SSD网络解析之bbox_util
bbox_util.hpp文件里定义了SSD中好几个层所需要用到的各种函数,bbox_util.cpp和bbox_util.cu文件对应于这些函数的具体实现。
目录
BBoxSize
ClipBBox
IsCrossBoundaryBBox
JaccardOverlap
EncodeBBox
DecodeBBox
DecodeBBoxes
IsEligibleMining
ComputeConfLoss
GetGroundTruth
GetPriorBBoxes
GetLocPredictions
MatchBBox
FindMatches
MineHardExamples
EncodeLocPrediction
EncodeConfPrediction
BBoxSize
函数申明如下:
// Compute bbox size.
float BBoxSize(const NormalizedBBox& bbox, const bool normalized = true); //默认normalized为true,即输出归一化后的边界框面积函数定义如下:
//计算边界框(bounding box)的面积
//注:参数normalized默认为true
float BBoxSize(const NormalizedBBox& bbox, const bool normalized) {
if (bbox.xmax() < bbox.xmin() || bbox.ymax() < bbox.ymin()) {
// If bbox is invalid (e.g. xmax < xmin or ymax < ymin), return 0.
return 0; //此情况下说明边界框参数有误
} else {
if (bbox.has_size()) {
return bbox.size();
} else {
float width = bbox.xmax() - bbox.xmin();
float height = bbox.ymax() - bbox.ymin();
if (normalized) {
return width * height; //返回诡归一化后的面积
} else {
// If bbox is not within range [0, 1]. 边界框参数没有归一化下,返回像素面积
return (width + 1) * (height + 1);
}
}
}
}ClipBBox
函数申明如下:
// Clip the NormalizedBBox such that the range for each corner is [0, 1].
void ClipBBox(const NormalizedBBox& bbox, NormalizedBBox* clip_bbox);函数定义如下:
//直接裁剪(直接归一化到输入图像内,即将超出输入图像部分裁剪掉)
void ClipBBox(const NormalizedBBox& bbox, NormalizedBBox* clip_bbox) {
clip_bbox->set_xmin(std::max(std::min(bbox.xmin(), 1.f), 0.f));
clip_bbox->set_ymin(std::max(std::min(bbox.ymin(), 1.f), 0.f));
clip_bbox->set_xmax(std::max(std::min(bbox.xmax(), 1.f), 0.f));
clip_bbox->set_ymax(std::max(std::min(bbox.ymax(), 1.f), 0.f));
clip_bbox->clear_size();
clip_bbox->set_size(BBoxSize(*clip_bbox));
clip_bbox->set_difficult(bbox.difficult());
}此函数其实是为了确保所有的边界框都在输入图像区域内。(SSD中默认不需要此确保,允许边界框有部分落在图像外面)
IsCrossBoundaryBBox
函数申明如下:
// Check if a bbox is cross boundary or not.
bool IsCrossBoundaryBBox(const NormalizedBBox& bbox);函数定义如下:
//判断该边界框是否有部分在输入图像之外
bool IsCrossBoundaryBBox(const NormalizedBBox& bbox) {
return bbox.xmin() < 0 || bbox.xmin() > 1 ||
bbox.ymin() < 0 || bbox.ymin() > 1 ||
bbox.xmax() < 0 || bbox.xmax() > 1 ||
bbox.ymax() < 0 || bbox.ymax() > 1;
}
JaccardOverlap
函数申明如下:
// Compute the jaccard (intersection over union IoU) overlap between two bboxes.
