ardupilot CAN和UAVCAN
目录
文章目录
- 目录
- 摘要
- 1. CAN bus and UAVCAN protocol
- 2.CAN bus support in Ardupilot
- 3.UAVCAN protocol
- 4.Initialization description
- 5.CAN总线驱动程序实施路线图
- 1.CAN类
- 2.CANManager class
- 6.ardupilot CAN总线代码学习
- 1.can总线设备初始化
- 2.can数据更新
摘要
本节主要学习ardupilot的CAN和UAVCAN,主要参考官网,欢迎批评指正。
1. CAN bus and UAVCAN protocol
在Ardupilot中对CAN总线消息传递的支持依赖于两个部分:
- 硬件CAN总线支持,通过HAL驱动程序完成。
- 负责处理所有高级工作的UAVCAN协议
2.CAN bus support in Ardupilot
硬件CAN总线支持的基础位于AP_HAL库中,由两个类组成:
- CAN类负责表示板上一个物理接口的。这个类管理接口的打开、设置和操作,是软件和硬件之间的主要连接点。
- CanManager类包装所有物理接口。它对接口进行枚举,提供对接口的访问,还保留用于访问UAVCAN管理类的连接点。
/**
* 单个非阻塞CAN接口------Single non-blocking CAN interface.
*/
class AP_HAL::CAN: public uavcan::ICanIface {
public:
/* CAN port open method
bitrate Selects the speed that the port will be configured to. If zero, the port speed is left unchanged.
return false - CAN port open failed
true - CAN port open succeeded
*/
virtual bool begin(uint32_t bitrate) = 0;
/*
CAN port close
*/
virtual void end() = 0;
/*
Reset opened CAN port
Pending messages to be transmitted are deleted and receive state and FIFO also reset.
All pending errors are cleared.
*/
virtual void reset() = 0;
/*
Test if CAN port is opened and initialized
return false - CAN port not initialized
true - CAN port is initialized
*/
virtual bool is_initialized() = 0;
/*
Return if CAN port has some untransmitted pending messages
return -1 - CAN port is not opened or initialized
0 - no messages are pending
positive - number of pending messages
*/
virtual int32_t tx_pending() = 0;
/*
Return if CAN port has received but yet read messages
return -1 - CAN port is not opened or initialized
0 - no messages are pending for read
positive - number of pending messages for read
*/
virtual int32_t available() = 0;
};
/**
*通用CAN驱动程序。----- Generic CAN driver.
*/
class AP_HAL::CANManager {
public:
CANManager(uavcan::ICanDriver* driver) : _driver(driver) {}
/* CAN port open method
Opens port with specified bit rate
bitrate - selects the speed that the port will be configured to. If zero, the port speed is left
unchanged.
can_number - the index of can interface to be opened
return false - CAN port open failed
true - CAN port open succeeded
*/
virtual bool begin(uint32_t bitrate, uint8_t can_number) = 0;
/*
Test if CAN manager is ready and initialized
return false - CAN manager not initialized
true - CAN manager is initialized
*/
virtual bool is_initialized() = 0;
virtual void initialized(bool val) = 0;
virtual AP_UAVCAN *get_UAVCAN(void) = 0;
virtual void set_UAVCAN(AP_UAVCAN *uavcan) = 0;
uavcan::ICanDriver* get_driver() { return _driver; }
private:
uavcan::ICanDriver* _driver;
};
作为实施新硬件的CAN总线支持的指南,可以使用以下路线图。
3.UAVCAN protocol
