java----GUI图形用户界面
GUI图形用户界面
一、GUI
GUI:Graphical User Interface(图形用户接口),用图形的方式,来显示计算机的操作界面。这样方便,直观。
CLI:Comandline User Interface(命令行用户接口),就是常见的Dos命令行操作。需要记忆一些命令,操作不直观。
Java为GUI提供了的对象都存在java.awt和javax.swing两个包中。
awt和swing:
java.awt:Abstract Window Toolkit(抽象窗口工具包),需要调用本地系统方法实现功能。属于重量级控件。有点依赖于平台。
javax.swing:在awt的基础上,建立的一套图形界面系统。其中提供了更多组件,而且完全由java实现。增强了可移植性,属轻量级控件。在任何系统上的运行界面都一样。
继承关系图:
Label:标签,用于封装文字。
CheckBox:复选框。
TextComponent:文本框。
Button:按钮。
Container:容器,是一个特殊的组件,该组件中可以通过add方法添加其他组件进来。
Window:窗口。
Panel:面板。
Frame:框架。
Dialog:对话框。
FileDialog:文件对话框。
布局管理器:容器中的组件的排放方式就是布局。
常见的布局管理器:
FlowLayout:(流式布局管理器)从左到右的顺序排列,Panel默认的布局管理器。
BorderLayout:(边界布局管理器)东,南,西,北,中。Frame默认的布局管理器。
GridLayout:(网格布局管理器)规则的矩阵。
CardLayout:(卡片布局管理器)选项卡。
GridBagLayout:(网格包布局管理器)非规则的矩阵。
Container:
add():将组件添加到容器,其实封装了集合进去。
Component add(Component comp)
将指定组件追加到此容器的尾部。
Component add(Component comp, int index)
将指定组件添加到此容器的给定位置上。
void add(Component comp, Object constraints)
将指定的组件添加到此容器的尾部。
void add(Component comp, Object constraints, int index)
使用指定约束,将指定组件添加到此容器的指定索引所在的位置上。
Component add(String name, Component comp)
将指定组件添加到此容器中。
import java.awt.*;
class Demo
{
public static void main(String []args){
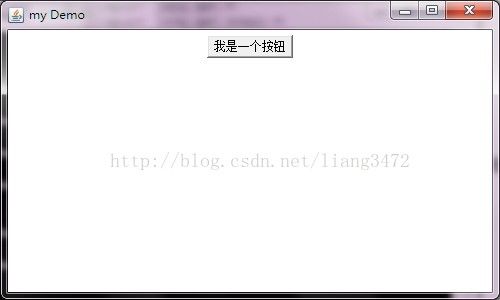
Frame f = new Frame("my Demo");
//设置窗体大小,第一个参数是宽,第二个参数是高。
f.setSize(500,300);
//设置窗体位置
f.setLocation(300,100);
//设置按钮
Button b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
//添加按钮到窗体
f.add(b);
//最初为不可见,要将其设置为可见。
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
分析:因为Frame默认是边界布局,有没有指定位置,所以默认为填充按钮。
为其添加FlowLayout布局
创建图形化界面步骤:
1.创建Frame窗体。
2.对窗体进行基本设置:比如:大小,位置,布局。
3.定义组件。
4.将组件通过窗体的add方法添加到窗体中。
5.让窗体显示。
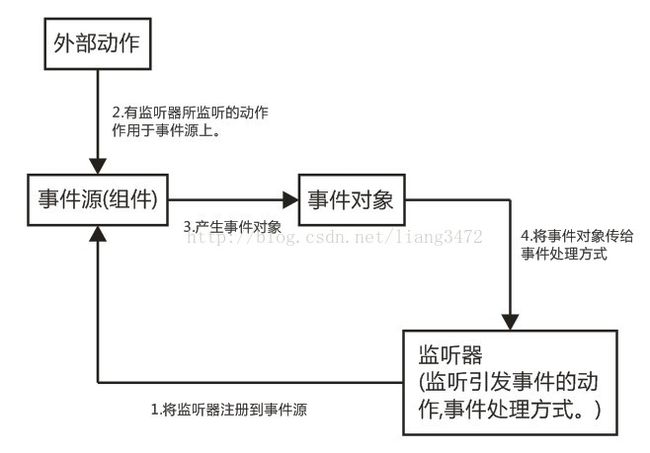
事件监听机制:
流程图
事件监听机制的特点:
1.事件源
2.事件
3.监听器
4.事件处理
事件源:就是awt包或者swing包中的那些图形界面组件。
事件:每一个事件源都有自己特有的对应事件和共享事件。
监听器:将可以触发某一事件的动作(不止一个动作)都已经封装到了监听器中。
以上三者在java中都已经定义好了,直接获取其对象来用就可以了。
练习:对产生的动作进行处理,点击窗体关闭按钮关闭程序。
在window类中找到addWindowListener(WindowListenen)。里面的参数WindowListener是一个接口,其中的方法需要全部复写才能创建对象。其有个子类WindowAdapter是一个抽象类,里面都复写了接口WindowListener的所以方法,可是这些方法里都是空的。目的就是让程序员自己写,调用哪个就覆盖哪个。因为空方法没有实现的意义,所以把WindowAdapter声明为abstract类,避免其实例化。WindowAdapter的出现简化了代码。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
public static void main(String []args){
Frame f = new Frame("my Demo");
f.setVisible(true);
f.setSize(500,300);
f.setLocation(300,100);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
Button b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
f.add(b);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
//窗口正处在关闭过程中时调用。
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
//关闭程序
System.out.println("我关");
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
练习:让按钮具备退出程序的功能。
按钮就是事件源,那么选择哪个监听器呢?
