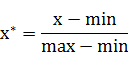kaggle 入门系列翻译(一) minst手写数据集
最近在学习kaggle相关,顺便翻译一下kaggle比赛中大牛的kernel吧,同时加强自己的理解,但愿能坚持下去吧。。
第一次就以minst 数字认真比赛开始吧:
精力有限,每一场比赛只能翻译打星最多的kernel:
本次的链接如下:
https://www.kaggle.com/yassineghouzam/introduction-to-cnn-keras-0-997-top-6
目录:
1、介绍
2、数据预处理
加载数据
检查缺失项
归一化和标准化
重组
标签one-hoting编码
拆分测试和训练集
3、CNN卷积神经网络
定义模型
设置最优化方式和退火算法
数据增强
4、模型评估
训练和评估曲线
混淆矩阵
5、预测和提交
下面详细介绍:
1、介绍
就是28*28的数据集,通过灰度的不同,来判断这个矩阵代表数字几,0~9
本文主要通过CNN深度学习的方式进行预测。
可以看出,这个主要参考了LeNet的结构。
首先加载所有需要用到的类库:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline //ipython特有的,python下会报错,用来开启画图模式
np.random.seed(2)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools
from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical # convert to one-hot-encoding
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau
sns.set(style='white', context='notebook', palette='deep')
2、数据预处理
加载数据
train = pd.read_csv("../input/train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("../input/test.csv")这边看过七月在线的教程,说这里有个鄙视链,一般参加比赛的,都会把训练集和测试机放在input文件夹下。。。
加载完之后可以看一下数据的样本分布如何:
Y_train = train["label"]
# Drop 'label' column
X_train = train.drop(labels = ["label"],axis = 1)
# free some space
del train
g = sns.countplot(Y_train)
Y_train.value_counts()得到如图结果:
1 4684
7 4401
3 4351
9 4188
2 4177
6 4137
0 4132
4 4072
8 4063
5 3795
Name: label, dtype: int64可以看出,分布还是比较均衡的。
检查缺失项
X_train.isnull().any().describe()test.isnull().any().describe()
结果发现很完整,无需处理了就
归一化和标准化
这里做了归一化,说可以减少照明的影响。
normlization 归一化
standardization 标准化
1、在分类、聚类算法中,需要使用距离来度量相似性的时候、或者使用PCA技术进行降维的时候,第二种方法(Z-score standardization)表现更好。
2、在不涉及距离度量、协方差计算、数据不符合正太分布的时候,可以使用第一种方法或其他归一化方法。比如图像处理中,将RGB图像转换为灰度图像后将其值限定在[0 255]的范围。
X_train = X_train / 255.0
test = test / 255.0重组
原有数据是784维度的,后面处理时希望把他变成图像那样的矩阵式,变成28*28的
X_train = X_train.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
test = test.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)这里因为是灰度图,所以最后一项只有1,如果是rbg这种,就得变成3了。
参数-1代表新数组的shape属性应该要与原来数组的一致,即新数组元素数量与原数组元素数量要相等。
标签one-hoting编码
最终分类的是10个类别,进行one-hot encoding:
Y_train = to_categorical(Y_train, num_classes = 10)拆分测试和训练集
random_seed = 2
X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val = train_test_split(X_train, Y_train, test_size = 0.1, random_state=random_seed)random_seed 随机数种子,貌似设不设置无所谓,只是让每次拆分的结果固定。
这里由于测试机是比较均衡的,所以这么分没问题,如果不均衡的话这么分就不行了,文章中说通过stratify = True可以解决。
正常应该可以通过下采样;或者将多的那部分样本拆分,拆分后的集合和少的那部分训练,而后将多个训练结果融合;
g = plt.imshow(X_train[0][:,:,0])通过这个方式看一下当前样本的形态。
3、CNN卷积神经网络
定义模型
这里使用keras框架实现cnn,keras底层选择的tensorflow。
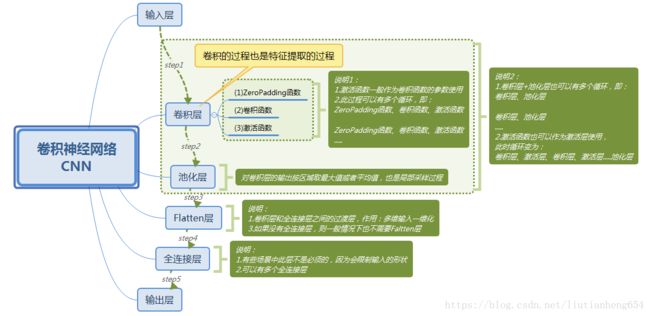
其中主要用到了以下几种层:
卷积层:(conv)使用多个表决器来扫描同一副图像得到不同的结果,同一个核w权重不变,不断扫描一幅图片,得到一个新的图片。
池化层:主要用于减少参数维数,防止过拟合。同时可以让数据具有一些不变性。
dropout:(不知道中文怎么翻译)防止过拟合,随机设置网络中部分节点权重为0.原理大概如下:有几次网络中,有节点a的权重不为0的情况下,分类结果是A,但是还有很多a权重为0的情况下,他依然分类结果A,可认为a对真实的分类其实意义不是特别大。