支持UAVCAN protocl是基于AP_UAVCAN类,这是包装与libuavcan交互的,并为ardupilot中存在的其他库提供访问点。它负责通过具有UAVCAN协议的CAN总线发送消息,接收消息,将消息转换为其他库可接受的形式,并提供libuaVCAN的循环更新。
AP_UAVCAN类 支持下面的信息
- 向伺服系统传输1010.arraycommand
- 接收1001.磁场强度
- 接收1028.静态气压
- 接收1029.静态温度
- 向ESCS传输1030.rawcommand
- 接收1060。修复从GNSS
- 接收来自GNSS的1061.辅助设备
所有传入消息的处理都是在ap_avcan类中进行的,这些消息被转换成最适合其他库的形式。使用或传输数据的库不应包括来自UAVCAN模块的UAVCAN头文件,而是应以自己的首选方式将所有数据发送到AP_UAVCAN类。
4.Initialization description
根据板和底层硬件的类型,可能需要采取其他措施来创建CAN驱动程序和UAVCAN接口类。
void Copter::init_ardupilot()
{
#if HAL_WITH_UAVCAN
BoardConfig_CAN.init();
#endif
}
void AP_BoardConfig_CAN::init()
{
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_INTERFACES; i++)
{
_st_driver_number[i] = (int8_t) _var_info_can[i]._driver_number;
_st_can_debug[i] = (int8_t) _var_info_can[i]._can_debug;
}
setup_canbus();
}
5.CAN总线驱动程序实施路线图
硬件CAN总线支持的基础位于AP_HAL库中,由两个类组成:
- 负责表示板上一个物理接口的CAN类。这个类管理接口的打开、设置和操作,是软件和硬件之间的主要连接点。
- CanManager类正在包装所有物理接口。它对接口进行枚举,提供对接口的访问,还保留用于访问UAVCAN管理类的连接点。
1.CAN类
新类应该基于AP_HAL::CAN类。
该类负责管理硬件,还负责管理Rx和Tx队列。除此之外,还提供了时间管理。
必要的方法如下:
-构造函数
- int init(const uint32_t bitrate, const OperatingMode mode)
用特定的波特率和操作模式初始化硬件CAN控制器。驱动程序应尽量匹配指定的波特率。操作模式是允许发送帧的正常模式,或者是仅用于接收帧的静默模式。此方法只能由begin()方法在内部使用。
-bool begin(uint32_t bitrate)
此方法应尝试用指定的比特率初始化CAN接口。
- void end()
完成CAN接口的实例
- void reset()
用以前的设置重新初始化接口
- bool is_initialized()
如果成功初始化CAN接口,则返回true
int32_t available()
此方法应返回RX队列的长度。
int32_t tx_pending()
此方法返回要传输的挂起消息数。
bool canacceptnewtxframe(const uavcan::canframe&frame)
如果用于传输的新消息可以放置在TX队列中,则此方法返回true。
bool isrxbufferempty()。
方法检查Rx队列是否为空。
uint64_t getErrorCount()
硬件故障和其他类型错误(例如队列溢出)的总数。如果接口未连接到总线,则可能持续增加。
uint32_t getvoluntarytxabortcount()。
驱动程序执行库要求在第一个错误时中止传输的次数。
无符号getrxqueuelength())
返回RX队列中挂起的帧数。
bool hadhactivity()。
返回自上次调用此方法以来,此iface是否至少有一个成功的IO。这是为配合iFace活动指示灯而设计的。
int16_t send(const uavcan::CanFrame& frame, uavcan::MonotonicTime tx_deadline, uavcan::CanIOFlags flags)
该方法负责将新帧放入发送队列。还提供了最大传输截止时间,如果截止时间已过,则驱动程序有责任从队列中删除帧。标志可以是none、loopback或abortonerror的组合。
int16_t receive(uavcan::CanFrame& out_frame, uavcan::MonotonicTime& out_ts_monotonic, uavcan::UtcTime& out_ts_utc, uavcan::CanIOFlags& out_flags)
该方法用RX队列中的第一条消息填充传递的引用中的所有数据。
2.CANManager class
新类应该基于ap_hal::canManager类。
必要的方法如下:
Constructor
int init(const uint32_t bitrate, const PX4CAN::OperatingMode mode, uint8_t can_number)
Initializes the specified CAN interface with specific bitrate and operating mode. This method is used internally only by begin() method.
bool begin(uint32_t bitrate, uint8_t can_number)
This method should try to initialize specified CAN interface with specified bitrate.
uavcan::CanSelectMasks makeSelectMasks(const uavcan::CanFrame* (&pending_tx)[uavcan::MaxCanIfaces])
This function returns select masks indicating which interfaces are available for read/write.