float JaccardOverlap(const NormalizedBBox& bbox1, const NormalizedBBox& bbox2,
const bool normalized = true);函数定义如下:
//计算bbox1和bbox2的交并比IOU
float JaccardOverlap(const NormalizedBBox& bbox1, const NormalizedBBox& bbox2,
const bool normalized) {
NormalizedBBox intersect_bbox;
IntersectBBox(bbox1, bbox2, &intersect_bbox); //取出两者的相交部分放入intersect_bbox
float intersect_width, intersect_height;
if (normalized) {
intersect_width = intersect_bbox.xmax() - intersect_bbox.xmin();
intersect_height = intersect_bbox.ymax() - intersect_bbox.ymin();
} else {
intersect_width = intersect_bbox.xmax() - intersect_bbox.xmin() + 1;
intersect_height = intersect_bbox.ymax() - intersect_bbox.ymin() + 1;
}
if (intersect_width > 0 && intersect_height > 0) {
float intersect_size = intersect_width * intersect_height; //计算相交部分的面积
float bbox1_size = BBoxSize(bbox1); //计算bbox1的面积
float bbox2_size = BBoxSize(bbox2); //计算bbox2的面积
return intersect_size / (bbox1_size + bbox2_size - intersect_size); //计算交并比(IOU=相交部分面积/(两者面积之和-相交部分面积))
} else {
return 0.; //IOU = 0
}
}
两个边界框之间的交并比IOU计算如下图:
EncodeBBox
函数申明如下:
// Encode a bbox according to a prior bbox.
void EncodeBBox(const NormalizedBBox& prior_bbox,
const vector& prior_variance, const CodeType code_type,
const bool encode_variance_in_target, const NormalizedBBox& bbox,
NormalizedBBox* encode_bbox); 函数定义如下:
//编码BBox函数(只用于编码地面实况框)
void EncodeBBox(
const NormalizedBBox& prior_bbox, const vector& prior_variance,
const CodeType code_type, const bool encode_variance_in_target,
const NormalizedBBox& bbox, NormalizedBBox* encode_bbox) {
if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CORNER) { //如果编码/解码类型为CORNER
if (encode_variance_in_target) {
encode_bbox->set_xmin(bbox.xmin() - prior_bbox.xmin()); //实质是在计算地面实况框相对于默认框的偏移量
encode_bbox->set_ymin(bbox.ymin() - prior_bbox.ymin());
encode_bbox->set_xmax(bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmax());
encode_bbox->set_ymax(bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymax());
} else {
// Encode variance in bbox.
CHECK_EQ(prior_variance.size(), 4);
for (int i = 0; i < prior_variance.size(); ++i) {
CHECK_GT(prior_variance[i], 0);
}
encode_bbox->set_xmin(
(bbox.xmin() - prior_bbox.xmin()) / prior_variance[0]); //偏移量直接除上prior_variance
encode_bbox->set_ymin(
(bbox.ymin() - prior_bbox.ymin()) / prior_variance[1]);
encode_bbox->set_xmax(
(bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmax()) / prior_variance[2]);
encode_bbox->set_ymax(
(bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymax()) / prior_variance[3]);
}
} else if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CENTER_SIZE) { //如果编码/解码类型为CENTER_SIZE(对应于论文中2.2节定位损失函数部分变量的定义函数)
float prior_width = prior_bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmin(); //计算默认框宽度
CHECK_GT(prior_width, 0);
float prior_height = prior_bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymin(); //计算默认框高度
CHECK_GT(prior_height, 0);
//计算默认框中心坐标
float prior_center_x = (prior_bbox.xmin() + prior_bbox.xmax()) / 2.;
float prior_center_y = (prior_bbox.ymin() + prior_bbox.ymax()) / 2.;
float bbox_width = bbox.xmax() - bbox.xmin(); //bbox的宽度
CHECK_GT(bbox_width, 0);
float bbox_height = bbox.ymax() - bbox.ymin();//bbox的高度
CHECK_GT(bbox_height, 0);
//计算bbox的中心坐标
float bbox_center_x = (bbox.xmin() + bbox.xmax()) / 2.;
float bbox_center_y = (bbox.ymin() + bbox.ymax()) / 2.;
if (encode_variance_in_target) { //在目标函数中编码variance
encode_bbox->set_xmin((bbox_center_x - prior_center_x) / prior_width);
encode_bbox->set_ymin((bbox_center_y - prior_center_y) / prior_height);
encode_bbox->set_xmax(log(bbox_width / prior_width));
encode_bbox->set_ymax(log(bbox_height / prior_height));
} else {
// Encode variance in bbox. 直接在bbox中编码variance
encode_bbox->set_xmin(
(bbox_center_x - prior_center_x) / prior_width / prior_variance[0]);
encode_bbox->set_ymin(
(bbox_center_y - prior_center_y) / prior_height / prior_variance[1]);
encode_bbox->set_xmax(
log(bbox_width / prior_width) / prior_variance[2]);
encode_bbox->set_ymax(
log(bbox_height / prior_height) / prior_variance[3]);
}
} else if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CORNER_SIZE) { //如果编码/解码类型为CORNER_SIZE
float prior_width = prior_bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmin();
CHECK_GT(prior_width, 0);
float prior_height = prior_bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymin();
CHECK_GT(prior_height, 0);
if (encode_variance_in_target) {
encode_bbox->set_xmin((bbox.xmin() - prior_bbox.xmin()) / prior_width);
encode_bbox->set_ymin((bbox.ymin() - prior_bbox.ymin()) / prior_height);
encode_bbox->set_xmax((bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmax()) / prior_width);
encode_bbox->set_ymax((bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymax()) / prior_height);
} else {
// Encode variance in bbox.