激活层(这里用了relu,但两者是一对多的关系)这层有时介绍网络时会包括在卷积层,是必须有的,可以预见,如果没有这一层的话,连续两个卷积层连在一起,可以w1(w2*x)可以理解为w*x,失去了意义。所以需要激活层。
扁平层:(Flatten layer) 全连接之前的过度层,多维转化为一维
网上有个图,画的比较好:
模型内容:首先是2个32核的卷积层,然后一个最大值池化层,然后一个dropout,然后两个64核的卷积层。之后池化,dropout,而后一个扁平层之后上激活函数,而后再一个dropout之后上激活函数。
# Set the CNN model
# my CNN architechture is In -> [[Conv2D->relu]*2 -> MaxPool2D -> Dropout]*2 -> Flatten -> Dense -> Dropout -> Out
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu', input_shape = (28,28,1)))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(256, activation = "relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))设置最优化方式和退火算法
为了让收敛加快,并尽量防止最终在最小值处不断摇摆,采用一个不断减小的步长。
(并尽量防止进入局部最小值,采用了模拟退火算法,这段还未理解到底有没有用)。
这里插一个模拟退火算法的理解:
模仿兵器淬火的过程,多次放在水里降温的过程。
相当于右半个余弦的样子,不断重复:就是步长慢慢减小到0后又一下子增加一节,然后再慢慢减少。
当连续三次结果没有优化的话,将训练步长减半。
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9, epsilon=1e-08, decay=0.0)
model.compile(optimizer = optimizer , loss = "categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])
learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_acc',
patience=3,
verbose=1,
factor=0.5,
min_lr=0.00001)
epochs = 1 # Turn epochs to 30 to get 0.9967 accuracy
batch_size = 86数据增强
为防止过拟合,我们可以通过对原有数据集的变换组合,生成新的数据集,从而让训练得到的模型更加鲁棒。
比如平移,缩放,旋转。
这里采用了四种方式:
旋转10度之内
缩放10%之内
水平移动10%以内
垂直移动10%以内
经过这个变换后产生的数据集,最终严重结果得到了1%的提升。
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset
samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0
featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset
samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std
zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening
rotation_range=10, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180)
zoom_range = 0.1, # Randomly zoom image
width_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width)
height_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images
vertical_flip=False) # randomly flip images
datagen.fit(X_train)
# Fit the model
history = model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(X_train,Y_train, batch_size=batch_size),
epochs = epochs, validation_data = (X_val,Y_val),
verbose = 2, steps_per_epoch=X_train.shape[0] // batch_size
, callbacks=[learning_rate_reduction])通过学习曲线看看能否收敛,看看算法效果如何。
4、模型评估
训练和评估曲线
# Plot the loss and accuracy curves for training and validation
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(history.history['loss'], color='b', label="Training loss")
ax[0].plot(history.history['val_loss'], color='r', label="validation loss",axes =ax[0])
legend = ax[0].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)
ax[1].plot(history.history['acc'], color='b', label="Training accuracy")
ax[1].plot(history.history['val_acc'], color='r',label="Validation accuracy")