PX4CAN* getIface(uint8_t iface_index)
Returns reference to the specified interface
uint8_t getNumIfaces()
Returns number of interfaces
bool hadActivity();
Whether at least one iface had at least one successful IO since previous call of this method. This is designed for use with iface activity LEDs.
bool is_initialized() override;
Returns true if the CAN manager was initialized successfully
void set_UAVCAN(AP_UAVCAN *uavcan)
Method stores the pointer to the UAVCAN instance
AP_UAVCAN *get_UAVCAN(void)
Method returns the pointer to the UAVCAN instance that is connected with this manager
6.ardupilot CAN总线代码学习
1.can总线设备初始化
步骤1:
void Copter::setup()
{
//加载var_info[]s中列出的变量的默认值---- Load the default values of variables listed in var_info[]s
AP_Param::setup_sketch_defaults();
//为直升机设置存储布局-------------------setup storage layout for copter
StorageManager::set_layout_copter();
//驱动设备初始化
init_ardupilot();
//初始化主循环计划程序------------------ initialise the main loop scheduler
scheduler.init(&scheduler_tasks[0], ARRAY_SIZE(scheduler_tasks), MASK_LOG_PM);
}
步骤2:
void Copter::init_ardupilot()
{
#if HAL_WITH_UAVCAN
BoardConfig_CAN.init();
#endif
}
这里要注意,若要开启Can总线,需要HAL_WITH_UAVCAN=1;在AP_HAL_Boards.h
#ifndef HAL_WITH_UAVCAN
#define HAL_WITH_UAVCAN 1
#endif
步骤3:调转到AP_BoardConfig库
void AP_BoardConfig_CAN::init()
{
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_INTERFACES; i++) //启动的can设备数量
{
_st_driver_number[i] = (int8_t) _var_info_can[i]._driver_number;
_st_can_debug[i] = (int8_t) _var_info_can[i]._can_debug;
}
setup_canbus(); //初始化Can总线
}
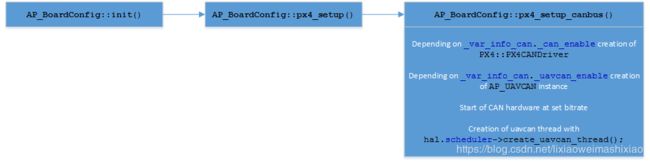
步骤4:调转到setup_canbus()函数
void AP_BoardConfig_CAN::setup_canbus(void)
{
// Create all drivers that we need
bool initret = true;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_INTERFACES; i++) {
// Check the driver number assigned to this physical interface
uint8_t drv_num = _var_info_can[i]._driver_number;
if (drv_num != 0 && drv_num <= MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_DRIVERS) {
if (hal.can_mgr[drv_num - 1] == nullptr) {
// CAN Manager is the driver
// So if this driver was not created before for other physical interface - do it
#if CONFIG_HAL_BOARD == HAL_BOARD_PX4 || CONFIG_HAL_BOARD == HAL_BOARD_VRBRAIN
const_cast (hal).can_mgr[drv_num - 1] = new PX4::PX4CANManager;
#elif CONFIG_HAL_BOARD == HAL_BOARD_LINUX
const_cast (hal).can_mgr[drv_num - 1] = new Linux::CANManager;
#elif CONFIG_HAL_BOARD == HAL_BOARD_CHIBIOS
const_cast (hal).can_mgr[drv_num - 1] = new ChibiOS::CANManager;
#endif
}
// For this now existing driver (manager), start the physical interface
if (hal.can_mgr[drv_num - 1] != nullptr) {
initret &= hal.can_mgr[drv_num - 1]->begin(_var_info_can[i]._can_bitrate, i);
} else {
printf("Failed to initialize can interface %d\n\r", i + 1);
}
}
}
bool any_uavcan_present = false;
if (initret) {
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_DRIVERS; i++) {
if (hal.can_mgr[i] == nullptr) {
continue;
}
hal.can_mgr[i]->initialized(true);
printf("can_mgr %d initialized well\n\r", i + 1);
if (_var_info_can_protocol[i]._protocol == UAVCAN_PROTOCOL_ENABLE) {
_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan = new AP_UAVCAN;
if (_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan == nullptr) {
AP_HAL::panic("Failed to allocate uavcan %d\n\r", i + 1);
continue;
}
AP_Param::load_object_from_eeprom(_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan, AP_UAVCAN::var_info);
hal.can_mgr[i]->set_UAVCAN(_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan);
