JavaFX官方教程(十二)之树动画示例
翻译自 树动画示例
本章提供有关树动画示例的详细信息。您将了解场景中的所有元素是如何创建和动画的。
图4-1显示了带树的场景。
图4-1树动画
项目和要素
树动画项目由几个文件组成。每个元素,如树叶,草叶等,都是在不同的类中创建的。在TreeGenerator类创建的所有元素的树。本Animator类包含了除驻留在草地动画所有动画GrassWindAnimation类。
示例中的场景包含以下元素:
-
与分支,叶子和花的树
-
草
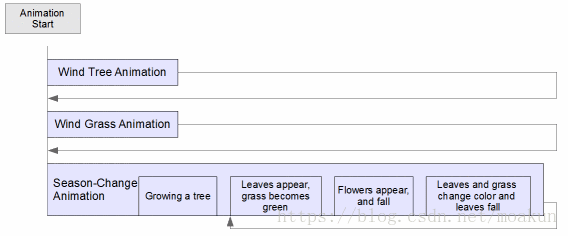
每个元素都以自己的方式进行动画处理。一些动画并行运行,其他动画按顺序运行。树木生长动画仅运行一次,而季节变化动画设置为无限运行。
图4-2动画时间轴
季节变化动画包括以下部分:
-
叶子和花朵出现在树上
-
花瓣落下并消失
-
叶子和草改变颜色
-
叶子落到地上消失
草
本节介绍草的创建和动画。
创造草
在树动画示例中,如图4-3所示,草由单独的草叶片组成,每个草叶片都使用Path并添加到列表中。然后每个刀片弯曲并着色。算法用于随机化叶片的高度,曲线和颜色,并将叶片分布在“地面”上。您可以指定刀片的数量和草覆盖的“地面”的大小。
图4-3草
例4-1创建草刀片
public class Blade extends Path {
public final Color SPRING_COLOR = Color.color(random() * 0.5, random() * 0.5
+ 0.5, 0.).darker();
public final Color AUTUMN_COLOR = Color.color(random() * 0.4 + 0.3, random()
* 0.1 + 0.4, random() * 0.2);
private final static double width = 3;
private double x = RandomUtil.getRandom(170);
private double y = RandomUtil.getRandom(20) + 20;
private double h = (50 * 1.5 - y / 2) * RandomUtil.getRandom(0.3);
public SimpleDoubleProperty phase = new SimpleDoubleProperty();
public Blade() {
getElements().add(new MoveTo(0, 0));
final QuadCurveTo curve1;
final QuadCurveTo curve2;
getElements().add(curve1 = new QuadCurveTo(-10, h, h / 4, h));
getElements().add(curve2 = new QuadCurveTo(-10, h, width, 0));
setFill(AUTUMN_COLOR); //autumn color of blade
setStroke(null);
getTransforms().addAll(Transform.translate(x, y));
curve1.yProperty().bind(new DoubleBinding() {
{
super.bind(curve1.xProperty());
}
@Override
protected double computeValue() {
final double xx0 = curve1.xProperty().get();
return Math.sqrt(h * h - xx0 * xx0);
}
}); //path of top of blade is circle
//code to bend blade
curve1.controlYProperty().bind(curve1.yProperty().add(-h / 4));
curve2.controlYProperty().bind(curve1.yProperty().add(-h / 4));
curve1.xProperty().bind(new DoubleBinding() {
final double rand = RandomUtil.getRandom(PI / 4);
{
super.bind(phase);
}
@Override
protected double computeValue() {
return (h / 4) + ((cos(phase.get() + (x + 400.) * PI / 1600 +
rand) + 1) / 2.) * (-3. / 4) * h;
}
});
}
}
为草运动创建时间轴动画
更改刀片顶部x坐标的时间轴动画用于创建草运动。
使用了几种算法使运动看起来很自然。例如,每个叶片的顶部以圆形而不是直线移动,并且叶片的侧面曲线使叶片看起来好像在风下弯曲。添加随机数以分离每个刀片运动。
例4-2草动画
class GrassWindAnimation extends Transition {
final private Duration animationTime = Duration.seconds(3);
final private DoubleProperty phase = new SimpleDoubleProperty(0);
final private Timeline tl = new Timeline(Animation.INDEFINITE);
public GrassWindAnimation(List blades) {
setCycleCount(Animation.INDEFINITE);
setInterpolator(Interpolator.LINEAR);
setCycleDuration(animationTime);
for (Blade blade : blades) {
blade.phase.bind(phase);
}
}
@Override
protected void interpolate(double frac) {
phase.set(frac * 2 * PI);
}
}
树
本节介绍如何创建和动画图4-4中显示的树。
图4-4树
分行
树由树枝,树叶和花组成。叶子和花朵画在树顶的树枝上。每个分支生成包括从父分支绘制的三个分支(一个顶部分支和两个侧分支)。您可以使用NUMBER_OF_BRANCH_GENERATIONSMain类中TreeGenerator的构造函数中传递的代码指定代数。例4-3显示了TreeGenerator类中的代码,该代码创建了树的树干(或根分支),并为后续代添加了三个分支。
