数据结构(10)-TrieTree(字典树)的实现
文章目录
- 1.1 什么是TrieTree
- 1.2 TrieTree的实现
- 1.3 重要方法
- 1.3 时间复杂度
- 1.4 经典应用
- 1.5 完整代码
Let’s Look Look What’s TrieTree!
1.1 什么是TrieTree
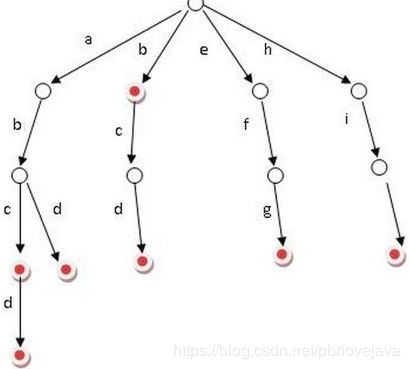
TrieTree又被称为字典树/单词查找树/前缀树,常用来做大量的词频分析以及排序大量字符串,是哈希树的一种变种形式,它最大的特点就是每一个节点中只存放字符串的一个字符,而树的一条边即该字符串或者是其前缀,这样的特性使得字典树被广泛地应用于海量字符串处理程序中.
1.2 TrieTree的实现
要实现TrieTree,首先需要定义其基础节点类:
private class Node {
//该节点代表的字符串前缀出现的次数
int count;
//以该节点为结束的字符的数量
int wordCount;
//记录该字符
char value;
//标识该节点是否代表单词结尾
private boolean isEnd;
//该节点的孩子节点
Node[] child;
private Node() {
count = 1;
isEnd = false;
child = new Node[MAX_SIZE];
}
}
其次是TrieTree成员变量的定义:
//每个节点下最多只能有从a-z这26个字符
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 26;
//字典树空根节点
private Node head;
再次是构造方法:
public TrieTree() {
//初始化Trie树头节点
Node node = new Node();
node.count = 1;
//根节点不包含单词字符
node.value = '*';
//声明子节点
node.child = new Node[MAX_SIZE];
head = node;
}
1.3 重要方法
- 1.插入字符串
public void insert(String word) {
if (word == null || "".equals(word)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("word cant be null");
}
buildNode(head, word);
}
private void buildNode(Node node, String word) {
char[] letters = word.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
//定位索引
int index = letters[i] - 'a';
if (node.child[index] != null) {
//已存在该字符节点,出现次数+1
node.child[index].count++;
} else {
//不存在该字符及诶单,创建
node.child[index] = new Node();
}
//为相应节点赋值并让其往下走
node.child[index].value = letters[i];
node = node.child[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
node.wordCount++;
}
- 2.查找前缀出现次数
public int findPreCount(String pre) {
if (pre == null || "".equals(pre.trim())) return -1;
return _findPreCount(head, pre);
}
private int _findPreCount(Node node, String pre) {
char[] letters = pre.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
int index = letters[i] - 'a';
if (node.child[index] != null) {
//存在该字符节点,继续往下找
node = node.child[index];
} else {
//无法匹配,则返回0
return 0;
}
}
return node.count;
}
- 3.查找特定字符串出现次数
public int findWordCount(String word) {
if (word == null || "".equals(word.trim())) return -1;
return _findWordCount(head, word);
}
private int _findWordCount(Node head, String word) {
char[] chars = word.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (head.child[chars[i] - 'a'] == null) return 0;
head = head.child[chars[i] - 'a'];
}
return head.isEnd ? head.wordCount : 0;
}
- 4.全体词频统计
public Map<String, Integer> wordCount() {
Map<String, Integer> res = new HashMap<>();
//使用回溯进行搜索
backTrace(res, head, "");
return res;
}
private void backTrace(Map<String, Integer> res, Node head, String oneRes) {
if (head != null) {
//回溯终止条件
if (head.isEnd) {
res.put(oneRes, head.wordCount);
}
//回溯搜索过程
Node[] child = head.child;
for (int i = 0; i < child.length; i++) {
if (child[i] != null) {
//还原字符
char ch = (char)(i + 'a');
//回溯搜索
backTrace(res, child[i], oneRes + ch);
}
}
return;
}
}
1.3 时间复杂度
1. 插入数据
插入数据的时间复杂度依赖于节点的遍历搜索结果,所以与单词的长度相关,为O(len)
2.查询数据
查询数据的时间复杂度依赖于需要查询的字符串长度,需要解析字符串的每个字符去搜索,所以为O(len)
1.4 经典应用
-
有一个1G大小的一个文件,里面每一行是一个词,词的大小不超过16字节,内存限制大小是1M。返回频数最高的100个词。
-----答:先使用TrieTree进行词频统计,再使用最小堆进行Top 100统计,最后求得词频最高的100个词. -
1000万字符串,其中有些是重复的,需要把重复的全部去掉,保留没有重复的字符串。请怎么设计和实现?