_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan->set_parent_can_mgr(hal.can_mgr[i]);
if (_var_info_can_protocol[i]._uavcan->try_init() == true) //这里需要注意的地方
{
any_uavcan_present = true;
} else {
printf("Failed to initialize uavcan interface %d\n\r", i + 1);
}
}
}
if (any_uavcan_present) {
// start UAVCAN working thread
hal.scheduler->create_uavcan_thread();
// Delay for magnetometer and barometer discovery
hal.scheduler->delay(5000);
}
}
}
分析函数1:_uavcan->try_init()这个函数初始化支持不同的can总线设备,这里我重点以电池信息为例
bool AP_UAVCAN::try_init(void)
{
if (_parent_can_mgr == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if (_initialized) {
return true;
}
if (!_parent_can_mgr->is_initialized()) {
return false;
}
_uavcan_i = UINT8_MAX;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_DRIVERS; i++) {
if (_parent_can_mgr == hal.can_mgr[i]) {
_uavcan_i = i;
break;
}
}
if(_uavcan_i == UINT8_MAX) {
return false;
}
auto *node = get_node();
if (node == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if (node->isStarted()) {
return false;
}
uavcan::NodeID self_node_id(_uavcan_node);
node->setNodeID(self_node_id);
char ndname[20];
snprintf(ndname, sizeof(ndname), "org.ardupilot:%u", _uavcan_i);
uavcan::NodeStatusProvider::NodeName name(ndname);
node->setName(name);
uavcan::protocol::SoftwareVersion sw_version; // Standard type uavcan.protocol.SoftwareVersion
sw_version.major = AP_UAVCAN_SW_VERS_MAJOR;
sw_version.minor = AP_UAVCAN_SW_VERS_MINOR;
node->setSoftwareVersion(sw_version);
uavcan::protocol::HardwareVersion hw_version; // Standard type uavcan.protocol.HardwareVersion
hw_version.major = AP_UAVCAN_HW_VERS_MAJOR;
hw_version.minor = AP_UAVCAN_HW_VERS_MINOR;
node->setHardwareVersion(hw_version);
const int node_start_res = node->start();
if (node_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN: node start problem\n\r");
}
uavcan::Subscriber *gnss_fix;
gnss_fix = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int gnss_fix_start_res = gnss_fix->start(gnss_fix_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (gnss_fix_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN GNSS subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
uavcan::Subscriber *gnss_aux;
gnss_aux = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int gnss_aux_start_res = gnss_aux->start(gnss_aux_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (gnss_aux_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN GNSS Aux subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
uavcan::Subscriber *magnetic;
magnetic = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int magnetic_start_res = magnetic->start(magnetic_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (magnetic_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN Compass subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
uavcan::Subscriber *magnetic2;
magnetic2 = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int magnetic_start_res_2 = magnetic2->start(magnetic_cb_2_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (magnetic_start_res_2 < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN Compass for multiple mags subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
uavcan::Subscriber *air_data_sp;
air_data_sp = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int air_data_sp_start_res = air_data_sp->start(air_data_sp_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (air_data_sp_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN Baro subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
uavcan::Subscriber *air_data_st;