答:通过关闭窗口示例了解到,想要知道哪个组件具备什么样的特有监听器,需要查看该组件对象的功能。通过查阅Button的描述,发现按钮支持一个特有监听addActionListener。通过复写ActionListener接口里的方法完成事件的处理。因为要求复写的方法只有一个,所以也就没有定义适配器。一般方法包含三个或三个以上才定义适配器。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
//定义该图形中所需的组件的引用
private Frame f;
private Button b;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
//对Frame进行基本设置
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
//setBounds设置窗体坐标和窗体大小
f.setBounds(300,100,500,300);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
//将组建添加到Frame中
f.add(b);
//加载事件到窗体上
myEvent();
//显示窗体
f.setVisible(true);
}
//事件
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
鼠标事件
例:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private Button b;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(300,100,500,300);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
f.add(b);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("OK");
}
});
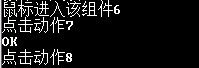
b.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter(){
private int count = 1;
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e){
System.out.println("鼠标进入该组件"+count++);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e){
System.out.println("点击动作"+count++);
}
});
}
}
建议:开发时建议使用ActionListener,因为支持按键。
练习:双击按钮。
MouseEvent:
int getClickCount()
返回与此事件关联的鼠标单击次数。 import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private Button b;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(300,100,500,300);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
f.add(b);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
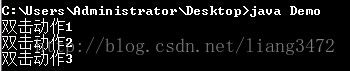
b.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter(){
private int count = 1;
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e){
//获取点击次数
if(e.getClickCount()==2){
System.out.println("双击动作"+count++);
}
}
});
}
}
练习:给按钮添加一个键盘监听
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private Button b;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(300,100,500,300);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
b = new Button("我是一个按钮");
f.add(b);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter(){
private int count = 1;
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e){
//获取点击次数
if(e.getClickCount()==2){
System.out.println("双击动作"+count++);
}
}
});
b.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
//如果按下Esc则程序退出
if(e.getKeyCode()==27)
System.exit(0);
//显示按键名和按键值
System.out.println(KeyEvent.getKeyText(e.getKeyCode())+"...."+e.getKeyCode());
if(e.isControlDown()&&e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
System.out.println("Ctrl+Enter");
}
});
}
}
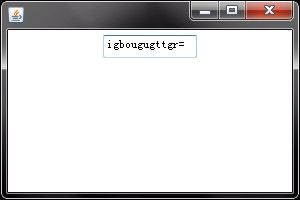
练习:文本框不能输入数字
KeyEvent从父类InputEvent继承了方法consume()。
void consume()
使用此事件,以便不会按照默认的方式由产生此事件的源代码来处理此事件。 import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