CHECK_EQ(prior_variance.size(), 4);
for (int i = 0; i < prior_variance.size(); ++i) {
CHECK_GT(prior_variance[i], 0);
}
encode_bbox->set_xmin(
(bbox.xmin() - prior_bbox.xmin()) / prior_width / prior_variance[0]);
encode_bbox->set_ymin(
(bbox.ymin() - prior_bbox.ymin()) / prior_height / prior_variance[1]);
encode_bbox->set_xmax(
(bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmax()) / prior_width / prior_variance[2]);
encode_bbox->set_ymax(
(bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymax()) / prior_height / prior_variance[3]);
}
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown LocLossType.";
}
} EncodeBBox()函数是对地面实况框进行编码的函数,这里主要讲SSD中用到的编码方式,即CENTER_SIZE模式。
所对应的是SSD论文中的2.2节部分,可参见此链接。
SSD中采用以下公式对地面实况框进行编码:
![]()
![]()
其中,![]() 代表地面实况框,
代表地面实况框,![]() 代表默认框(先验框),也就是相对于默认框进行编码地面实况框。
代表默认框(先验框),也就是相对于默认框进行编码地面实况框。
注:地面实况框和默认框中的数据是左上角和右下角坐标。
DecodeBBox
函数申明如下:
// Decode a bbox according to a prior bbox.
void DecodeBBox(const NormalizedBBox& prior_bbox,
const vector& prior_variance, const CodeType code_type,
const bool variance_encoded_in_target, const bool clip_bbox,
const NormalizedBBox& bbox, NormalizedBBox* decode_bbox); 函数定义如下:
//真正的解码BBox函数
void DecodeBBox(
const NormalizedBBox& prior_bbox, const vector& prior_variance,
const CodeType code_type, const bool variance_encoded_in_target,
const bool clip_bbox, const NormalizedBBox& bbox,
NormalizedBBox* decode_bbox) {
if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CORNER) { //如果编码/解码类型为CORNER(即按左上角和右下角偏移进行编码/解码)
if (variance_encoded_in_target) { //如果在目标函数中编码variance,则直接在默认框的基础上添加偏移量即可
// variance is encoded in target, we simply need to add the offset
// predictions.
decode_bbox->set_xmin(prior_bbox.xmin() + bbox.xmin()); //预测框中的数据其实是相对默认框而言的偏移量
decode_bbox->set_ymin(prior_bbox.ymin() + bbox.ymin());
decode_bbox->set_xmax(prior_bbox.xmax() + bbox.xmax());
decode_bbox->set_ymax(prior_bbox.ymax() + bbox.ymax());
} else {//否则variance在bbox中编码,即需要相应调整预测偏移量
// variance is encoded in bbox, we need to scale the offset accordingly.