air_data_st = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int air_data_st_start_res = air_data_st->start(air_data_st_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (air_data_st_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN Temperature subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
//这里是我们研究的地方,只要弄明白一处的实现就可以理解其他地方
uavcan::Subscriber *battery_info_st;
battery_info_st = new uavcan::Subscriber(*node);
const int battery_info_start_res = battery_info_st->start(battery_info_st_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
if (battery_info_start_res < 0) {
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN BatteryInfo subscriber start problem\n\r");
return false;
}
act_out_array[_uavcan_i] = new uavcan::Publisher(*node);
act_out_array[_uavcan_i]->setTxTimeout(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(20));
act_out_array[_uavcan_i]->setPriority(uavcan::TransferPriority::OneLowerThanHighest);
esc_raw[_uavcan_i] = new uavcan::Publisher(*node);
esc_raw[_uavcan_i]->setTxTimeout(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(20));
esc_raw[_uavcan_i]->setPriority(uavcan::TransferPriority::OneLowerThanHighest);
rgb_led[_uavcan_i] = new uavcan::Publisher(*node);
rgb_led[_uavcan_i]->setTxTimeout(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(20));
rgb_led[_uavcan_i]->setPriority(uavcan::TransferPriority::OneHigherThanLowest);
_led_conf.devices_count = 0;
/*
* Informing other nodes that we're ready to work.
* Default mode is INITIALIZING.
*/
node->setModeOperational();
_initialized = true;
debug_uavcan(1, "UAVCAN: init done\n\r");
return true;
}
分析其中的电池信息函数:const int battery_info_start_res = battery_info_st->start(battery_info_st_cb_arr[_uavcan_i]);
首先看battery_info_st->start函数,这个是一个回调函数,最终把battery_info_st_cb_arr[_uavcan_i])传入
/**
* Begin receiving messages.开始接受信息
* Each message will be passed to the application via the callback.
* Returns negative error code.
*/
int start(const Callback& callback)
{
stop();
if (!coerceOrFallback(callback, true))
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("Subscriber", "Invalid callback");
return -ErrInvalidParam;
}
callback_ = callback;
return BaseType::startAsMessageListener();
}
其中battery_info_st_cb_arr是一个指针数组函数
static void (*battery_info_st_cb_arr[2])(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure& msg)
= { battery_info_st_cb0, battery_info_st_cb1 };
static void battery_info_st_cb0(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure& msg)
{ battery_info_st_cb(msg, 0); }
static void battery_info_st_cb1(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure& msg)
{ battery_info_st_cb(msg, 1); }
static void (*battery_info_st_cb_arr[2])(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure& msg)
= { battery_info_st_cb0, battery_info_st_cb1 };
static void battery_info_st_cb(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure& msg, uint8_t mgr)
{
AP_UAVCAN *ap_uavcan = AP_UAVCAN::get_uavcan(mgr);
if (ap_uavcan == nullptr) {
return;
}
AP_UAVCAN::BatteryInfo_Info *state = ap_uavcan->find_bi_id((uint16_t) msg.battery_id);
if (state == nullptr) {
return;
}
state->temperature = msg.temperature;
state->voltage = msg.voltage;
state->current = msg.current;
state->full_charge_capacity_wh = msg.full_charge_capacity_wh;
state->remaining_capacity_wh = msg.remaining_capacity_wh;
state->status_flags = msg.status_flags;
// after all is filled, update all listeners with new data
ap_uavcan->update_bi_state((uint16_t) msg.battery_id);
}
到这里就可以看到ap_uavcan->update_bi_state((uint16_t) msg.battery_id);这个是更新获取的电池信息,只有不停的回调才有数据更新,因此重点还是如何实现回调函数运作的