-----答:先将这些字符串放入TrieTree中,然后使用回溯搜索获取所有的字符串即可.
1.5 完整代码
/**
* @Auther: ARong
* @Date: 19-9-3 上午9:57
* @Description: 使用Java实现字典树
**/
public class TrieTree {
//每个节点下最多只能有从a-z这26个字符
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 26;
//字典树空根节点
private Node head;
//字典树节点
private class Node {
//该节点代表的字符串前缀出现的次数
int count;
//以该节点为结束的字符的数量
int wordCount;
//记录该字符
char value;
//标识该节点是否代表单词结尾
private boolean isEnd;
//该节点的孩子节点
Node[] child;
private Node() {
count = 1;
isEnd = false;
child = new Node[MAX_SIZE];
}
}
public TrieTree() {
//初始化Trie树头节点
Node node = new Node();
node.count = 1;
//根节点不包含单词字符
node.value = '*';
//声明子节点
node.child = new Node[MAX_SIZE];
head = node;
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 在Trie树中插入字符串
* @param: [word]
* @return: void
* @date: 上午10:09 19-9-3
*/
public void insert(String word) {
if (word == null || "".equals(word)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("word cant be null");
}
buildNode(head, word);
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 用word构建字典树
* @param: [head, word]
* @return: void
* @date: 上午10:15 19-9-3
*/
private void buildNode(Node node, String word) {
char[] letters = word.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
//定位索引
int index = letters[i] - 'a';
if (node.child[index] != null) {
//已存在该字符节点,出现次数+1
node.child[index].count++;
} else {
//不存在该字符及诶单,创建
node.child[index] = new Node();
}
//为相应节点赋值并让其往下走
node.child[index].value = letters[i];
node = node.child[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
node.wordCount++;
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 查找前缀出现次数
* @param: [pre]
* @return: data_struct.TrieTree.Node
* @date: 上午10:30 19-9-3
*/
public int findPreCount(String pre) {
if (pre == null || "".equals(pre.trim())) return -1;
return _findPreCount(head, pre);
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 查找前缀出现次数
* @param: [node, pre]
* @return: void
* @date: 上午10:31 19-9-3
*/
private int _findPreCount(Node node, String pre) {
char[] letters = pre.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
int index = letters[i] - 'a';
if (node.child[index] != null) {
//存在该字符节点,继续往下找
node = node.child[index];
} else {
//无法匹配,则返回0
return 0;
}
}
return node.count;
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 搜索特定单词出现的次数
* @param: [word]
* @return: int
* @date: 下午8:24 19-9-5
*/
public int findWordCount(String word) {
if (word == null || "".equals(word.trim())) return -1;
return _findWordCount(head, word);
}
private int _findWordCount(Node head, String word) {
char[] chars = word.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (head.child[chars[i] - 'a'] == null) return 0;
head = head.child[chars[i] - 'a'];
}
return head.isEnd ? head.wordCount : 0;
}
/**
* @auther: Arong
* @description: 全部词频数量统计
* @param: []
* @return: java.util.List>
* @date: 下午9:33 19-9-5
*/
public Map<String, Integer> wordCount() {
Map<String, Integer> res = new HashMap<>();
//使用回溯进行搜索
backTrace(res, head, "");
return res;
}
private void backTrace(Map<String, Integer> res, Node head, String oneRes) {
if (head != null) {
//回溯终止条件
if (head.isEnd) {
res.put(oneRes, head.wordCount);
}
//回溯搜索过程
Node[] child = head.child;
for (int i = 0; i < child.length; i++) {
if (child[i] != null) {
//还原字符
char ch = (char)(i + 'a');
//回溯搜索
backTrace(res, child[i], oneRes + ch);
}
}
return;
}
}
}