Netty4(二)服务端和客户端实现
本文介绍netty4实现的服务端和单连接客户端,并实现通信
- 目标
- 代码UML类图
- 服务端
- 客户端
- Netty4实现服务端
- Netty4实现客户端
- 测试
- 小结
目标
用netty4实现一个服务端和客户端,两者之间可以进行测试通信
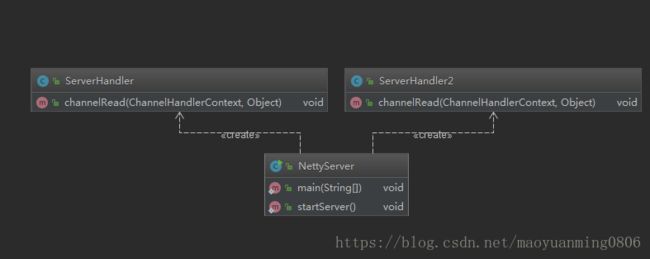
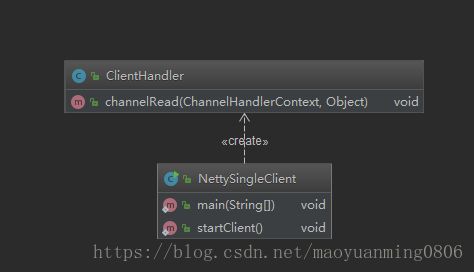
代码UML类图
服务端
客户端
Netty4实现服务端
服务类
package com.mym.netty.server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
/**
* netty服务端
*/
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
startServer();
}
public static void startServer(){
//1.定义server启动类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//2.定义工作组:boss分发请求给各个worker:boss负责监听端口请求,worker负责处理请求(读写)
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//3.定义工作组
serverBootstrap.group(boss,worker);
//4.设置通道channel
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);//A
//serverBootstrap.channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory(NioServerSocketChannel.class));//旧版本的写法,但是此过程在A中有同样过程
//5.添加handler,管道中的处理器,通过ChannelInitializer来构造
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
//此方法每次客户端连接都会调用,是为通道初始化的方法
//获得通道channel中的管道链(执行链、handler链)
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("serverHandler1",new ServerHandler());
pipeline.addLast("serverHandler2",new ServerHandler2());
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());
System.out.println("success to initHandler!");
}
});
//6.设置参数
//设置参数,TCP参数
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 2048); //连接缓冲池的大小
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);//维持链接的活跃,清除死链接
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);//关闭延迟发送
//7.绑定ip和port
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind("0.0.0.0", 9099).sync();//Future模式的channel对象
//7.5.监听关闭
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); //等待服务关闭,关闭后应该释放资源
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("server start got exception!");
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//8.优雅的关闭资源
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
Handler1
package com.mym.netty.server;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/*
* ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter:ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter是ChannelInboundHandler的一个简单实现,默认情况下不会做任何处理,
* 只是简单的将操作通过fire*方法传递到ChannelPipeline中的下一个ChannelHandler中让链中的下一个ChannelHandler去处理。
*
* SimpleChannelInboundHandler:SimpleChannelInboundHandler支持泛型的消息处理,默认情况下消息处理完将会被自动释放,无法提供
* fire*方法传递给ChannelPipeline中的下一个ChannelHandler,如果想要传递给下一个ChannelHandler需要调用ReferenceCountUtil#retain方法。
* */
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("ServerHandler receive msg:"+msg.toString());
//写消息:先得到channel,在写如通道然后flush刷新通道把消息发出去。
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("this is ServerHandler reply msg happend at !"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//把消息往下一个Handler传
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}Handler2
package com.mym.netty.server;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class ServerHandler2 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("ServerHandler2 receive msg:"+msg.toString());
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("this is ServerHandler2 reply msg happend at !"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}Netty4实现客户端
客户端服务类
package com.mym.netty.client;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* netty客户端
*/
public class NettySingleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
startClient();
}
public static void startClient(){
//1.定义服务类
Bootstrap clientBootstap = new Bootstrap();
//2.定义执行线程组
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//3.设置线程池
clientBootstap.group(worker);
//4.设置通道
clientBootstap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
//5.添加Handler
clientBootstap.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client channel init!");
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("StringDecoder",new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("StringEncoder",new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("ClientHandler",new ClientHandler());
}
});
//6.建立连接
ChannelFuture channelFuture = clientBootstap.connect("0.0.0.0",9099);
try {
//7.测试输入
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while(true){
System.out.println("请输入:");
String msg = bufferedReader.readLine();
channelFuture.channel().writeAndFlush(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//8.关闭连接
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
} 客户端的handler
package com.mym.netty.client;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client receive msg:"+msg.toString());
}
}测试
启动服务端和客户端后,客户端发送nihao!服务端回应,然后客户端发送hello,服务端回应。
服务端输出
success to initHandler!
ServerHandler receive msg:nihao!
ServerHandler2 receive msg:nihao!
ServerHandler receive msg:hello
ServerHandler2 receive msg:hello客户端输出
client channel init!
请输入:
nihao!
请输入:
client receive msg:this is ServerHandler reply msg happend at !1531893027697this is ServerHandler2 reply msg happend at !1531893027698
hello
请输入:
client receive msg:this is ServerHandler reply msg happend at !1531893045446this is ServerHandler2 reply msg happend at !1531893045447小结
需要注意的是,服务端和客户端除了启动类和socket channel不一样以外,其他几乎一致的操作。
本文的客户端是单连接,下文将介绍多连接客户端的操作。