void AP_UAVCAN::update_bi_state(uint8_t id)
{
// Go through all listeners of specified node and call their's update methods
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < AP_UAVCAN_MAX_BI_NUMBER; i++) {
if (_bi_id[i] != id) {
continue;
}
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < AP_UAVCAN_MAX_LISTENERS; j++) {
if (_bi_BM_listener_to_id[j] != i) {
continue;
}
_bi_BM_listeners[j]->handle_bi_msg(_bi_id_state[i].voltage, _bi_id_state[i].current, _bi_id_state[i].temperature); //到这里就是更新电池信息
}
}
}
//更新电池信息
void AP_BattMonitor_UAVCAN::handle_bi_msg(float voltage, float current, float temperature)
{
_state.temperature = temperature;
_state.voltage = voltage;
_state.current_amps = current;
uint32_t tnow = AP_HAL::micros();
uint32_t dt = tnow - _state.last_time_micros;
// update total current drawn since startup
if (_state.last_time_micros != 0 && dt < 2000000) {
// .0002778 is 1/3600 (conversion to hours)
float mah = (float) ((double) _state.current_amps * (double) dt * (double) 0.0000002778f);
_state.consumed_mah += mah;
_state.consumed_wh += 0.001f * mah * _state.voltage;
}
// record time
_state.last_time_micros = tnow;
_state.healthy = true;
}
因此我们继续分析回调函数,如何传入回调的
*开始接收消息。
*每个消息都将通过回调传递给应用程序。
*返回负错误代码。
int start(const Callback& callback)
{
stop();
if (!coerceOrFallback(callback, true))
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("Subscriber", "Invalid callback");
return -ErrInvalidParam;
}
callback_ = callback;
return BaseType::startAsMessageListener();
}
重点是callback_ = callback;
Callback callback_;
template = UAVCAN_CPP11
typename Callback_ = std::function&)>
#else
typename Callback_ = void (*)(const ReceivedDataStructure&)
#endif
分析最终是通过typename Callback_ = std::function
template
class UAVCAN_EXPORT ReceivedDataStructure : public DataType_, Noncopyable
{
const IncomingTransfer* const _transfer_; ///< Such weird name is necessary to avoid clashing with DataType fields
template
Ret safeget() const
{
if (_transfer_ == UAVCAN_NULLPTR)
{
return Ret();
}
return (_transfer_->*Fun)();
}
protected:
ReceivedDataStructure()
: _transfer_(UAVCAN_NULLPTR)
{ }
ReceivedDataStructure(const IncomingTransfer* arg_transfer)
: _transfer_(arg_transfer)
{
UAVCAN_ASSERT(arg_transfer != UAVCAN_NULLPTR);
}
public:
typedef DataType_ DataType;
MonotonicTime getMonotonicTimestamp() const
{
return safeget();
}
UtcTime getUtcTimestamp() const { return safeget(); }
TransferPriority getPriority() const { return safeget(); }
TransferType getTransferType() const { return safeget(); }
TransferID getTransferID() const { return safeget(); }
NodeID getSrcNodeID() const { return safeget(); }
uint8_t getIfaceIndex() const { return safeget(); }
bool isAnonymousTransfer() const { return safeget(); }
};
2.can数据更新
步骤1:
void Scheduler::init()
{
// setup the uavcan thread - this will call tasks at 1kHz
#if HAL_WITH_UAVCAN
_uavcan_thread_ctx = chThdCreateStatic(_uavcan_thread_wa,
sizeof(_uavcan_thread_wa),
APM_UAVCAN_PRIORITY, /* Initial priority. */
_uavcan_thread, /* Thread function. */
this); /* Thread parameter. */
#endif
}
步骤2:
#if HAL_WITH_UAVCAN
void Scheduler::_uavcan_thread(void *arg)
{
Scheduler *sched = (Scheduler *)arg;
chRegSetThreadName("apm_uavcan");
while (!sched->_hal_initialized) {
sched->delay_microseconds(20000);
}
while (true) {
sched->delay_microseconds(300);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_NUMBER_OF_CAN_INTERFACES; i++) {
if (AP_UAVCAN::get_uavcan(i) != nullptr) {
CANManager::from(hal.can_mgr[i])->_timer_tick();
}
}
}
}
#endif
