Spring AOP动态代理原理与实现方式
AOP:面向切面、面向方面、面向接口是一种横切技术
横切技术运用:
1.事务管理: (1)数据库事务:(2)编程事务(3)声明事物:Spring AOP-->声明事物
2.日志处理:
3.安全验证: Spring AOP---OOP升级
静态代理原理:目标对象:调用业务逻辑 代理对象:日志管理
表示层调用--->代理对象(日志管理)-->调用目标对象
动态代理原理:spring AOP采用动态代理来实现
(1)实现InvocationHandler接口
(2)创建代理类(通过java API)
Proxy.newProxyInstance(动态加载代理类,代理类实现接口,使用handler);
(3)调用invoke方法(虚拟机自动调用方法)
日志处理
//调用目标对象
method.invoke("目标对象","参数");
日志处理
通过代理对象--(请求信息)-->目标对象---(返回信息)----> 代理对象
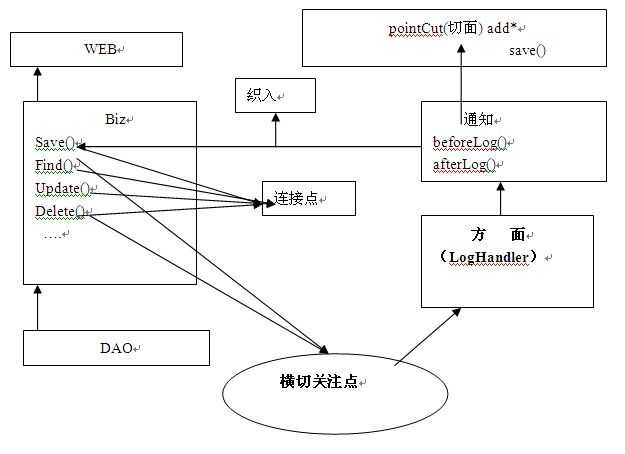
Spring 动态代理中的基本概念
1、关注点(concern)
一个关注点可以是一个特定的问题,概念、或者应用程序的兴趣点。总而言之,应用程序必须达到一个目标
安全验证、日志记录、事务管理都是一个关注点
在oo应用程序中,关注点可能已经被代码模块化了还可能散落在整个对象模型中
2、横切关注点(crosscutting concern)
如何一个关注点的实现代码散落在多个类中或方法中
3、方面(aspect)
一个方面是对一个横切关注点模块化,它将那些原本散落在各处的,
用于实现这个关注点的代码规整在一处
4、建议(advice)通知
advice是point cut执行代码,是方面执行的具体实现
5、切入点(pointcut)
用于指定某个建议用到何处
6、织入(weaving)
将aspect(方面)运用到目标对象的过程
7、连接点(join point)
程序执行过程中的一个点
通知类型:
try{
//前置通知
//环绕通知
//调用目标对象方法
//环绕通知
//后置通知
}catch(){
//异常通知
}finally{
//终止通知
}
流程图
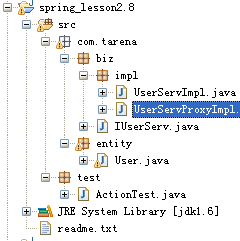
一.静态代理原理实例:
项目结构图:
IUserServ接口代码
public interface IUserServ {
List findAllUser();
int deleteUserById(User user);
int saveUser(User user);
}
UserServImpl实现类代码
public class UserServImpl implements IUserServ {
public int deleteUserById(User user) {
System.out.println("******执行删除方法******");
return 0;
}
public List findAllUser() {
System.out.println("*******执行查询方法*******");
return null;
}
public int saveUser(User user) {
System.out.println("*******执行添加方法********");
return 0;
}
} UserServProxyImpl实现类代码
//代理类:完成日志输出
public class UserServProxyImpl implements IUserServ {
// 访问目标对象(UserServImpl)
// 代理对象(UserServProxyImpl)
// 创建目标对象
private IUserServ iuserServ ;//= new UserServImpl();
public UserServProxyImpl(IUserServ iuserServ){
this.iuserServ = iuserServ;
}
public int deleteUserById(User user) {
beforeLog();
//调用目标对象里方法
iuserServ.deleteUserById(user);
afterLog();
return 0;
}
public List findAllUser() {
beforeLog();
//调用目标对象里方法
iuserServ.findAllUser();
afterLog();
return null;
}
public int saveUser(User user) {
beforeLog();
//调用目标对象里方法
iuserServ.saveUser(user);
afterLog();
return 0;
}
private void beforeLog() {
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
private void afterLog() {
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
} ActionTest测试类代码
public class ActionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用户访问代理对象---信息->目标对象
IUserServ iuserServ = new UserServProxyImpl(new UserServImpl());
iuserServ.findAllUser();
}
}运行结果:
开始执行
*******执行查询方法*******
执行完毕
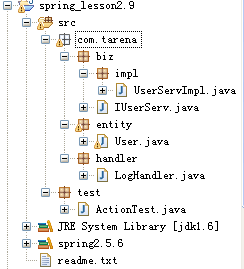
二.动态代理实例
项目结构图:
IUserServ接口代码与UserServImpl实现类代码和上述代码相同
LogHandler类代码
public class LogHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//目标对象
private Object targetObject;
/**
* 创建动态代理类
* @return object(代理类)
*/
public Object createProxy(Object targetObject){
this.targetObject = targetObject;
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
targetObject.getClass().getClassLoader(),
