第二章 Nginx服务器的安装部署【下】
概述:接着上一节
- 获取Nginx服务器安装文件的路径
- nginx服务器安装部署之前的准备工作
- Windows平台下nignx服务器的安装部署
- Linux平台下Nignx服务器的编译和安装
- 认识Nginx服务器的配置文件,以及如何进行基本配置
- 初步学习通过优化Nginx配置,提高Nginx服务器的性能
- 展示一个Nginx配置的完整实例
2.4、Nginx服务器基础配置指令
找安装配置文件, 安装目录根目录/conf/nginx.conf (这里取消注释部分)
worker_processes 1; #全局生效
events {
worker_connections 1024; #在Events部分中生效
}
http {
include mime.types; #以下指令在http部分中生效
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80; #以下指令在http的server部分中生效
server_name localhost;
location / { #以下指令在 http/server的location中生效
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
2.4.1、nginx.conf 文件的结构
... #全局块
events {
... #events块
}
http { # http块
... #http全局块
server { #server块
... #server全局块
location [PARTERN] { #location 块
}
location [PARTERN] { #location 块
}
}
server { #server块
... #server全局块
location [PARTERN] { #location 块
}
location [PARTERN] { #location 块
}
}
....
}2.4.1.1、全局块
全局变量, 通常配置Nginx服务器的用户(组)、允许生成的worker process数、Nginx进程PID存放路径,日志的存放路径和类型以及配置文件引入等
2.4.1.2、events块
指令主要影响Nginx服务器与用户的网络连接。常用设置开启多个工作进程在网络连接进行序列化,是否允许同时接收多个网络连接、事件模型类型、每个工作进程可以同时支持最大连接数量
2.4.1.3、http块
这是重要部分,代理,缓存,日志等
2.4.1.4、server块
这个与虚拟机有关,每个Server块就相当于一台虚拟主机
最常见配置 本虚拟主机的监听配置和本虚拟机主机的名称或IP配置
2.4.1.5、location块
一个server可以由多个location块,location类似Spring mapper映射一样
2.4.2、配置运行Nginx服务器用户(组)
语法:
user user [group];
user :指定可以运行Nginx服务器的用户
group 可选项,指定可以运行Nginx服务器的用户组
如果希望所有用户都可以启动服务
注释这条语句或者user nobody nobody; (注意以分号结尾)
2.4.3、配置允许生成的Worker process数
语法: worker-processes number | auto;
number ,指定Nginx进程最多可以产生的Worker process数 (默认值为1)
auto , 设置此值,Nginx进程将自动检测
2.4.4、配置Nginx进程PID存放路径
语法:pid file;
file: 指定存放路径和文件名称(默认值将此文件放置到安装目录/logs下,名字为nginx.pid,
例如: pid sbin/web_nginx (必须到文件)只能在全局块配置
2.4.5、配置错误日志的存放路径
语法:error_log file | stderr [debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit | alert | emerg
error_log logs/error.log error;
2.4.6、配置文件的引入
include file; (可以放置到任意位置)
file : 文件路径 (注意具有访问权限)
2.4.7、设置网络连接的序列化
accept_mutex on | off; 防止多个进程抢工作,直接序列化分配即可
2.4.8、设置是否允许同时接收多个网络连接
multi_accept on | off;
2.4.9、 事情驱动模型的选择
语法:use method (只能配置在events块中)
可选内容有,select、poll、kqueue、epoll、rtsig、/dev/poll 以及 eventport
2.4.10、配置最大连接数
worker_connections number; (只能event块中进行配置)
默认值为512
2.4.11、定义MIME-Type
include mime.types
default_type application/octet-stream; (如果不写默认是text/plain)
2.4.12、自定义服务日志
全局设置的是软件运行的日志
服务日志:提供服务的日志,
两个指令分别是access_log 和log_format指令
语法结构: access_log path[format [buffer=size]];
path: 配置服务日志的文件存放的路径和名称
format:可选项,自定义服务日志的格式字符串,也可以通过log_format设置
size, 配置临时存放日志的内存缓存区大小
这个指令可以配置到http块、server块或location块进行设置
例如:access_log logs/access.log combined; (combined是默认值日志格式字符串)