步骤3:
void CANManager::_timer_tick()
{
if (!initialized_) return;
if (p_uavcan != nullptr) {
p_uavcan->do_cyclic();
}
}
步骤4:
void AP_UAVCAN::do_cyclic(void)
{
if (!_initialized) {
hal.scheduler->delay_microseconds(1000);
return;
}
auto *node = get_node();
const int error = node->spin(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(1)); //注意这个函数
if (error < 0) {
hal.scheduler->delay_microseconds(100);
return;
}
if (_SRV_armed) {
bool sent_servos = false;
if (_servo_bm > 0) {
// if we have any Servos in bitmask
uint32_t now = AP_HAL::micros();
const uint32_t servo_period_us = 1000000UL / unsigned(_servo_rate_hz.get());
if (now - _SRV_last_send_us >= servo_period_us) {
_SRV_last_send_us = now;
SRV_send_servos();
sent_servos = true;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < UAVCAN_SRV_NUMBER; i++) {
_SRV_conf[i].servo_pending = false;
}
}
}
// if we have any ESC's in bitmask
if (_esc_bm > 0 && !sent_servos) {
SRV_send_esc();
}
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < UAVCAN_SRV_NUMBER; i++) {
_SRV_conf[i].esc_pending = false;
}
}
if (led_out_sem_take()) {
led_out_send();
led_out_sem_give();
}
}
步骤5:const int error = node->spin(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(1)); //注意这个函数
int spin(MonotonicDuration duration)
{
if (started_)
{
return INode::spin(duration);
}
return -ErrNotInited;
}
int spin(MonotonicDuration duration)
{
return getScheduler().spin(getMonotonicTime() + duration);
}
int Scheduler::spin(MonotonicTime deadline)
{
if (inside_spin_) // Preventing recursive calls
{
UAVCAN_ASSERT(0);
return -ErrRecursiveCall;
}
InsideSpinSetter iss(*this);
UAVCAN_ASSERT(inside_spin_);
int retval = 0;
while (true)
{
const MonotonicTime dl = computeDispatcherSpinDeadline(deadline);
retval = dispatcher_.spin(dl); //最终执行的地方
if (retval < 0)
{
break;
}
const MonotonicTime ts = deadline_scheduler_.pollAndGetMonotonicTime(getSystemClock());
pollCleanup(ts, unsigned(retval));
if (ts >= deadline)
{
break;
}
}
return retval;
}
int Dispatcher::spin(MonotonicTime deadline)
{
int num_frames_processed = 0;
do
{
CanIOFlags flags = 0;
CanRxFrame frame;
const int res = canio_.receive(frame, deadline, flags);
if (res < 0)
{
return res;
}
if (res > 0)
{
if (flags & CanIOFlagLoopback)
{
handleLoopbackFrame(frame);
}
else
{
num_frames_processed++;
handleFrame(frame); //处理
}
notifyRxFrameListener(frame, flags);
}
}
while (sysclock_.getMonotonic() < deadline);
return num_frames_processed;
}
步骤6:handleFrame(frame);
void Dispatcher::handleFrame(const CanRxFrame& can_frame)
{
RxFrame frame;
if (!frame.parse(can_frame)) //这里进行解析CAN数据
{
// This is not counted as a transport error
UAVCAN_TRACE("Dispatcher", "Invalid CAN frame received: %s", can_frame.toString().c_str());
return;
}
if ((frame.getDstNodeID() != NodeID::Broadcast) &&
(frame.getDstNodeID() != getNodeID()))
{
return;
}
switch (frame.getTransferType())
{
case TransferTypeMessageBroadcast:
{
lmsg_.handleFrame(frame); //数据广播
break;
}
case TransferTypeServiceRequest:
{
lsrv_req_.handleFrame(frame);
break;
}
case TransferTypeServiceResponse:
{
lsrv_resp_.handleFrame(frame);
break;
}
default:
{
UAVCAN_ASSERT(0);
break;
}
}
}
void Dispatcher::ListenerRegistry::handleFrame(const RxFrame& frame)
{
TransferListener* p = list_.get();
while (p)
{
TransferListener* const next = p->getNextListNode();
if (p->getDataTypeDescriptor().getID() == frame.getDataTypeID())
{
p->handleFrame(frame); // p may be modified,注意这个函数
}
else if (p->getDataTypeDescriptor().getID() < frame.getDataTypeID()) // Listeners are ordered by data type id!
