Netty框架使用
前言
首先在使用Netty框架的时候需要了解Netty是一个什么东西。
- Netty是由JBOSS提供的一个java开源框架。Netty提供异步的、事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具,用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序。也就是说,Netty 是一个基于NIO的客户、服务器端编程框架。
- 使用Netty 可以确保你快速和简单的开发出一个网络应用,例如实现了某种协议的客户,服务端应用。Netty相当简化和流线化了网络应用的编程开发过程,例如,TCP和UDP的socket服务开发。
- “快速”和“简单”并不用产生维护性或性能上的问题。Netty 是一个吸收了多种协议的实现经验,这些协议包括FTP,SMTP,HTTP,各种二进制,文本协议,并经过相当精心设计的项目,最终,Netty 成功的找到了一种方式,在保证易于开发的同时还保证了其应用的性能,稳定性和伸缩性。
下面就来看看第一个使用Netty搭建的应用
一、开发环境
首先我们需要准备对应的全套的Netty的jar包,这些可以参考Netty的官方网站
Netty的官网是:http://netty.io
当然也可以访问第三方的中文网站 http://ifeve.com/netty5-user-guide/
准备Netty4+
Eclipse或者IDEA
我这里使用的是IDEA
Netty客户端和服务器端描述
一般情况下,在实际使用的时候更多的关注于服务器端的开发,而很少关注客户端的开发,因为对于不同的业务逻辑会有不同的客户端实现,但是对于这些客户端来说服务器端只有一个。服务器会写数据到客户端并且处理多个客户端的并发连接。从理论上来说,限制程序性能的因素只有系统资源和JVM。为了方便理解,这里举了个生活例子,在山谷或高山上大声喊,你会听见回声,回声是山返回的;
在这个例子中,你是客户端,山是服务器。喊的行为就类似于一个Netty客户端将数据发送到服务器,听到回声就类似于服务器将相同的数据返回给你,你离开山谷就断开了连接,但是你可以返回进行重连服务器并且可以发送更多的数据。
逻辑分析
首先Netty是一个网络框架,所以说就要涉及到客户端和服务器端,这样的话就需要分析一下客户端和服务器端各自具有什么样子的作用,根据具体的作用设计对应的代码。
- 客户端连接到服务器
- 建立连接后,发送或接收数据
- 服务器处理所有的客户端连接
这个是建立一个网络应用必须的三个步骤。下面就是具体的按照这三个步骤编写
开始创建应用
首先创建一个服务器端的程序代码如下
服务器端代码
public class ServerHelloWorld {
//创建线程组,监听客户端的请求
private EventLoopGroup acceptorGroup = null;
//处理客户端相关操作线程组,负责处理与客户端端的请求操作。
private EventLoopGroup clientGroup = null;
//服务器启动相关配置信息
private ServerBootstrap bootstrap = null;
public ServerHelloWorld() {
init();
}
//初始化
private void init() {
//初始化线程组
acceptorGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//处理客户端逻辑
clientGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//初始化配置信息
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//绑定监听线程组
bootstrap.group(acceptorGroup, clientGroup);
//设置通信模式为NIO模式同步非阻塞
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
//设定缓存区的大小,单位是字节
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
//SO_SNDBUF 表示发送缓冲区,SO_RCVBUF 表示接收缓存区,SO_KEEPALIVE 表示是否开启心跳检查,保证连接有效
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 16 * 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 16 * 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
}
/**
* 监听处理逻辑
* @param port 监听端口
* @param acceptorHandlers 处理器
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public ChannelFuture doAccept(int port, final ChannelHandler... acceptorHandlers) throws InterruptedException {
/**
* childHandler 是服务端的BootStrap独有的方法是用于提供处理对象,提供处理对象可以一次性的增加若干个处理逻辑
* 类似责任链模式的处理逻辑,也就是说你增加A 和B两个处理逻辑,在处理逻辑的时候会按照A 和 B 的顺序进行依次处理
*
* ChannelInitializer 用于提供处理器的一个模型对象,这个模型对象,其中定义了一个方法initChannel
*
* initChannel 这个方法适用于初始化处理逻辑责任链条的。可以保证服务端的BootStrap只初始化一次处理器,尽量提供处理器的重用,
* 减少了反复创建处理器的操作
*/
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(acceptorHandlers);
}
});
/**
* bind 方法 用来绑定处理端口,ServerBootstrap可以绑定多个监听端口。多次调用bind方法即可
*
* sync 方法开始启动监听逻辑,返回ChannelFuture 返回结果是监听成功后的未来结果,可以使用
* 这个ChannelFuture实现后续的服务器与客户端的交互所以要获取这个ChannelFuture对象
*/
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
//ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
//ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
return future;
}
/**
* 回收方法
* shutdownGracefully 是一个安全关闭的方法,可以保证不放弃任何一个以接收的客户端请求
*/
public void release(){
this.acceptorGroup.shutdownGracefully();
this.clientGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChannelFuture future = null;
ServerHelloWorld server = null;
try{
server = new ServerHelloWorld();
//建立连接
future = server.doAccept(8081, new ServerHandler());
System.out.println("server started.");
//关闭连接,回收资源
future.channel().closeFuture();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (null != future){
try {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (null!=server){
server.release();
}
}
}
}
对于服务器端的程序来说,创建了两个线程组EventLoopGroup,这里需要通过原理图来详细的说明一下。
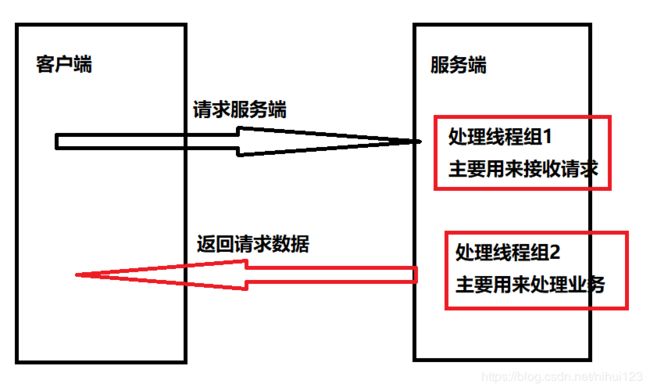
首先对于上面的图来说我们可以看到,在服务器端创建了两个线程组,这个两个线程组一个用来接收请求,一个用来处理业务逻辑,之前提到Netty是使用NIO来设计的,也就是说是同步非阻塞的一种IO。对于NIO、AIO、BIO等来说这些概念在后面的更新中会有总结到,现在就是简单的提供这样的一个概念。
