隐马尔可夫模型 HMM 原理及实现
简介
隐马尔可夫模型(Hidden Markov Model,HMM)创立于20世纪70年代。主要用于行为识别,语音识别,文字识别等。
原理简述
隐马尔可夫模型由五个部分组成:状态空间S,观测空间O,初始状态概率空间PI,状态概率转移矩阵P以及观测值生成概率矩阵Q。另外,隐马尔可夫模型还包括一条观测链,一条隐藏链。(后面将详述)下面是隐马尔可夫模型示意图:
因此整个过程就是观测值随状态的转移而生成,而我们所关心的是通过已有的观测值来判断其隐藏的状态,即通过一长串的观测序列推算导致这一结果的可能的状态序列。例如:有两枚不同的硬币(一枚正面抛掷后正面朝上的概率比较大,另一个反面朝上的概率比较大),现在一个人按照其习惯每次选择其中的一枚硬币抛掷,共抛掷N次,将结果记录下来(设正面为1,反面为0),之后你就可以利用隐马尔可夫模型,通过已有结果反推这个人每次使用哪枚硬币进行投掷的。
实现方法
要实现上面所述原理就必须解决三个问题:评估问题(evaluation),解码问题(decoding)和学习问题(learning)
1、评估问题,即评估当前状态为真实状态的可能性。
最简单的方法有前向算法和后向算法(当然也可以联合使用这两种算法)。
前向算法:从前递归,一层一层计算概率,最后再求总和。
1)t=0(事实上 t 的首项应该为1,但是考虑到编程的方便这里就设首项为0)
![]() ,即 alpha(i,t)=PI(i)*Q(i,t)(伪代码,这只是为了表示方便易懂,与之后的代码可能会有出入)
,即 alpha(i,t)=PI(i)*Q(i,t)(伪代码,这只是为了表示方便易懂,与之后的代码可能会有出入)
PS:alpha(i,t)指t时刻状态为Si的概率(下面同义),PI(i)为状态Si的初始概率,Q(i,t)指的是 t 时刻观测值Vt由状态Si生成的概率。
2)t>0 && t<=n
![]() ,即alpha(t,i)=Sum[ alpha(j,t-1)*P(j,i)*Q(i,t) ]
,即alpha(t,i)=Sum[ alpha(j,t-1)*P(j,i)*Q(i,t) ]
PS:P(j,i)指由状态 Sj 转移到 Si 的概率
3)
PS:对应后面的Java类为 AlgorithmFront.java
后向算法:与前向算法相反
1)t>=0 && t
![]() ,即beta(i,t)=Sum[ beta(j,t+1)*P(i,j)*Q(j,t+1) ]
,即beta(i,t)=Sum[ beta(j,t+1)*P(i,j)*Q(j,t+1) ]
PS:beta(i,t)表示t时刻状态为Si的条件下,从t+1时刻到n生成相应观测序列的概率。
2)t=n
![]()
PS:因为下一个时刻就已结束,所以无论是什么状态都是确定的,所以概率都为1。
3)
PS:对应后面的Java类为 AlgorithmBack.java
2、解码问题,即如何根据观测值,状态转移概率矩阵,生成概率矩阵得到真正的状态序列。(有时候你完全可以根据先验知识给参数设值,这样就无需 学习步骤(Learning) 便可以解码了)
Viterbi算法:基本原理就是计算概率每一步最高时对应的状态序列
1)初始化
2)递归
3)终止
![]() ,
,![]()
PS:![]() 表示 n 时刻沿着X1,X2,...Xn 且在 n 时刻状态Xn=Si 产生相应观测序列的最大概率
表示 n 时刻沿着X1,X2,...Xn 且在 n 时刻状态Xn=Si 产生相应观测序列的最大概率
4)回溯
PS:对应的后面的Java类为 HMMDecisionVbImp.java
3、学习问题,即如何通过观测值来获取初始状态概率,状态转移概率矩阵以及生成概率矩阵。
Baum-Welch算法:
Step1: 随机产生一组参数,并代入评估函数(evaluation,例如前向算法),计算结果。
Step2: 利用参数估算初始状态概率,状态转移概率矩阵以及生成概率矩阵
由于:
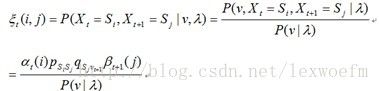 ,即kis(i,j,t)=alpha(i,t)*P(i,j)*Q(j,t+1)*beta(j,t+1)
,即kis(i,j,t)=alpha(i,t)*P(i,j)*Q(j,t+1)*beta(j,t+1)
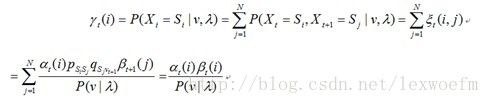 ,即gamma(i,t)=alpha(i,t)*beta(i,t)
,即gamma(i,t)=alpha(i,t)*beta(i,t)
PS:a)伪代码中并没有除以![]() ,这主要是为了减少运算量,因为之后计算状态概率矩阵、生成矩阵这项都会被约掉。
,这主要是为了减少运算量,因为之后计算状态概率矩阵、生成矩阵这项都会被约掉。
b)kis(i,j,t)即,表示t时刻为状态Si,t+1时刻为状态Sj的概率
c)gamma(i,t)即,表示t时刻状态为Si的概率
d)相应的Java类为 Gammas.java,Ksis.java
所以:
1)估计概率转移概率矩阵
2)估计初始状态概率
![]() ,(注意,实际编程实现时这里还需除以之前漏除的
,(注意,实际编程实现时这里还需除以之前漏除的![]() )
)
3)估计概率生成矩阵
Step3: 将刚估计的参数代入 评估函数 进行计算,并与上一次评估的结果做比较,若差异小于某个阈值(thresh,例如 0.05)则接受。否则继续迭代计算。
PS:相应的Java类为 HMMLearnBwImp.java
Java具体实现
基础类 Package lxwo.utils
1、AlgorithmFront
package lxwo.utils;
public class AlgorithmFront{
private double[] Api;
private double[][] AP;
private double[][] AQ;
private int[] V;
public AlgorithmFront(double[] Api, double[][] AP, double[][] AQ, int[] V) {
this.Api = Api;
this.AP = AP;
this.AQ = AQ;