例4-3根分支
private List generateBranches(Branch parentBranch, int depth) {
List branches = new ArrayList<>();
if (parentBranch == null) { // add root branch
branches.add(new Branch());
} else {
if (parentBranch.length < 10) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
branches.add(new Branch(parentBranch, Type.LEFT, depth));
branches.add(new Branch(parentBranch, Type.RIGHT, depth));
branches.add(new Branch(parentBranch, Type.TOP, depth));
}
return branches;
} 为了使树看起来更自然,每个子代生成分支以与父分支成一定角度生长,并且每个子分支小于其父分支。子角度使用随机值计算。例4-4提供了用于创建子分支的代码。
例4-4子分支
public Branch(Branch parentBranch, Type type, int depth) {
this();
SimpleDoubleProperty locAngle = new SimpleDoubleProperty(0);
globalAngle.bind(locAngle.add(parentBranch.globalAngle.get()));
double transY = 0;
switch (type) {
case TOP:
transY = parentBranch.length;
length = parentBranch.length * 0.8;
locAngle.set(getRandom(10));
break;
case LEFT:
case RIGHT:
transY = parentBranch.length - getGaussianRandom(0,
parentBranch.length, parentBranch.length / 10, parentBranch.length / 10);
locAngle.set(getGaussianRandom(35, 10) * (Type.LEFT == type ? 1 :
-1));
if ((0 > globalAngle.get() || globalAngle.get() > 180) && depth <
4) {
length = parentBranch.length * getGaussianRandom(0.3, 0.1);
} else {
length = parentBranch.length * 0.6;
}
break;
}
setTranslateY(transY);
getTransforms().add(new Rotate(locAngle.get(), 0, 0));
globalH = getTranslateY() * cos(PI / 2 - parentBranch.globalAngle.get() *
PI / 180) + parentBranch.globalH;
setBranchStyle(depth);
addChildToParent(parentBranch, this);
}
叶子和花
叶子在顶部树枝上创建。因为叶子是与树的分支同时创建的,所以叶子被缩放为0 leaf.setScaleX(0)并leaf.setScaleY(0)在树生长之前隐藏它们,如例4-5所示。当它们落下时,使用相同的技巧来隐藏树叶。为了营造更自然的外观,树叶的绿色色调略有不同。此外,叶子颜色根据叶子的位置而变化; 较深的色调应用于位于树冠中部下方的叶子。
例4-5叶形和放置
public class Leaf extends Ellipse {
public final Color AUTUMN_COLOR;
private final int N = 5;
private List petals = new ArrayList<>(2 * N + 1);
public Leaf(Branch parentBranch) {
super(0, parentBranch.length / 2., 2, parentBranch.length / 2.);
setScaleX(0);
setScaleY(0);
double rand = random() * 0.5 + 0.3;
AUTUMN_COLOR = Color.color(random() * 0.1 + 0.8, rand, rand / 2);
Color color = new Color(random() * 0.5, random() * 0.5 + 0.5, 0, 1);
if (parentBranch.globalH < 400 && random() < 0.8) { //bottom leaf is darker
color = color.darker();
}
setFill(color);
}
} Flower在Flower类中创建,然后添加到TreeGenerator类中树的顶部分支。您可以指定花朵中的花瓣数量。花瓣是分布在圆圈中的椭圆,有些重叠。与草和叶子类似,花瓣以不同深浅的粉红色着色。
动画树元素
本节介绍树动画示例中用于为树和季节更改设置动画的技术。并行转换用于启动场景中的所有动画,如例4-6所示。
例4-6主要动画
final Transition all = new ParallelTransition(new GrassWindAnimation(grass),
treeWindAnimation, new SequentialTransition(branchGrowingAnimation,
seasonsAnimation(tree, grass)));
all.play();
种树
树生长动画仅在树动画示例的开头运行一次。应用程序启动顺序转换动画,以便一个接一个地生成分支,如例4-7所示。最初长度设置为0.根分支大小和角度在TreeGenerator类中指定。目前,每一代都在两秒钟内生长。
例4-7开始分支增长动画的顺序转换
SequentialTransition branchGrowingAnimation = new SequentialTransition();例4-8中的代码创建了树增长动画:
例4-8分支增长动画