targetObject.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
Object obj = null;
try {
beforeLog();
//obj: 目标对象--->代理对象的返回值--->返回给调用者的信息
//this.invoke("目标对象","代理对象给目标对象传递参数");
//调用目标对象中方法
obj = method.invoke(targetObject, args);
afterLog();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
//日志管理方法
private void beforeLog(){
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
private void afterLog(){
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
ActionTest测试类代码:
public class ActionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建代理对象iuserServ
LogHandler handler = new LogHandler();
IUserServ iuserServ = (IUserServ)handler.createProxy(new UserServImpl());
iuserServ.deleteUserById(new User());
}
}运行结果:
开始执行
******执行删除方法******
执行完毕
三.Spring AOP使用(2.x版本之前)
项目结构图:
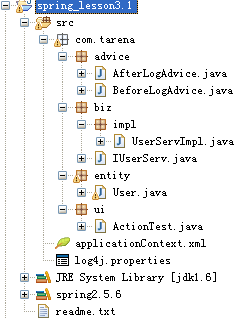
IUserServ接口代码与UserServImpl实现类代码和上述代码相同
配置步骤:
1、配置目标对象(applicationContext.xml)
2、配置通知
(a)前置通知(BeforeLogAdvice)
public class BeforeLogAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* Method method:调用目标对象的方法
* Object[] args:发送给目标对象的参数列表
* Object target:目标对象
*/
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target)
throws Throwable {
beforeLog();
}
private void beforeLog(){
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
}
(b)后置通知(AfterLogAdvice)
public class AfterLogAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
/**
* Object returnValue:目标对象返回值
* Method method:目标对象方法名
* Object[] args:目标对象参数列表
* Object target:目标对象
*/
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method,
Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
afterLog();
}
private void afterLog(){
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
(c)在spring容器中,让容器管理通知(applicationContext.xml)
3、配置代理对象(applicationContext.xml)
com.tarena.biz.IUserServ
beforeLogAdvice
afterLogAdvice
4.访问()
Spring容器:通过代理对象调用-->织入通知--->目标对象
程序员:访问代理对象
测试类(ActionTest):
public class ActionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
IUserServ iuserServ = (IUserServ)ac.getBean("userServProxy");
iuserServ.deleteUserById(new User());
iuserServ.findAllUser();
}
}运行结果:
开始执行
******执行删除方法******
执行完毕
开始执行
*******执行查询方法*******
执行完毕
四.Spring AOP使用(2.x版本之后)这种方式需要额外添加两个jar包,
存放位置在spring-framework-2.5.6.SEC01\lib\aspectj文件夹下。
项目结构图
IUserServ接口代码与UserServImpl实现类代码和上述代码相同
LogAdvice中
public class LogAdvice {
public void beforeLog(){
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
public void afterLog(){
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
applicationContext.xml中
测试类:
public class ActionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
IUserServ iuserServ = (IUserServ)ac.getBean("userServImpl");
iuserServ.deleteUserById(new User());
iuserServ.findAllUser();
iuserServ.saveUser(new User());
}
}运行结果
******执行删除方法******
*******执行查询方法*******
开始执行
*******执行添加方法********
执行完毕
注:如果要在业务层所有的方法前后添加日志文件,则需要更改为以下配置
运行结果:
开始执行
******执行删除方法******
执行完毕
开始执行
*******执行查询方法*******
执行完毕
开始执行
*******执行添加方法********
执行完毕