this.V = V;
}
public double calculate(int step) {
double Result = 0.0;
for (int Pindex = 0; Pindex < this.AP.length; Pindex++)
Result += this.alpha(Pindex, step);
return Result;
}
public double alpha(int toI, int step) {
double tempValue = 0.0;
if (step > 0) {
for (int pindex = 0; pindex < this.AP.length; pindex++)
tempValue += this.alpha(pindex, step - 1)* this.AP[pindex][toI] * this.AQ[toI][this.V[step]];
} else
tempValue = Api[toI] * this.AQ[toI][this.V[step]];
return tempValue;
}
public double[] getApi() {
return Api;
}
public void setApi(double[] api) {
Api = api;
}
public double[][] getAP() {
return AP;
}
public void setAP(double[][] aP) {
AP = aP;
}
public double[][] getAQ() {
return AQ;
}
public void setAQ(double[][] aQ) {
AQ = aQ;
}
public int[] getV() {
return V;
}
public void setV(int[] v) {
V = v;
}
}
2、AlgorithmBack
package lxwo.utils;
public class AlgorithmBack{
private double[] Api;
private double[][] AP;
private double[][] AQ;
private int[] V;
public AlgorithmBack(double[] Api, double[][] AP, double[][] AQ, int[] V){
this.Api = Api;
this.AP = AP;
this.AQ = AQ;
this.V = V;
}
public double calculate(int step){
double Result = 0.0;
for (int Pindex = 0; Pindex < this.AP.length; Pindex++)
Result += this.belta(Pindex, step);
return Result;
}
public double belta(int fromI,int step){
double tempValue = 0.0;
if(step
}else{
tempValue = 1.0;
}
return tempValue;
}
public double[] getApi() {
return Api;
}
public void setApi(double[] api) {
Api = api;
}
public double[][] getAP() {
return AP;
}
public void setAP(double[][] aP) {
AP = aP;
}
public double[][] getAQ() {
return AQ;
}
public void setAQ(double[][] aQ) {
AQ = aQ;
}
public int[] getV() {
return V;
}
public void setV(int[] v) {
V = v;
}
}
3、 Ksis
package lxwo.utils;
public class Ksis {
private double[] Api;
private double[][] AP;
private double[][] AQ;
private int[] V;
public Ksis(double[] Api, double[][] AP, double[][] AQ, int[] V){
this.Api = Api;
this.AP = AP;
this.AQ = AQ;
this.V = V;
}
public double calculate(int i,int j,int step){
AlgorithmFront f1 = new AlgorithmFront(this.Api,this.AP,this.AQ,this.V);
AlgorithmBack f2 = new AlgorithmBack(this.Api,this.AP,this.AQ,this.V);
// Considering the amount of calculation, we don't divide the result by p(V|lambda)
return f1.alpha(i, step)*this.AP[i][j]*this.AQ[j][this.V[step+1]]*f2.belta(j, step+1);
}
public double sumKsi(int i,int j, int T){
double tempValue = 0.0;
for(int pindex=0;pindex
return tempValue;
}
}
4、Gammas
package lxwo.utils;
public class Gammas {
private double[] Api;
private double[][] AP;
private double[][] AQ;
private int[] V;
public Gammas(double[] Api, double[][] AP, double[][] AQ, int[] V){
this.Api = Api;