private Animation animateBranchGrowing(List branchGeneration) {
ParallelTransition sameDepthBranchAnimation = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Branch branch : branchGeneration) {
Timeline branchGrowingAnimation = new Timeline(new KeyFrame(duration,
new KeyValue(branch.base.endYProperty(), branch.length)));
PauseTransition pauseTransition = new PauseTransition();
pauseTransition.setOnFinished(t -> branch.base.setStrokeWidth(branch.length / 25));
sameDepthBranchAnimation.getChildren().add(
new SequentialTransition(
pauseTransition,
branchGrowingAnimation));
}
return sameDepthBranchAnimation;
} 因为所有分支线都是同时计算和创建的,所以它们可以作为点出现在场景中。代码引入了一些技巧来隐藏线条之前的线条。在示例中,代码duration.one millisecond暂停转换的时间不明显。在例4-9中,base.setStrokeWidth(0)代码在每代生成动画动画之前将分支宽度设置为0。
例4-9树木生长动画优化
private void setBranchStyle(int depth) {
base.setStroke(Color.color(0.4, 0.1, 0.1, 1));
if (depth < 5) {
base.setStrokeLineJoin(StrokeLineJoin.ROUND);
base.setStrokeLineCap(StrokeLineCap.ROUND);
}
base.setStrokeWidth(0);
}
}
创造树冠运动
在种植树的同时,风动画开始了。树枝,树叶和花朵在一起移动。
树风动画类似于草动画动画,但它更简单,因为只有树枝的角度改变。为了使树木运动看起来自然,不同分支世代的弯曲角度是不同的。分支的生成越高(分支越小),弯曲的越多。例4-10提供了风动画的代码。
例4-10风动画
private Animation animateTreeWind(List branchGeneration, int depth) {
ParallelTransition wind = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Branch brunch : branchGeneration) {
final Rotate rotation = new Rotate(0);
brunch.getTransforms().add(rotation);
Timeline windTimeline = new Timeline(new KeyFrame(WIND_CYCLE_DURATION,
new KeyValue(rotation.angleProperty(), depth * 2)));
windTimeline.setAutoReverse(true);
windTimeline.setCycleCount(Animation.INDEFINITE);
wind.getChildren().add(windTimeline);
}
return wind;
}
动画季节变化
季节变化动画实际上是在树长大后开始的,并且无限运行。示例4-11中的代码调用所有季节动画:
例4-11开始季节动画
private Transition seasonsAnimation(final Tree tree, final List grass) {
Transition spring = animateSpring(tree.leafage, grass);
Transition flowers = animateFlowers(tree.flowers);
Transition autumn = animateAutumn(tree.leafage, grass);
SequentialTransition sequentialTransition = new SequentialTransition(spring, flowers, autumn);
return sequentialTransition;
}
private Transition animateSpring(List leafage, List grass) {
ParallelTransition springAnimation = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Blade blade : grass) {
springAnimation.getChildren().add(new FillTransition(GRASS_BECOME_GREEN_DURATION, blade,
(Color) blade.getFill(), blade.SPRING_COLOR));
}
for (Leaf leaf : leafage) {
ScaleTransition leafageAppear = new ScaleTransition(LEAF_APPEARING_DURATION, leaf);
leafageAppear.setToX(1);
leafageAppear.setToY(1);
springAnimation.getChildren().add(leafageAppear);
}
return springAnimation;
} 一旦所有树枝生长,叶片开始按照例4-12中的指示出现。
示例4-12启动Spring动画和显示叶子的并行转换
private Transition animateSpring(List leafage, List grass) {
ParallelTransition springAnimation = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Blade blade : grass) {