decode_bbox->set_xmin(
prior_bbox.xmin() + prior_variance[0] * bbox.xmin()); //直接乘上variance
decode_bbox->set_ymin(
prior_bbox.ymin() + prior_variance[1] * bbox.ymin());
decode_bbox->set_xmax(
prior_bbox.xmax() + prior_variance[2] * bbox.xmax());
decode_bbox->set_ymax(
prior_bbox.ymax() + prior_variance[3] * bbox.ymax());
}
} else if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CENTER_SIZE) { //如果编码/解码方式为CENTER_SIZE(对应于论文2.2节定位损失函数部分变量定义函数的反函数)
float prior_width = prior_bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmin(); //默认框宽度
CHECK_GT(prior_width, 0);
float prior_height = prior_bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymin(); //默认框高度
CHECK_GT(prior_height, 0);
//计算默认框的中心坐标
float prior_center_x = (prior_bbox.xmin() + prior_bbox.xmax()) / 2.;
float prior_center_y = (prior_bbox.ymin() + prior_bbox.ymax()) / 2.;
float decode_bbox_center_x, decode_bbox_center_y;
float decode_bbox_width, decode_bbox_height;
if (variance_encoded_in_target) {
// variance is encoded in target, we simply need to retore the offset
// predictions.
decode_bbox_center_x = bbox.xmin() * prior_width + prior_center_x;
decode_bbox_center_y = bbox.ymin() * prior_height + prior_center_y;
decode_bbox_width = exp(bbox.xmax()) * prior_width;
decode_bbox_height = exp(bbox.ymax()) * prior_height;
} else {
// variance is encoded in bbox, we need to scale the offset accordingly.
decode_bbox_center_x =
prior_variance[0] * bbox.xmin() * prior_width + prior_center_x;
decode_bbox_center_y =
prior_variance[1] * bbox.ymin() * prior_height + prior_center_y;
decode_bbox_width =
exp(prior_variance[2] * bbox.xmax()) * prior_width;
decode_bbox_height =
exp(prior_variance[3] * bbox.ymax()) * prior_height;
}
decode_bbox->set_xmin(decode_bbox_center_x - decode_bbox_width / 2.); //依旧转化为标准的左上角,右下角格式
decode_bbox->set_ymin(decode_bbox_center_y - decode_bbox_height / 2.);
decode_bbox->set_xmax(decode_bbox_center_x + decode_bbox_width / 2.);
decode_bbox->set_ymax(decode_bbox_center_y + decode_bbox_height / 2.);
} else if (code_type == PriorBoxParameter_CodeType_CORNER_SIZE) { //如果编码/解码方式为CORNER_SIZE(即按左上角和右下角相对默认框宽高度偏移量进行编码/解码)
float prior_width = prior_bbox.xmax() - prior_bbox.xmin();
CHECK_GT(prior_width, 0);
float prior_height = prior_bbox.ymax() - prior_bbox.ymin();
CHECK_GT(prior_height, 0);
if (variance_encoded_in_target) {
// variance is encoded in target, we simply need to add the offset
// predictions.
decode_bbox->set_xmin(prior_bbox.xmin() + bbox.xmin() * prior_width);
decode_bbox->set_ymin(prior_bbox.ymin() + bbox.ymin() * prior_height);
decode_bbox->set_xmax(prior_bbox.xmax() + bbox.xmax() * prior_width);
decode_bbox->set_ymax(prior_bbox.ymax() + bbox.ymax() * prior_height);
} else {
// variance is encoded in bbox, we need to scale the offset accordingly.