this.AP = AP;
this.AQ = AQ;
this.V = V;
}
public double calculate(int i,int step){
AlgorithmFront f1 = new AlgorithmFront(this.Api,this.AP,this.AQ,this.V);
AlgorithmBack f2 = new AlgorithmBack(this.Api,this.AP,this.AQ,this.V);
// Considering the amount of calculation, we don't divide the result by p(V|lambda)
return f1.alpha(i, step)*f2.belta(i, step);//step+1
}
public double sumGamma(int i, int T){
double tempValue = 0.0;
for(int pindex=0;pindex
return tempValue;
}
}
核心类 Package lxwo.core
1、HMMDecision & HMMDecisionVbImp
package lxwo.core;
public interface HMMDecision {
public int[] recognize(int step);
}
package lxwo.core;
public class HMMDecisionVbImp implements HMMDecision {
private double[] pi;
private double[][] P;
private double[][] Q;
private int[] V;
private int[]phi;
public HMMDecisionVbImp(double[] pi, double[][] P, double[][] Q, int[] V) {
this.pi = pi;
this.P = P;
this.Q = Q;
this.V = V;
this.phi = new int[this.V.length];
for(int i=0;i
}
@Override
public int[] recognize(int step) {
int[] tempFlag = new int[this.phi.length];
double sumTempMax = 0.0;
for(int dindex=0;dindex
if(tempVal>sumTempMax){
sumTempMax = tempVal;
tempFlag = this.phi.clone();
tempFlag[step]=dindex;
}
}
return tempFlag;
}
private double delta(int toI,int step) {
double tempValue = 1.0;
if (step == 0) {
tempValue = this.pi[toI]*this.Q[toI][step];
} else {
double tempMax = 0.0;
for(int jindex=0;jindex
if(tempV>tempMax){
tempMax = tempV;
this.phi[step-1]=jindex;
}
}
tempValue = tempMax*this.Q[toI][this.V[step]];
}
return tempValue;
}
}
2、HMMLearn& HMMLearnBwImp
package lxwo.core;
public interface HMMLearn {
public boolean learn();
}
package lxwo.core;
import lxwo.utils.AlgorithmFront;
import lxwo.utils.Gammas;
import lxwo.utils.Ksis;
public class HMMLearnBwImp implements HMMLearn {
private double[] pi;
private double[][] P;
private double[][] Q;
private int[] V;
private double thresh;
private int deadline;
public HMMLearnBwImp(double[] pi, double[][] P, double[][] Q, int[] V,
double thresh, int deadline) {
this.pi = pi;
this.P = P;
this.Q = Q;
this.V = V;
this.thresh = thresh;
this.deadline = deadline;
}
@Override
public boolean learn() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double flag1 = 0.0;
double flag2 = 0.0;
double flag3 = 0.0;
double[] tpi = new double[this.pi.length];
double[][] tP = new double[this.P.length][this.P[0].length];
double[][] tQ = new double[this.Q.length][this.Q[0].length];
int count = 0;
double diff = 1000.0;
flag3 = new AlgorithmFront(pi, P, Q, V).calculate(this.V.length - 1);
do {
count++;
// evaluate
flag1 = flag3;
// recalculate pi
double tempM1 = new AlgorithmFront(this.pi, this.P, this.Q, this.V)
