莫烦PyTorch学习笔记(三)——分类
本文主要是用PyTorch来实现一个简单的分类任务。
编辑器:spyder
1.引入相应的包及建立数据集
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# make fake data
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
# torch can only train on Variable, so convert them to Variable
x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
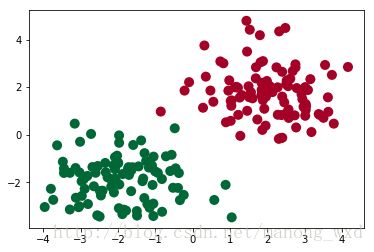
# draw the data
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
plt.show()torch.normal()在这里返回的是大小为100x2的Tensor,每个元素的标准差为1(通过normal的第二个参数设置获得)。torch.cat()拼接Tensor,第二个参数表示拼接的维度。0表示为按纵向拼接,这里拼接后的大小为400x2,1表示横向拼接,该参数默认为0。
输入模型的数据应该是浮点型,类别标签为整型。这里通过type()进行设置。
2.建立神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer
x = self.out(x)
return x
net = Net(n_feature=2, n_hidden=10, n_output=2) # define the network
print(net) # net architecture这里的网络跟前一篇回归中的是一样的,只不过输入输出的维度发生了点变化。
Net (
(hidden): Linear (2 -> 10)
(out): Linear (10 -> 2)
)3.训练网络
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
for t in range(100):
out = net(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(out, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target), the target label is NOT one-hotted
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients在这里我们是进行分类任务,所以我们采用交叉熵torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()作为损失函数。损失函数中包含了LogSoftMax的计算,所以直接将网络全连接层的输出输进损失函数即可。其内部运行原理见下式:
loss(x, class) = -log(exp(x[class]) / (\sum_j exp(x[j])))
= -x[class] + log(\sum_j exp(x[j]))4.可视化训练过程
plt.ion() # something about plotting
for t in range(100):
...
if t % 2 == 0:
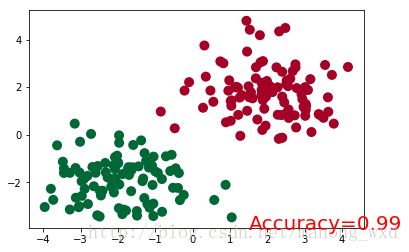
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(F.softmax(out), 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy().squeeze()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = sum(pred_y == target_y)/200.
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()torch.max()返回的是两个Variable,第一个Variable存的是最大值,第二个存的是其对应的位置索引index。这里我们想要得到的是索引,所以后面用[1]。