f.setBounds(300,100,300,200);
tf = new TextField();
tf.setColumns(10);
f.add(tf);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
int kc = e.getKeyCode();
System.out.println(kc);
if(kc>=KeyEvent.VK_0&&kc<=KeyEvent.VK_9)
e.consume();//将满足条件的按键不录入。
}
});
}
}
练习:在文本框中输入目录,点击“转到”按钮,将该目录中的文件与文件夹名称列在下面的文本区域中。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
private Button b;
private TextArea ta;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
f.setBounds(300,200,500,400);
tf = new TextField(50);
f.add(tf);
b = new Button("转到");
f.add(b);
ta = new TextArea(20,57);
f.add(ta);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
getFile();
}
});
}
public void getFile(){
ta.setText("");
File file = new File(tf.getText());
if(!(file.exists()&&file.isDirectory())){
System.out.println("非法路径");
}
else{
String[] listfile = file.list();
for(String thisfile : listfile){
ta.append(thisfile+"\r\n");
}
}
}
}
Dialog:对话框。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
private Button b;
private TextArea ta;
private Dialog d;
private Label l;
private Button ok;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
f.setBounds(300,200,500,400);
tf = new TextField(50);
f.add(tf);
b = new Button("转到");
f.add(b);
ta = new TextArea(20,57);
f.add(ta);
//创建对话框对象
d = new Dialog(f,true);
//设置对话框布局
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
//设置对话框位置,大小。
d.setBounds(450,300,200,100);
//创建标签
l = new Label();
//加入到对话框中
d.add(l);
//创建按钮
ok = new Button("确定");
//加入到对话框中
d.add(ok);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
getFile();
}
});
//对话框的关闭
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
//对话框的确定
ok.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
}
public void getFile(){
ta.setText("");
File file = new File(tf.getText());
if(!(file.exists()&&file.isDirectory())){
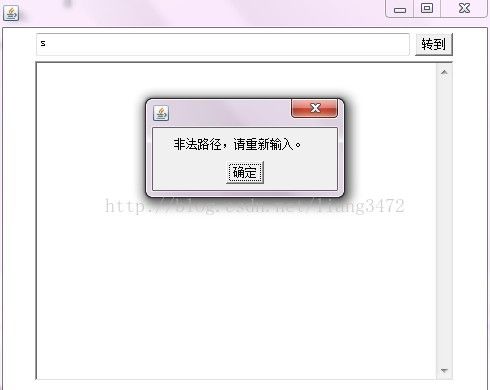
//提示信息
l.setText("非法路径,请重新输入。");
//当路径错误,弹出对话框
d.setVisible(true);
}
else{
String[] listfile = file.list();
for(String thisfile : listfile){
ta.append(thisfile+"\r\n");
}
}
}
}
练习:要求输完目录后,按回车可执行。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
private Button b;
private TextArea ta;
private Dialog d;
private Label l;
private Button ok;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
f.setBounds(300,200,500,400);
tf = new TextField(50);
f.add(tf);
b = new Button("转到");
f.add(b);
ta = new TextArea(20,57);
f.add(ta);
//创建对话框对象
d = new Dialog(f,true);
//设置对话框布局
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
//设置对话框位置,大小。
d.setBounds(450,300,200,100);
//创建标签
l = new Label();
//加入到对话框中
d.add(l);
//创建按钮
ok = new Button("确定");
//加入到对话框中
d.add(ok);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
getFile();
}
});
//对话框的关闭