在建立服务器端的时候,会看到一个ServerBootstrap 对象,这个表示服务器端,当然在客户端有一个与这个类对等的类BootStrap类,这两个类为链接的建立提供了很多的配置项信息。
服务端业务处理逻辑
**
*
* @ChannelHandler.Sharable 这个注解表示当前是一个可以分享的处理器,,服务注册此Handler,可以分享给多个客户端使用
* 如果不使用这个注解的话,每次客户端请求时,必须为客户端重新创建一个新的处理器Handler对象
*
* bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
* @Override
* protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
* ch.pipeline().addLast(new XXXHandler());
* }
* });
* 建议自己开发的时候就会使的Handler是可共享的
*
* 如果Handler是一个可分享的,一定避免定义一个可以写的实例变量。不安全
*
*/
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 业务处理逻辑 用于处理读取数据请求的逻辑。它里面的方法和参数如下
* @param ctx 上下文对象,其中包含于客户端建立连接的所有资源,比如说对应的Channel
* @param msg 读取到的数据,默认类型是bytebuf 这个ByteBuf 是对ByteBuffer的一个封装。简化了操作
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//强制类型转换
ByteBuf readBuffer = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 创建一个字节数组,用于保存缓存中的数据。readableBytes 在原生的ByteBuffer也有同样的功能的方法
byte[] tempDatas = new byte[readBuffer.readableBytes()];
//读取到对应的数据 可以直接读取,这个不需要考虑复位的问题,
readBuffer.readBytes(tempDatas);
String message = new String(tempDatas,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("from client :"+message);
if ("exit".equals(message)){
//如果客户端断开连接,则关闭上下文
ctx.close();
return;
}
String line = "server message to client!";
//写操作自动释放缓存,避免内存溢出的问题。
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8")));
/**
* 如果调用的是write方法,不会刷新缓存,缓存中的数据不会发送到客户端,必须调用flush方法进行强制刷出
* ctx.write(msg);
* ctx.flush();
*/
}
/**
* 异常处理逻辑
* ChannelHandlerContext关闭代表当前与客户端的连接处理逻辑,当客户端异常退出的时候这个异常也会执行
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server exceptionCaught method run …… ");
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端代码
public class ClientHelloWorld {
//处理请求线程组
private EventLoopGroup group = null;
//服务启动相关配置信息
private Bootstrap bootstrap = null;
public ClientHelloWorld(){
init();
}
private void init(){
group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//定义线程组
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
}
public ChannelFuture doRequest(String host, int port, final ChannelHandler ... handlers) throws InterruptedException {
this.bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
/**
* 客户端的Handler没有childHandler方法,只有Handler方法
* 这个方法与服务器的方法是类似的。
* 客户端必须绑定处理器,也就说必须调用Handler方法
* @param ch
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(handlers);
}
});
//建立连接
ChannelFuture future = this.bootstrap.connect(host,port).sync();
return future;
}
public void release(){
this.group.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClientHelloWorld client = null;
ChannelFuture future = null;
try{
client = new ClientHelloWorld();
future = client.doRequest("localhost",8081,new ClientHandler());
Scanner scanner = null;
while (true){
scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter message send to server (enter exit close client)");
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if ("exit".equals(line)){
future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8"))).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
break;
}
future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8")));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (null!=client){
client.release();
}
if (null!=future){
try {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
客户端逻辑处理逻辑
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
//强制类型转换
ByteBuf readBuffer = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 创建一个字节数组,用于保存缓存中的数据。readableBytes 在原生的ByteBuffer也有同样的功能的方法
byte[] tempDatas = new byte[readBuffer.readableBytes()];
//读取到对应的数据 可以直接读取,这个不需要考虑复位的问题,
readBuffer.readBytes(tempDatas);
System.out.println("from server " + new String(tempDatas, "UTF-8"));
}finally {
//用于避免内存溢出
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptionCaught method run …… ");
ctx.close();
}
}
总结
Netty是一个比较高效的网络应用框架,在很多的项目中都使用到了Netty。弥补了原生的的IO的很多的缺陷,但是也有很多不足的地方,需要更具具体的使用情况进行开发。