decode_bbox->set_xmin(
prior_bbox.xmin() + prior_variance[0] * bbox.xmin() * prior_width);
decode_bbox->set_ymin(
prior_bbox.ymin() + prior_variance[1] * bbox.ymin() * prior_height);
decode_bbox->set_xmax(
prior_bbox.xmax() + prior_variance[2] * bbox.xmax() * prior_width);
decode_bbox->set_ymax(
prior_bbox.ymax() + prior_variance[3] * bbox.ymax() * prior_height);
}
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown LocLossType.";
}
float bbox_size = BBoxSize(*decode_bbox);
decode_bbox->set_size(bbox_size); //记录解码后的预测框面积
if (clip_bbox) { //是否进行裁剪
ClipBBox(*decode_bbox, decode_bbox);
}
} DecodeBBox()函数根据不同的编码/解码方式(code_type)对边界框进行解码,这里也只说明SSD中所采用的CENTER_SIZE编码/解码模式。
实际上上面EncodeBBox()函数中对地面实况框的编码方式也适用于预测框,我们所得到的预测数据是预测框相对默认框编码后的结果,所以解码过程就是上述公式的反过程(反函数):
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
其中,![]() 代表地面实况框,
代表地面实况框,![]() 代表默认框。
代表默认框。
注:预测框中的数据是相对默认框编码后的中心坐标和长宽;地面实况框和默认框中的数据是左上角和右下角坐标,这一点需要区分。但经过此解码函数后输出的是预测框真正的左上角坐标和右下角坐标。
DecodeBBoxes
函数申明如下:
// Decode a set of bboxes according to a set of prior bboxes.
void DecodeBBoxes(const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const CodeType code_type, const bool variance_encoded_in_target,
const bool clip_bbox, const vector& bboxes,
vector* decode_bboxes); 函数定义如下:
//解码BBox(只用于解码预测框)
/*
参数prior_bboxes:默认框
参数prior_variances:默认框坐标variance
参数code_type:编码/解码类型
参数variance_encoded_in_target:判断是否在定位损失目标中编码默认框的variance参数
参数clip_bbox:是否裁剪BBox
参数bboxes:某一输入图像对应的所有预测框数据
参数decode_bboxes:输出的解码BBox
*/
void DecodeBBoxes(
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const CodeType code_type, const bool variance_encoded_in_target,
const bool clip_bbox, const vector& bboxes,
vector* decode_bboxes) {
CHECK_EQ(prior_bboxes.size(), prior_variances.size());
CHECK_EQ(prior_bboxes.size(), bboxes.size());
int num_bboxes = prior_bboxes.size(); //所有默认框数目
if (num_bboxes >= 1) {
CHECK_EQ(prior_variances[0].size(), 4);
}
decode_bboxes->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < num_bboxes; ++i) {
NormalizedBBox decode_bbox;
//对每一个预测框进行解码(预测框中的数据其实是相对默认框的偏移量,所以要进行解码获得真正的预测框数据)
DecodeBBox(prior_bboxes[i], prior_variances[i], code_type,
variance_encoded_in_target, clip_bbox, bboxes[i], &decode_bbox);
decode_bboxes->push_back(decode_bbox);
}
}
此函数调用DecodeBBox()函数真正实现边界框的解码。
IsEligibleMining
函数(在线函数)定义如下:
//判断是否符合挖掘条件
inline bool IsEligibleMining(const MiningType mining_type, const int match_idx,
const float match_overlap, const float neg_overlap) {
if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_MAX_NEGATIVE) {//如果挖掘类型为MAX_NEGATIVE
return match_idx == -1 && match_overlap < neg_overlap; //如果不匹配且IOU小于设定的上限,则返回true
} else if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_HARD_EXAMPLE) { //如果挖掘类型为HARD_EXAMPLE,则一律返回true
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
ComputeConfLoss
函数申明如下:
// Compute the confidence loss for each prior from conf_data.
// conf_data: num x num_preds_per_class * num_classes blob.
// num: the number of images.
// num_preds_per_class: number of predictions per class.
// num_classes: number of classes.
// background_label_id: it is used to skip selecting max scores from
// background class.
// loss_type: compute the confidence loss according to the loss type.
// all_match_indices: stores mapping between predictions and ground truth.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth bboxes from the batch.