{
break;
}
else
{
; // Nothing to do with this one
}
p = next;
}
}
void TransferListener::handleFrame(const RxFrame& frame)
{
if (frame.getSrcNodeID().isUnicast()) // Normal transfer
{
const TransferBufferManagerKey key(frame.getSrcNodeID(), frame.getTransferType());
TransferReceiver* recv = receivers_.access(key);
if (recv == UAVCAN_NULLPTR)
{
if (!frame.isStartOfTransfer())
{
return;
}
TransferReceiver new_recv;
recv = receivers_.insert(key, new_recv);
if (recv == UAVCAN_NULLPTR)
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("TransferListener", "Receiver registration failed; frame %s", frame.toString().c_str());
return;
}
}
TransferBufferAccessor tba(bufmgr_, key);
handleReception(*recv, frame, tba); //注意这个函数
}
else if (frame.getSrcNodeID().isBroadcast() &&
frame.isStartOfTransfer() &&
frame.isEndOfTransfer() &&
frame.getDstNodeID().isBroadcast()) // Anonymous transfer
{
handleAnonymousTransferReception(frame);
}
else
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("TransferListener", "Invalid frame: %s", frame.toString().c_str()); // Invalid frame
}
}
**步骤7:handleReception(*recv, frame, tba); **
void TransferListener::handleReception(TransferReceiver& receiver, const RxFrame& frame,
TransferBufferAccessor& tba)
{
switch (receiver.addFrame(frame, tba))
{
case TransferReceiver::ResultNotComplete:
{
perf_.addErrors(receiver.yieldErrorCount());
break;
}
case TransferReceiver::ResultSingleFrame:
{
perf_.addRxTransfer();
SingleFrameIncomingTransfer it(frame);
handleIncomingTransfer(it);
break;
}
case TransferReceiver::ResultComplete:
{
perf_.addRxTransfer();
const ITransferBuffer* tbb = tba.access();
if (tbb == UAVCAN_NULLPTR)
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("TransferListener", "Buffer access failure, last frame: %s", frame.toString().c_str());
break;
}
if (!checkPayloadCrc(receiver.getLastTransferCrc(), *tbb))
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("TransferListener", "CRC error, last frame: %s", frame.toString().c_str());
break;
}
MultiFrameIncomingTransfer it(receiver.getLastTransferTimestampMonotonic(),
receiver.getLastTransferTimestampUtc(), frame, tba);
handleIncomingTransfer(it);
it.release();
break;
}
default:
{
UAVCAN_ASSERT(0);
break;
}
}
}
步骤8:到这里我们需要注意的是handleIncomingTransfer(it);函数,是如何实现回调的
template
void GenericSubscriber::handleIncomingTransfer(IncomingTransfer& transfer)
{
ReceivedDataStructureSpec rx_struct(&transfer);
/*
* Decoding into the temporary storage
*/
BitStream bitstream(transfer);
ScalarCodec codec(bitstream);
const int decode_res = DataStruct::decode(rx_struct, codec);
// We don't need the data anymore, the memory can be reused from the callback:
transfer.release();
if (decode_res <= 0)
{
UAVCAN_TRACE("GenericSubscriber", "Unable to decode the message [%i] [%s]",
decode_res, DataSpec::getDataTypeFullName());
failure_count_++;
node_.getDispatcher().getTransferPerfCounter().addError();
return;
}
/*
* Invoking the callback,这里可以看到就是插入回调函数
*/
handleReceivedDataStruct(rx_struct);
}