legend = ax[1].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)混淆矩阵
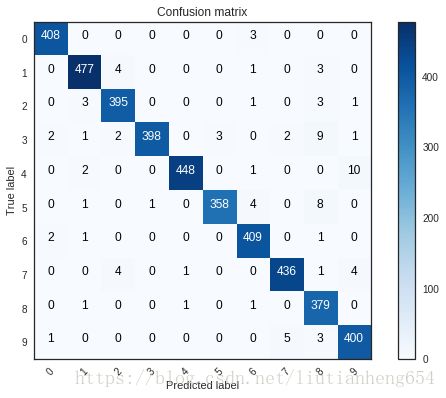
通过混淆矩阵来看看模型的性能,看看还有没有什么能改进的:
# Look at confusion matrix
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""
This function prints and plots the confusion matrix.
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
"""
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j],
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
# Predict the values from the validation dataset
Y_pred = model.predict(X_val)
# Convert predictions classes to one hot vectors
Y_pred_classes = np.argmax(Y_pred,axis = 1)
# Convert validation observations to one hot vectors
Y_true = np.argmax(Y_val,axis = 1)
# compute the confusion matrix
confusion_mtx = confusion_matrix(Y_true, Y_pred_classes)
# plot the confusion matrix
plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mtx, classes = range(10)) 可以看出相对42000的数据量,结果已经很好了,只有4有些会被五分类为9,我们可以看一下为什么。
# Display some error results
# Errors are difference between predicted labels and true labels
errors = (Y_pred_classes - Y_true != 0)
Y_pred_classes_errors = Y_pred_classes[errors]
Y_pred_errors = Y_pred[errors]
Y_true_errors = Y_true[errors]
X_val_errors = X_val[errors]
def display_errors(errors_index,img_errors,pred_errors, obs_errors):
""" This function shows 6 images with their predicted and real labels"""
n = 0
nrows = 2
ncols = 3
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows,ncols,sharex=True,sharey=True)
for row in range(nrows):
for col in range(ncols):
error = errors_index[n]
ax[row,col].imshow((img_errors[error]).reshape((28,28)))
ax[row,col].set_title("Predicted label :{}\nTrue label :{}".format(pred_errors[error],obs_errors[error]))
n += 1
# Probabilities of the wrong predicted numbers
Y_pred_errors_prob = np.max(Y_pred_errors,axis = 1)
# Predicted probabilities of the true values in the error set
true_prob_errors = np.diagonal(np.take(Y_pred_errors, Y_true_errors, axis=1))
# Difference between the probability of the predicted label and the true label
delta_pred_true_errors = Y_pred_errors_prob - true_prob_errors
# Sorted list of the delta prob errors
sorted_dela_errors = np.argsort(delta_pred_true_errors)
# Top 6 errors
most_important_errors = sorted_dela_errors[-6:]
# Show the top 6 errors
display_errors(most_important_errors, X_val_errors, Y_pred_classes_errors, Y_true_errors)可以看出来,这个人都没办法分。。写的太丑了。所以忽略不计了。
5、预测和提交
后面就是预测并提交了
# predict results
results = model.predict(test)
# select the indix with the maximum probability
results = np.argmax(results,axis = 1)
results = pd.Series(results,name="Label")
submission = pd.concat([pd.Series(range(1,28001),name = "ImageId"),results],axis = 1)
submission.to_csv("cnn_mnist_datagen.csv",index=False)第一次就到这了,后面会把这一篇慢慢完善,下一篇房价那个或者泰坦尼克号的吧。。欢迎交流啊,邮箱:[email protected]