// all_conf_loss: stores the confidence loss per location for each image.
template
void ComputeConfLoss(const Dtype* conf_data, const int num,
const int num_preds_per_class, const int num_classes,
const int background_label_id, const ConfLossType loss_type,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
vector >* all_conf_loss); 函数定义如下:
//计算置信度损失
/*
参数conf_data:置信度预测
参数num:输入图像数目
参数num_preds_per_class:默认框数目
参数num_classes:目标类别
参数background_label_id:背景label
参数loss_type:置信度损失类型
参数all_match_indices:存储着预测框与地面实况框间的匹配对(本质就是索引号)
参数all_gt_bboxes:存储着所有图像的地面实况框
参数all_conf_loss:输出参数,存储所有的置信度损失
*/
template
void ComputeConfLoss(const Dtype* conf_data, const int num,
const int num_preds_per_class, const int num_classes,
const int background_label_id, const ConfLossType loss_type,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
vector >* all_conf_loss) {
CHECK_LT(background_label_id, num_classes); //检查背景label
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_match_indices.size());
all_conf_loss->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { //循环遍历所有图像
vector conf_loss;
const map >& match_indices = all_match_indices[i];
for (int p = 0; p < num_preds_per_class; ++p) { //循环遍历所有默认框/预测框
int start_idx = p * num_classes;
// Get the label index.
int label = background_label_id; //找不到匹配对象,label就是背景类
for (map >::const_iterator it =
match_indices.begin(); it != match_indices.end(); ++it) { //遍历所有类别(当share_location为true时,这里只遍历一次)
const vector& match_index = it->second;
CHECK_EQ(match_index.size(), num_preds_per_class); //检查是否等于默认框/预测框数目
if (match_index[p] > -1) { //如果当前预测框存在匹配对象(-1为无匹配对象;-2为忽略的预测框)
CHECK(all_gt_bboxes.find(i) != all_gt_bboxes.end());
const vector& gt_bboxes =
all_gt_bboxes.find(i)->second;
CHECK_LT(match_index[p], gt_bboxes.size());
label = gt_bboxes[match_index[p]].label(); //取出该预测框匹配上的地面实况框中目标的类别
CHECK_GE(label, 0);
CHECK_NE(label, background_label_id);
CHECK_LT(label, num_classes);
// A prior can only be matched to one gt bbox.
break; //由于一个默认框/预测框只对应匹配一个地面实况框(但是一个地面实况框可以对应多个预测框/默认框),故一旦找到其匹配的地面实况框,就直接退出当前for循环
}
}
Dtype loss = 0;
if (loss_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_SOFTMAX) { //如果置信度损失为SOFTMAX型
CHECK_GE(label, 0);
CHECK_LT(label, num_classes);
// Compute softmax probability. 计算softmax概率
// We need to subtract the max to avoid numerical issues. 减去最大值避免数值问题
Dtype maxval = conf_data[start_idx];
for (int c = 1; c < num_classes; ++c) { //遍历所有类别,找到类别概率最大的那一个
maxval = std::max(conf_data[start_idx + c], maxval);
}
Dtype sum = 0.;
for (int c = 0; c < num_classes; ++c) {
sum += std::exp(conf_data[start_idx + c] - maxval); //计算softmax公式中的分母部分
}
Dtype prob = std::exp(conf_data[start_idx + label] - maxval) / sum; //计算当前预测框中目标的softmax概率(包括背景类)
loss = -log(std::max(prob, Dtype(FLT_MIN))); //计算当前预测框的置信度损失
} else if (loss_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_LOGISTIC) { //如果置信度损失为LOGISTIC型
int target = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < num_classes; ++c) {
if (c == label) {
target = 1;
} else {
target = 0;
}
Dtype input = conf_data[start_idx + c];
loss -= input * (target - (input >= 0)) -
log(1 + exp(input - 2 * input * (input >= 0)));
}
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown conf loss type.";
}
conf_loss.push_back(loss);
}
conf_data += num_preds_per_class * num_classes; //指针位置移动到下一张图像起始处
all_conf_loss->push_back(conf_loss);
}
} 此函数用于计算置信度损失,且此处只说明SSD所采用的softmax损失函数来计算置信度损失, softmax损失函数如下:
其中,![]() ,代表softmax的第
,代表softmax的第![]() 个输出值;
个输出值;![]() 代表我们的真实值(标签,采用one hot结构,即当属于第c类时,
代表我们的真实值(标签,采用one hot结构,即当属于第c类时,![]() ,其余均为0)。
,其余均为0)。
函数中的置信度损失,即根据所属的类别按上述公式计算损失(只是为了数值上可行,减去了最大值)。
GetGroundTruth
函数申明如下:
// Retrieve bounding box ground truth from gt_data.