取消记录日志功能
access_log off;
语法: log_format name string ..; (只能在http块中配置)
name: 格式字符串的名称,默认的名字为combined
string: 服务日志的格式字符串。用$引用定义变量,单引号引用结果
log_format exampleLog '$remote_addr - [$time_local] $request ' '$status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer ' '$http_user_agent'
2.4.13、配置允许sendfile方式传输文件
sendfile on | off; 默认是off (可以在http块、server块或者 location块中进行配置)
sendfile_max_chunk size 分块的大小
例如: sendfile_max_chunk 128k;
2.4.14、配置用户连接超时时间
语法: keepalive_timeout timeout[header_timeout]; (可以在http块,server块或location块中配置)
timeout 服务端对连接保持的时间,默认值为75s;
header_time ,可选项,在应答报文头部的keep-alive域设置超时时间:“Keep-Alive:timeout=header_timeout”
keepalive_timeout 120s 100s;
2.4.15、单连接请求数上限
语法:keepalive_requests number; 默认值100, 单次连接最多可请求100次
2.4.16、配置网络监听
有三种方式:
第一种:listen address[:port] [default_server] [setfib=number] [backlog=number] [rcvbuf=size] [sndbuf=size] [deferred][accept_filter=filter][bind] [ssl];
第二种:listen port [default_server] [setfib=number] [backlog=number] [rcvbuf=size] [sndbuf=size] [deferred][accept_filter=filter][bind] [ssl];
第三种:listen unix:path [default_server] [setfib=number] [backlog=number] [rcvbuf=size] [sndbuf=size] [deferred][accept_filter=filter][bind] [ssl];
address, IP地址,如果是IPv6的地址,需要使用中括号“[]”括起来,比如[fe90::1]等
port:端口号,默认值80端口
path,socket文件路径,例如 /var/run/nginx.sock等
default_server, 标识符,将此虚拟机主机设置为address:port默认主机
setfib+number socket关联路由表
backlog=number 允许最多多少网络连接同时处于挂起状态
rcvbuf=size socket 接收缓存区大小
sndbuf=size socket发送缓存区大小
deferred: 将accept()设置为Deferred模式
accept_filter=filter 过滤连接
ssl ,标识符,设置ssl模式进行连接
默认配置:
listen *:80 | *:8000;
listen 192.168.1.10:8000; 监听具体IP,具体端口的连接
listen 192.168.1.10 default_server backlog=1024;(设置具体连接请求默认值由此虚拟主机处理,并且允许最多1024网络连接同时处于挂起状态)
2.4.17、基于名称的虚拟主机配置
语法:server_name name ...;
多个域名用空格分割
支持通配符
“~”作为正则表达式开头, “$”作为正则表达式结尾
例如: server_name ~^www\d+\.myserver\.com$;
匹配方式优先级:
- 准确匹配server_name
- 通配符在开始时匹配server_name成功
- 通配符在结尾时匹配server_name成功
- 正则表达式匹配server_name成功
2.4.18、基于IP的虚拟主机配置
Linux操作系统支持IP别名添加。配置基于IP的虚拟机,即为Nginx服务器提供的每台虚拟机配置一个不同的IP,因此需要将网卡设置为同时能够监听多个IP地址。
命令:ipconfig 显示ip配置信息
添加两个IP的别名 172.19.238.80 和 172.19.238.81
#ifconfig eth0:0 172.19.238.80 netmask 255.255.240.0 up
#ifconfig eth0:1 172.19.238.81 netmask 255.255.240.0 up
如上方法设置系统重启之后将不予保存,需要重新配置,为了完成一劳永逸
# echo "ifconfig eth0:0 172.19.238.80 netmask 255.255.240.0 up" >> /etc/rc.local
# echo "ifconfig eth0:1 172.19.238.81 netmask 255.255.240.0 up" >> /etc/rc.local
...
http {
...
server {
listen 80;
server_name 172.19.238.80;
...
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 172.19.238.81;
...
}
...