.calculate(this.V.length - 1);
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < tpi.length; i1++)
tpi[i1] = (new Gammas(this.pi, this.P, this.Q, this.V)
.calculate(i1, 0)) / tempM1; // 'cause we don't divide it before, so we should make up here
// recalculate P
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < this.P.length; i2++)
for (int j2 = 0; j2 < this.P[0].length; j2++)
tP[i2][j2] = (new Ksis(this.pi, this.P, this.Q, this.V)
.sumKsi(i2, j2, this.V.length - 1))
/ (new Gammas(this.pi, this.P, this.Q, this.V)
.sumGamma(i2, this.V.length - 1));
// recalculate Q
for (int i3 = 0; i3 < this.Q.length; i3++) {
double tempM2 = new Gammas(this.pi, this.P, this.Q, this.V)
.sumGamma(i3, this.V.length);
for (int j3 = 0; j3 < this.V.length; j3++)
tQ[i3][this.V[j3]] += (new Gammas(this.pi, this.P, this.Q,
this.V).calculate(i3, j3)) / tempM2;
}
// re-evaluate
flag2 = new AlgorithmFront(tpi, tP, tQ, V)
.calculate(this.V.length - 1);
flag3 = flag2;
// reset args
this.pi = tpi.clone();
this.P = tP.clone();
this.Q = tQ.clone();
tQ = new double[this.Q.length][this.Q[0].length];
diff = Math.abs(flag1 - flag2);
} while (diff > thresh && count < this.deadline);
System.out.println("count: "+count);
if (count == this.deadline && diff > this.thresh)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public double[] getPi() {
return pi;
}
public void setPi(double[] pi) {
this.pi = pi;
}
public double[][] getP() {
return P;
}
public void setP(double[][] p) {
P = p;
}
public double[][] getQ() {
return Q;
}
public void setQ(double[][] q) {
Q = q;
}
}
测试类 Package lxwo.test
package lxwo.test;
import lxwo.core.HMMDecision;
import lxwo.core.HMMDecisionVbImp;
import lxwo.core.HMMLearnBwImp;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
* 实验:用两种骰子(0,1)投掷,其中一个骰子为正常的(0),另一个为灌铅(1),出现456的可能性较大。
* 代码中用012345代替123456
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] api = { 0.5, 0.5 };
double[][] P = { { 0.9, 0.1 }, { 0.2, 0.8 }};
double[][] Q = { { 0.2, 0.16, 0.16, 0.16, 0.16, 0.16 }, {0, 0, 0.10, 0.30, 0.30, 0.30 } };
int[] V = {5,1,2,4,5,4,2,1,0,5};// -5,1,2,-4,-5,-4,2,1,0,5 这里标记符号的表示用第二种骰子投掷的
HMMLearnBwImp hlbi = new HMMLearnBwImp(api, P, Q, V, 0.05, 100);
if (hlbi.learn()) {
System.out.println("result:");
HMMDecision hd = new HMMDecisionVbImp(hlbi.getPi(), hlbi.getP(), hlbi.getQ(), V);
int[] result = hd.recognize(V.length-1);
for(int r:result)
System.out.print(r+"\t");
System.out.println();
} else {
System.out.println("Fail!");
}
}
}
观测序列:5,1,2,4,5,4,2,1,0,5
结果:0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0
除了第一项估计有误,其余都正确。(这里只是用一条观测值序列做的测试,如果有多条观测值,预测结果会好很多)
PS:由于这只是简单的实现HMM,因此其真正的实用性还不强(如果你把观测值加到>20个,其运算时间将是巨大的,因此实际应用中还需对上述代码进行改进)