// gt_data: 1 x 1 x num_gt x 7 blob. 个人感觉此处注释错了,应该是8而不是7(实际上是一行数据)
// num_gt: the number of ground truth.
// background_label_id: the label for background class which is used to do
// santity check so that no ground truth contains it.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth for each image. Label of each bbox is
// stored in NormalizedBBox.
template
void GetGroundTruth(const Dtype* gt_data, const int num_gt,
const int background_label_id, const bool use_difficult_gt,
map >* all_gt_bboxes); 函数定义如下:
//从gt_data中恢复地面实况
template
void GetGroundTruth(const Dtype* gt_data, const int num_gt,
const int background_label_id, const bool use_difficult_gt,
map >* all_gt_bboxes) {
all_gt_bboxes->clear(); //先进行clear,保证为空
for (int i = 0; i < num_gt; ++i) {
int start_idx = i * 8; //一个地面实况占8个数据
int item_id = gt_data[start_idx];
if (item_id == -1) {
continue;
}
int label = gt_data[start_idx + 1]; //取出当前地面实况中的目标属于哪一类别
CHECK_NE(background_label_id, label) //CHECK_NE为不等于
<< "Found background label in the dataset."; //标签中不能有背景类
bool difficult = static_cast(gt_data[start_idx + 7]);
if (!use_difficult_gt && difficult) {
// Skip reading difficult ground truth.当use_difficult_gt = false时跳过困难的地面实况
continue;
}
NormalizedBBox bbox;
bbox.set_label(label); //存储目标类别
bbox.set_xmin(gt_data[start_idx + 3]); //存储地面实况框的左上角x坐标
bbox.set_ymin(gt_data[start_idx + 4]); //存储地面实况框的左上角y坐标
bbox.set_xmax(gt_data[start_idx + 5]); //存储地面实况框的右下角x坐标
bbox.set_ymax(gt_data[start_idx + 6]); //存储地面实况框的右下角y坐标
bbox.set_difficult(difficult); //存储是否为difficult
float bbox_size = BBoxSize(bbox); //获取地面实况框面积
bbox.set_size(bbox_size);
(*all_gt_bboxes)[item_id].push_back(bbox);
}
}
注:C++中的map的使用可以参见此链接,其中的第一个参数为关键字,每一个关键字都是唯一的,第二个参数根据关键字进行存储。上述代码中的item_id就是关键字(int型),代表输入的图像标号,目的是为了将某一张输入图像的所有地面实况和该张图像利用map对应起来。
即all_gt_bboxes->first代表输入批量图像中的第几张图;all_gt_bboxes->second存储对应该张图的所有地面实况(严格上应该用迭代器的形式引用first和second,此处只是为了说明方便)。
从中可以看出,每一个地面实况框在gt_data中占8个位,例如:
gt_data[0]:表示第一个地面实况框属于输入图像中的哪一张图像(输入图像是一个batch)
gt_data[1]:第一个地面实况框中目标的类别标签(如果存在目标)
gt_data[2]:无实际意义
gt_data[3]:第一个地面实况框的左上角x坐标
gt_data[4]:第一个地面实况框的左上角y坐标
gt_data[5]:第一个地面实况框的右下角x坐标
gt_data[6]:第一个地面实况框的右下角y坐标
GetPriorBBoxes
函数申明如下:
// Get prior bounding boxes from prior_data.
// prior_data: 1 x 2 x num_priors * 4 x 1 blob.(实际上是一行数据)
// num_priors: number of priors.
// prior_bboxes: stores all the prior bboxes in the format of NormalizedBBox.