}
2.4.19 配置location块
语法结构: location [= | ~ | ~* | ^~] uri {....}
uri 变量是待匹配的请求字符串
“=” 用于标准uri前(不含正则表达式)
“~”, 用于表示正则表达式,并且区分大小写
"~*", 用于表示uri包含正则表达式,并且不区分大小写
“^~” 用于标准uri前
2.4.20、配置请求的根目录
语法: root path;
path 为Nginx服务器接收到请求以后查找资源的根目录路径。Path是预设变量, $document_root($符号引用)
例如
location /data/
{
root /locationtest1;
}2.4.21、更改location的URI
语法: alias path;
例子:
location ~ ^/data/(.+\.(htm|htm))$
{
alias /locationtest1/other/$1;
}
2.4.22、设置网站的默认首页
语法: index file ...; 默认值index.html
location ~ ^/data/(.+)/web/ $
{
index index.$1.html index.my1.html index.html;
}2.4.23、设置网站的错误页面
一般来说, HTTP 2XX 代表请求正常完成, HTTP3XX代表网站重定向, HTTP4XX代表客户端出现错误, HTTP 5XX代表服务器出现错误。
语法: error_page code ... [=[response]] uri
code 要处理HTTP错误代码
response 可选项将code指定的错误代码转化为新的错误代码reponse
uri 错误页面的路径或者网址 ,如果是路径是以nginx安装路径下html目录为根目录的相对目录
例如:
error_page 404 /404.html
error_page 403 http://somewebsite.com/forbidden.html;
希望nginx服务使用 "/myserver/errorpages/404.html" 页面响应404错误
error_page 404 / 404.html
之后添加location块
location /404.html
{
root /myserver/errorpages/ //重定向这个目录下
}
2.4.24、基于IP配置Nginx的访问权限
Nginx配置通过两种支持基本访问权限的控制,其中一种有HTTP标准模块ngx_http_access_module 支持的,通过IP来判断客户端是否拥有对Nginx的访问权限
allow address | CIDR | all;
address 允许访问的客户端IP,不允许同时设置多个,设置多个,使用多条allow指令
CIDR 允许访问的客户端的CIDR地址。 主机/端口, 201.80.12.20/80
all 代表允许所有客户端访问
现在也支持IPv6地址
另个指令deny ,禁止访问Nginx的客户端IP
语法:deny address | CIDR | all;
两个指令可以在http块、server块或者location块中配置
注意all用法
location / {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
deny all;
}2.4.25、基于密码配置Nginx的访问权限
Nginx还支持基于HTTPBasic Authentication协议认证,用于识别用户名和密码
由HTTP 标准模块ngx_http_auth_basic_module支持
auth_basic 指令,用于开启或关闭验证功能
语法:auth_basic string | off;
string 开启该认证,并配置验证时的指示信息
off, 关闭认证功能
auth_basic_user_file 指令, 用于设置包含用户名和密码信息的文件路径
语法: auth_basic_user_file file ;
file为文件的绝对路径
密码文件支持明文或者密文
明文的格式:
name1:password1
name2:password2:comment
name3:password3加密可以使用crypt()函数, 或者htpasswd命令生成。
如果没有htpasswd命令,需要安装httpd
# yum install -y httpd
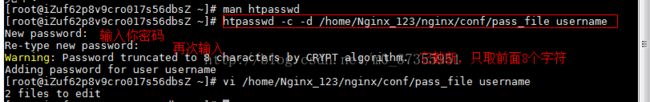
开始生成密码文件
# htpasswd -c -d /home/Nginx_123/nginx/conf/pass_file username
2.5、Nginx服务器基本配置实例
###全局块 开始 #####
user nobody nobody; #配置允许运行Nginx服务器的用户和用户组
worker_processes 3; #配置允许Nginx进程生成的Worker processes数
error_log logs/error.log; #配置Nginx服务器运行时错误日志存放路径
pid nginx.pid; # 配置Nginx服务器运行时的pid文件存放路径和名称
###全局块 结束 ####
####events 块 开始 ####
events {
use epoll; # 配置事件驱动模型
worker_connections 1024; #配置最大连接数量
}
### events块 结束 ###
### http 块 开始 ####
http {
include mime.types; # 定义MIME-Type
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on; #配置允许使用sendfile方式传输
keepalive_timeout 65; #配置连接超时时间
log_format access.log '$remote_addr-[$time_local]-"$request"-"$http_user_agent"';
#### server 块 开始 ####
##配置 虚拟主机 myserver1
server{
listen 8081; # 配置监听端口和主机名称(基于名称)
server_name myServer1;
access_log /myweb/server1/log/access.log; #配置请求处理日志存放路径
error_page 404 /404.html; # 配置错误页面
location /server1/location1 { # 配置处理/server1/location1请求的location
root /myweb;
index index.svr1-locl.htm;
}
location /server1/location2 { # 配置处理/server1/location2请求的location
root /myweb;
index index.svr1-loc2.htm;
}
}
##配置 虚拟主机 myserver2
server{
listen 8082; # 配置监听端口和主机IP(基于IP)
server_name 192.168.1.2;
access_log /myweb/server2/log/access.log; #配置请求处理日志存放路径
error_page 404 /404.html; # 配置错误页面
location /server2/location1 { # 配置处理/server2/location1请求的location
root /myweb;
index index.svr2-locl.htm;
}
location /svr2/loc2 { # 配置location的URI进行更改
alias /myweb/server2/location2/;
index index.svr2-loc2.htm;
}
location = /404.html {
root /myweb/;
index 404.html;
}
}
#### server块 结束 ####
}
#### http 块 结束 ####语法: auth_basic_user_file file ;
file为文件的绝对路径
密码文件支持明文或者密文
明文的格式: