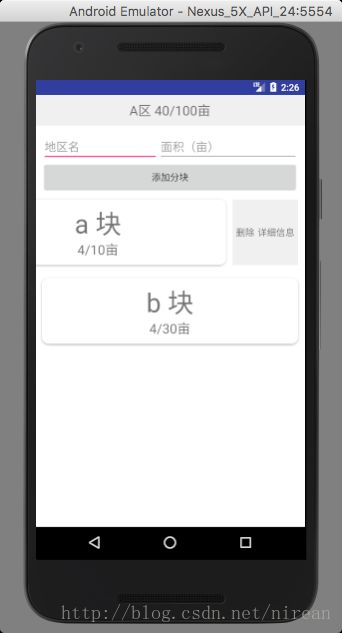
Android 实现左滑出现删除选项
滑动删除的部分主要包含两个部分, 一个是内容区域(用于放置正常显示的view),另一个是操作区域(用于放置删除按钮)。默认情况下,操作区域是不显示的,内容区域的大小是填充整个容 器,操作区域始终位于内容区域的右面。当开始滑动的时候,整个容器中的所有子view都像左滑动,如果操作区域此时是不可见的,设置为可见。
实现思路就是自定义一个layout SwipeLayout继承自FrameLayout。SwipeLayout包含两个子view,第一个子view是内容区域,第二个子view是操作 区域。滑动效果的控制,主要就是通过检测SwipeLayout的touch事件来实现,Android support库里其实已经提供了ViewDragHelper来进行监听touch事件。
1、首先需要对LinearLayout进行重载
具体分析看注解
package com.example.mac.agriculturemanagement;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewCompat;
import android.support.v4.widget.ViewDragHelper;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* Created by mac on 2017/6/15.
*/
//条目滑动效果
public class SlideLayout extends LinearLayout {
private ViewDragHelper mDragHelper;
private View contentView;
private View actionView;
private int dragDistance;
private final double AUTO_OPEN_SPEED_LIMIT = 800.0;
private int draggedX;
public SlideLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public SlideLayout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public SlideLayout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
//初始化
public void init (){
mDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, new DragHelperCallback());
}
@Override
public boolean callOnClick() {
return super.callOnClick();
}
/*当你触摸屏幕,移动的时候,就会回调这个方法。
它会返回两个参数。第一个参数,就是你触摸的那个控件。
第二个就是ID。
返回值又代表什么呢?返回ture,就是代笔允许拖动这个控件。
返回false就代表不允许拖动这个控件.。这里我只允许拖动主控件。*/
//把容器的事件处理委托给ViewDragHelper对象
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (mDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
contentView = getChildAt(0);
actionView = getChildAt(1);
actionView.setVisibility(GONE);
}
//设置拖动的距离为actionView的宽度
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
dragDistance = actionView.getMeasuredWidth();
//System.out.println("rightTop"+actionView.getTop());
}
private class DragHelperCallback extends ViewDragHelper.Callback {
//用来确定contentView和actionView是可以拖动的
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View view, int i) {
return view == contentView || view == actionView;
}
//被拖动的view位置改变的时候调用,如果被拖动的view是contentView,
// 我们需要在这里更新actionView的位置
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
draggedX = left;
if (changedView == contentView) {
actionView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
} else {
contentView.offsetLeftAndRight(dx);
}
//actionView 是否可见
//0 -------- VISIBLE 可见
//4 -------- INVISIBLE 不可见但是占用布局空间
//8 -------- GONE 不可见也不占用布局空间
if (actionView.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
actionView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
if (left==25)
{
actionView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
invalidate(); //刷新View
}
//用来限制view在x轴上拖动
//@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
if (child == contentView) {
final int leftBound = getPaddingLeft();
final int minLeftBound = -leftBound - dragDistance;
final int newLeft = Math.min(Math.max(minLeftBound, left), 25);
//System.out.println("content "+newLeft);
return newLeft;
} else {
//getMeasuredWidth()获取全部长度 包括隐藏的
final int minLeftBound = getPaddingLeft() + contentView.getMeasuredWidth() - dragDistance;
final int maxLeftBound = getPaddingLeft() + contentView.getMeasuredWidth() + getPaddingRight();
final int newLeft = Math.min(Math.max(left, minLeftBound), maxLeftBound);
System.out.println("action "+newLeft);
return newLeft;
}
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
//System.out.println("top "+top);
if(top!=25)
{
top=25;
}
return top;
}
//用来限制view可以拖动的范围
//@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return dragDistance;
}
@Override
public int getViewVerticalDragRange(View child) {
return 0;
}
//根据滑动手势的速度以及滑动的距离来确定是否显示actionView。
// smoothSlideViewTo方法用来在滑动手势之后实现惯性滑动效果
//@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
boolean settleToOpen = false;
if (xvel > AUTO_OPEN_SPEED_LIMIT) {
settleToOpen = false;
} else if (xvel < -AUTO_OPEN_SPEED_LIMIT) {
settleToOpen = true;
} else if (draggedX <= -dragDistance / 2) {
settleToOpen = true;
} else if (draggedX > -dragDistance / 2) {
settleToOpen = false;
}
final int settleDestX = settleToOpen ? -dragDistance : 0;
mDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(contentView, settleDestX, 0);
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(SlideLayout.this);
}
}
}
因为我给我的LinearLayout设置了外边距,所以在向左滑动的过程,出现上下的滑动,并且该条目的原始位置也偏移。为了解决该问题,首先需要根据自己设置的margin值来修改一下的数据
将onViewPositionChanged中添加
if (left==25)
{
actionView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}修改为适合的数据,来防止右侧的滑块不隐藏
再添加上
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
//System.out.println("top "+top);
if(top!=25)
{
top=25;
}
return top;
}来限制其上下移动 top的值依旧需要自己琢磨
2、编写布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.example.mac.agriculturemanagement.SlideLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/text_border"
android:elevation="3dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/mark"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="TextView"
android:textSize="40dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/markSquare"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="TextView"
android:textSize="20dp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#f0f0f0"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/showInfo"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/textView6"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView6"
android:text="详细信息" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="删除" />
RelativeLayout>
LinearLayout>
com.example.mac.agriculturemanagement.SlideLayout>
LinearLayout>具体效果
但目前还存在一个问题
ListView每一个条目的点击事件和滑动事件不能共存。网上说是因为事件的触发是逐层向下传递到进行处理该事件的部件,再逐层向上返 回处理结果。可能是某一曾事件被错误的部件阻断。希望懂得大佬解答一下