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
//对话框的确定
ok.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
//回车执行
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
if(e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){
getFile();
}
}
});
}
public void getFile(){
ta.setText("");
File file = new File(tf.getText());
if(!(file.exists()&&file.isDirectory())){
//提示信息
l.setText("非法路径,请重新输入。");
//当路径错误,弹出对话框
d.setVisible(true);
}
else{
String[] listfile = file.list();
for(String thisfile : listfile){
ta.append(thisfile+"\r\n");
}
}
}
}MenuBar:菜单栏,菜单条。往Frame里添加菜单栏用setMenuBar();方法。
例:
import java.awt.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private Menu m;
private MenuBar mb;
private MenuItem mi;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(500,200,300,200);
//创建菜单栏
mb = new MenuBar();
//创建菜单
m = new Menu("文件");
//创建菜单项
mi = new MenuItem("退出");
//在Frame添加菜单栏
f.setMenuBar(mb);
//菜单栏里添加菜单
mb.add(m);
//在菜单里添加菜单项
m.add(mi);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
练习:添加子条目,并添加相应事件
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private Menu m;
private MenuBar mb;
private MenuItem mi;
//添加子菜单
private Menu m1;
//添加条目
private MenuItem mi1;
private MenuItem mi2;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(500,200,300,200);
mb = new MenuBar();
mi = new MenuItem("退出");
m = new Menu("文件");
//创建子菜单
m1 = new Menu("子菜单");
//创建条目
mi1 = new MenuItem("条目1");
mi2 = new MenuItem("条目2");
f.setMenuBar(mb);
mb.add(m);
//在子菜单条目
m1.add(mi1);
m1.add(mi2);
//在菜单里添加子菜单
m.add(m1);
m.add(mi);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
//窗体上退出
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
//菜单上退出
mi.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
FileDialog:类显示一个对话框窗口,用户可以从中选择文件。
例如:打开文件,保存文件。
static int LOAD
此常量值指示文件对话框窗口的作用是查找要读取的文件。
static int SAVE
此常量值指示文件对话框窗口的作用是查找要写入的文件。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private MenuBar mb;
private Menu m;
private MenuItem mi1,mi2,mi3;
private FileDialog openDia;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame();
f.setBounds(500,200,300,200);
mb = new MenuBar();
m = new Menu("菜单");
mi1 = new MenuItem("打开");
mi2 = new MenuItem("另存为");
mi3 = new MenuItem("退出");
m.add(mi1);
m.add(mi2);
m.add(mi3);
mb.add(m);
f.setMenuBar(mb);
//定义打开对话框
openDia = new FileDialog(f,"打开",FileDialog.LOAD);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
//监听打开动作
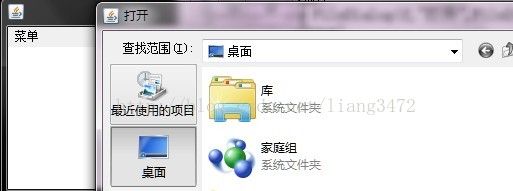
mi1.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
//弹出对话框
openDia.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
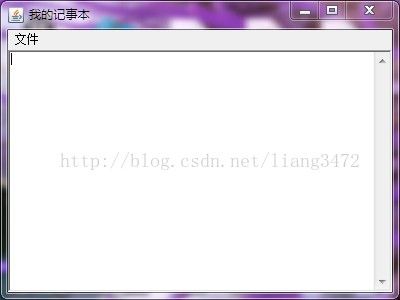
练习:写一个记事本软件,具有打开和保存操作。
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class Demo
{
private Frame f;
private TextArea ta;
private MenuBar mb;
private Menu m;
