} //空参构造
public Coder(String name,String id,double salary) {
super(name,id,salary);
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("我的姓名是:" + this.getName() + ",我的工号是:" + this.getId() + ",我的工资是:"
+ this.getSalary() + ",我的工作内容是敲代码");
}
}
//项目经理
class Manager extends Employee {
private int bonus; //奖金
public Manager() {} //空参构造
public Manager(String name,String id,double salary,int bonus) {
super(name,id,salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("我的姓名是:" + this.getName() + ",我的工号是:" + this.getId() + ",我的工资是:"
+ this.getSalary() + ",我的奖金是:" + bonus + ",我的工作内容是管理");
}
}
09.15_面向对象(抽象类中的面试题)
- A:面试题1
- 一个抽象类如果没有抽象方法,可不可以定义为抽象类?如果可以,有什么意义?
- 可以
- 这么做目的只有一个,就是不让其他类创建本类对象,交给子类完成
- B:面试题2
- abstract不能和哪些关键字共存
案例:
- abstract不能和哪些关键字共存
class Demo4_Abstract {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
/*
* A:面试题1
* 一个抽象类如果没有抽象方法,可不可以定义为抽象类?如果可以,有什么意义?
* 可以
* 这么做目的只有一个,就是不让其他类创建本类对象,交给子类完成
* B:面试题2
* abstract不能和哪些关键字共存
abstract和static
被abstract修饰的方法没有方法体
被static修饰的可以用类名.调用,但是类名.调用抽象方法是没有意义的
abstract和final
被abstract修饰的方法强制子类重写
被final修饰的不让子类重写,所以他俩是矛盾
abstract和private
被abstract修饰的是为了让子类看到并强制重写
被private修饰不让子类访问,所以他俩是矛盾的
*/
abstract class Demo {
//public static abstract void print(); //错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和static
//public final abstract void print(); //错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和final
private abstract void print(); //错误: 非法的修饰符组合: abstract和private
}
09.16_面向对象(接口的概述及其特点)
- A:接口概述
- 从狭义的角度讲就是指java中的interface
- 从广义的角度讲对外提供规则的都是接口
- B:接口特点
- a:接口用关键字interface表示
- interface 接口名 {}
- b:类实现接口用implements表示
- class 类名 implements 接口名 {}
- c:接口不能实例化
- 那么,接口如何实例化呢?
- 按照多态的方式来实例化。
- d:接口的子类
- a:可以是抽象类。但是意义不大。
- b:可以是具体类。要重写接口中的所有抽象方法。(推荐方案)
- a:接口用关键字interface表示
- C:案例演示
- 接口特点
案例:
- 接口特点
class Demo1_Interface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Inter i = new Inter(); //接口不能被实例化,因为调用抽象方法没有意义
Inter i = new Demo(); //父类引用指向子类对象
i.print();
}
}
interface Inter {
public abstract void print(); //接口中的方法都是抽象的
}
class Demo implements Inter {
public void print() {
System.out.println("print");
}
}
09.17_面向对象(接口的成员特点)
- A:接口成员特点
- 成员变量只能是常量,并且是静态的并公共的。
* 默认修饰符:public static final
* 建议:自己手动给出。 - 构造方法:接口没有构造方法。
- 成员方法:只能是抽象方法。
* 默认修饰符:public abstract
* 建议:自己手动给出。
- 成员变量只能是常量,并且是静态的并公共的。
- B:案例演示
- 接口成员特点
案例:
- 接口成员特点
class Demo2_Interface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo d = new Demo();
d.print();
System.out.println(Inter.num);
}
}
interface Inter {
public static final int num = 10;
//public Inter(){} 接口中没有构造方法
/*public void print() { 接口中不能定义非抽象方法
}*/
public abstract void print();
}
class Demo /extends Object/ implements Inter { //一个类不写继承任何类,默认继承Object类
public void print() {
//num = 20;
System.out.println(num);
}
public Demo() {
super();
}
}
09.18_面向对象(类与类,类与接口,接口与接口的关系)
- A:类与类,类与接口,接口与接口的关系
- a:类与类:
- 继承关系,只能单继承,可以多层继承。
- b:类与接口:
- 实现关系,可以单实现,也可以多实现。
- 并且还可以在继承一个类的同时实现多个接口。
- c:接口与接口:
- 继承关系,可以单继承,也可以多继承。
- a:类与类:
- B:案例演示
- 类与类,类与接口,接口与接口的关系
案例:
- 类与类,类与接口,接口与接口的关系
class Demo3_Interface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
interface InterA {
public abstract void printA();
}
interface InterB {
public abstract void printB();
}
interface InterC extends InterB,InterA {
}
//class Demo implements InterA,implements InterB { //这么做不允许是非法的
class Demo extends Object implements InterA,InterB {
public void printA() {
System.out.println("printA");
}
public void printB() {
System.out.println("printB");
}
}
09.19_面向对象(抽象类和接口的区别)
A:成员区别
- 抽象类:
- 成员变量:可以变量,也可以常量
- 构造方法:有
- 成员方法:可以抽象,也可以非抽象
- 接口:
- 成员变量:只可以常量
- 成员方法:只可以抽象
- 抽象类:
B:关系区别
- 类与类
- 继承,单继承
- 类与接口
- 实现,单实现,多实现
- 接口与接口
- 继承,单继承,多继承
- 类与类
C:设计理念区别
- 抽象类 被继承体现的是:”is a”的关系。抽象类中定义的是该继承体系的共性功能。
- 接口 被实现体现的是:”like a”的关系。接口中定义的是该继承体系的扩展功能。
- 对事物本质的抽象用抽象类,对事物功能的扩展用接口
09.20_面向对象(猫狗案例加入跳高功能分析及其代码实现)
- A:案例演示
- 动物类:姓名,年龄,吃饭,睡觉。
- 猫和狗
- 动物培训接口:跳高
案例:
class Test1_Animal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat("加菲",8);
c.eat();
c.sleep();
JumpCat jc = new JumpCat("跳高猫",3);
jc.eat();
jc.sleep();
jc.jump();
}
}
abstract class Animal {
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
public Animal() {} //空参构造
public Animal(String name,int age) {//有参构造
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) { //设置姓名
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { //获取姓名
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) { //设置年龄
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() { //获取年龄
return age;
}
public abstract void eat(); //吃饭
public abstract void sleep(); //睡觉
}
interface Jumping { //跳高的接口
public void jump();
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public Cat() {} //空参构造
public Cat(String name,int age) {//有参构造
super(name,age);
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("侧着睡");
}
}
class JumpCat extends Cat implements Jumping {
public JumpCat() {} //空参构造
public JumpCat(String name,int age) {//有参构造
super(name,age);
}
public void jump() {
System.out.println("猫跳高");
}
}
总结起来好累啊!