springAnimation.getChildren().add(new FillTransition(GRASS_BECOME_GREEN_DURATION, blade,
(Color) blade.getFill(), blade.SPRING_COLOR));
}
for (Leaf leaf : leafage) {
ScaleTransition leafageAppear = new ScaleTransition(LEAF_APPEARING_DURATION, leaf);
leafageAppear.setToX(1);
leafageAppear.setToY(1);
springAnimation.getChildren().add(leafageAppear);
}
return springAnimation;
} 当所有叶子都可见时,花开始出现,如例4-13所示。顺序过渡用于逐渐显示花朵。花外观的延迟在例4-13的顺序转换代码中设定。花只出现在树冠上。
例4-13显示鲜花
private Transition animateFlowers(List flowers) {
ParallelTransition flowersAppearAndFallDown = new ParallelTransition();
for (int i = 0; i < flowers.size(); i++) {
final Flower flower = flowers.get(i);
for (Ellipse pental : flower.getPetals()) {
FadeTransition flowerAppear = new FadeTransition(FLOWER_APPEARING_DURATION, petal);
flowerAppear.setToValue(1);
flowerAppear.setDelay(FLOWER_APPEARING_DURATION.divide(3).multiply(i + 1));
flowersAppearAndFallDown.getChildren().add(new SequentialTransition(new SequentialTransition(
flowerAppear,
fakeFallDownAnimation(petal))));
}
}
return flowersAppearAndFallDown;
} 一旦所有花朵出现在屏幕上,它们的花瓣就会开始下降。在示例4-14的代码中,鲜花被复制,并且隐藏了第一组鲜花以便稍后显示。
例4-14复制花瓣
private Ellipse copyEllipse(Ellipse petalOld, Color color) {
Ellipse ellipse = new Ellipse();
ellipse.setRadiusX(petalOld.getRadiusX());
ellipse.setRadiusY(petalOld.getRadiusY());
if (color == null) {
ellipse.setFill(petalOld.getFill());
} else {
ellipse.setFill(color);
}
ellipse.setRotate(petalOld.getRotate());
ellipse.setOpacity(0);
return ellipse;
}复制的花瓣开始逐一落到地上,如例4-15所示。花瓣在地面上五秒后消失。花瓣的下落轨迹不是直线,而是计算出的正弦曲线,因此花瓣似乎在它们落下时旋转。
实施例4-15脱落花
Animation fakeLeafageDown = fakeFallDownEllipseAnimation(leaf, leaf.AUTUMN_COLOR,
node -> {
node.setScaleX(0);
node.setScaleY(0);
});当所有的花朵从场景中消失时,下一季的变化就开始了。叶子和草变黄,叶子落下并消失。实施例4-15中使用的相同算法使花瓣落下用于显示落叶。例4-16中的代码启用了秋季动画。
例4-16动画秋季变化的动画
private Transition animateAutumn(List leafage, List grass) {
ParallelTransition autumn = new ParallelTransition();
ParallelTransition yellowLeafage = new ParallelTransition();
ParallelTransition dissappearLeafage = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Leaf leaf : leafage) {
final FillTransition toYellow =
new FillTransition(LEAF_BECOME_YELLOW_DURATION, leaf, null, leaf.AUTUMN_COLOR);
Animation fakeLeafageDown = fakeFallDownEllipseAnimation(leaf,
leaf.AUTUMN_COLOR,node -> {
node.setScaleX(0);
node.setScaleY(0);
});
dissappearLeafage.getChildren().add(fakeLeafageDown);
}
ParallelTransition grassBecomeYellowAnimation = new ParallelTransition();
for (final Blade blade : grass) {
final FillTransition toYellow =new
FillTransition(GRASS_BECOME_YELLOW_DURATION, blade, (Color) blade.getFill(),
blade.AUTUMN_COLOR);
toYellow.setDelay(Duration.seconds(1 * random()));
grassBecomeYellowAnimation.getChildren().add(toYellow);
}
autumn.getChildren().addAll(grassBecomeYellowAnimation, new
SequentialTransition(yellowLeafage, dissappearLeafage));
return autumn;
} 在所有叶子从地面消失之后,春天动画开始时将草绿色着色并显示叶子。
应用文件
NetBeans项目
-
tree_animation.zip