private MenuItem mi1,mi2,mi3;
private FileDialog openDia,saveDia;
private Label la;
private Button ok;
private Dialog d;
private File file = null;
Demo(){
init();
}
public static void main(String []args){
new Demo();
}
public void init(){
f = new Frame("我的记事本");
f.setBounds(300,200,400,300);
ta = new TextArea();
f.add(ta);
mb = new MenuBar();
m = new Menu("文件");
mi1 = new MenuItem("打开");
mi2 = new MenuItem("另存为");
mi3 = new MenuItem("退出");
m.add(mi1);
m.add(mi2);
m.add(mi3);
mb.add(m);
f.setMenuBar(mb);
openDia = new FileDialog(f,"打开",FileDialog.LOAD);
saveDia = new FileDialog(f,"另存为",FileDialog.SAVE);
la = new Label();
ok = new Button("确定");
d = new Dialog(f,"错误",true);
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
d.setBounds(400,300,300,100);
d.add(la);
d.add(ok);
f.setVisible(true);
myEvent();
}
public void myEvent(){
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
ok.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
mi3.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
//菜单中的打开事件处理方式
mi1.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
//弹出窗口
openDia.setVisible(true);
//当什么都没选时返回
if(openDia.getDirectory()==null||openDia.getFile()==null){
return;
}
//将路径和文件名封装成对象
file = new File(openDia.getDirectory(),openDia.getFile());
//判断文件是否存在,如果不存在弹出对话框。
if(!file.exists()){
la.setText("您要打开的文件不存在。");
d.setVisible(true);
}
else
//调用打开文件操作
openFile(file);
}
});
mi2.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
//判断是否要弹出对话框。如果文件已存在则不弹出对话框,如果文件不存在则弹出对话框。
if(file==null){
//弹出对话框
saveDia.setVisible(true);
//当什么都没选时返回
if(saveDia.getDirectory()==null||saveDia.getFile()==null){
return;
}
//将路径和文件名封装成对象
file = new File(saveDia.getDirectory(),saveDia.getFile());
}
//调用保存文件操作
saveFile(file);
}
});
}
//打开文件
public void openFile(File file){
BufferedReader br = null;
try{
//清空文本框
ta.setText("");
//读取数据
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine())!=null){
ta.append(line+"\r\n");
}
}
catch(IOException e){
la.setText("读取文件失败,请重新操作");
d.setVisible(true);
}
finally{
try{
if(br!=null)
br.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException("关闭读取流失败");
}
}
}
//保存文件
public void saveFile(File file){
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try{
//写入数据
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
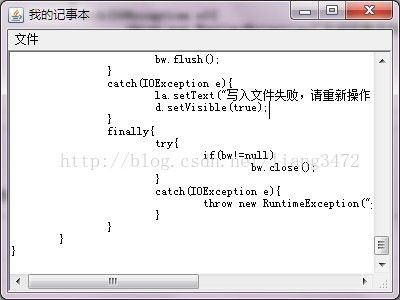
bw.write(ta.getText());
bw.flush();
}
catch(IOException e){
la.setText("写入文件失败,请重新操作");
d.setVisible(true);
}
finally{
try{
if(bw!=null)
bw.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException("关闭读取流失败");
}
}
}
}
jar包双击执行:
1.带包编译
javac -d 存储路径 xxxx.java
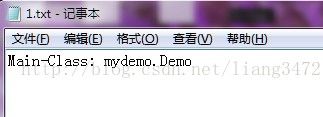
2.编写配置清单
Main-Class: mydemo.Demo+回车(固定格式)。
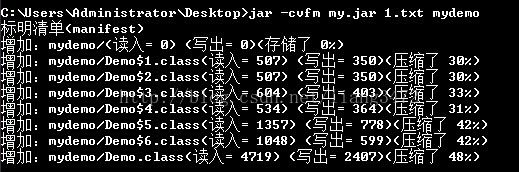
3.打包
jar -cvfm压缩后的名字 配置清单包名
4.双击运行