// prior_variances: stores all the variances needed by prior bboxes.
template
void GetPriorBBoxes(const Dtype* prior_data, const int num_priors,
vector* prior_bboxes,
vector >* prior_variances); 函数定义如下:
//恢复所有的默认框
template
void GetPriorBBoxes(const Dtype* prior_data, const int num_priors,
vector* prior_bboxes,
vector >* prior_variances) {
prior_bboxes->clear();
prior_variances->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < num_priors; ++i) {
int start_idx = i * 4;
NormalizedBBox bbox;
bbox.set_xmin(prior_data[start_idx]); //默认框左上角x坐标
bbox.set_ymin(prior_data[start_idx + 1]); //默认框左上角y坐标
bbox.set_xmax(prior_data[start_idx + 2]); //默认框右下角x左边
bbox.set_ymax(prior_data[start_idx + 3]); //默认框右下角y坐标
float bbox_size = BBoxSize(bbox); //获取默认框面积
bbox.set_size(bbox_size);
prior_bboxes->push_back(bbox);
}
//此部分感觉可以和上面的for循环合并到一起
//取出各默认框四个坐标的variance
for (int i = 0; i < num_priors; ++i) {
int start_idx = (num_priors + i) * 4;
vector var;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
var.push_back(prior_data[start_idx + j]);
}
prior_variances->push_back(var);
}
} 输入参数num_priors为默认框(SSD论文中的default box)总数。
每个默认框在prior_data中占4位,例如:
prior_data[0]:第一个默认框左上角x坐标
prior_data[1]:第一个默认框左上角y坐标
prior_data[2]:第一个默认框右下角x坐标
prior_data[3]:第一个默认框右下角y坐标
注:每一层所有特征图之间共享同一组默认框的参数(默认框大小/坐标等),原因在于对于同一层而言,无论该层的batch size,channel是多少,该层的每一张特征图大小是一样的,且整个网络输入的batch size张图像大小也是一样的,由此默认框对应到输入图像上的位置是一样的,故可以共享。当然定位预测数据是不共享的(但对不同的目标类别可以共享),毕竟每张输入图像的目标及其位置不同,需要不同的数据来进行定位。
GetLocPredictions
函数申明如下:
// Get location predictions from loc_data.
// loc_data: num x num_preds_per_class * num_loc_classes * 4 blob.(实际上是一行数据)
// num: the number of images.
// num_preds_per_class: number of predictions per class.
// num_loc_classes: number of location classes. It is 1 if share_location is
// true; and is equal to number of classes needed to predict otherwise.
// share_location: if true, all classes share the same location prediction.
// loc_preds: stores the location prediction, where each item contains
// location prediction for an image.
template
void GetLocPredictions(const Dtype* loc_data, const int num,
const int num_preds_per_class, const int num_loc_classes,
const bool share_location, vector* loc_preds);
函数定义如下:
//恢复定位预测
/*
参数loc_data:定位预测数据
参数num:批量数(即data层的batch size)
参数num_preds_per_class:所设置的所有默认框数目
参数num_loc_classes:当共享时,为1;不共享时,为目标类数(即由目标间共不共享定位预测决定,默认为共享)
参数share_location:目标间共不共享定位预测
参数loc_preds:输出变量,保存所有的定位预测
*/
template
void GetLocPredictions(const Dtype* loc_data, const int num,
const int num_preds_per_class, const int num_loc_classes,
const bool share_location, vector* loc_preds) {
loc_preds->clear();
if (share_location) { //是否共享
CHECK_EQ(num_loc_classes, 1); //如果共享,检查num_loc_classes == 1
}
loc_preds->resize(num); //根据批量数重新调整loc_preds大小
//循环取出每一张输入图像上的所有默认框对应的预测框的预测数据
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { //循环每一张输入图像
LabelBBox& label_bbox = (*loc_preds)[i];
for (int p = 0; p < num_preds_per_class; ++p) {
int start_idx = p * num_loc_classes * 4;
for (int c = 0; c < num_loc_classes; ++c) {
int label = share_location ? -1 : c;
if (label_bbox.find(label) == label_bbox.end()) {
label_bbox[label].resize(num_preds_per_class); //根据num_loc_classes的大小调整的大小
}
label_bbox[label][p].set_xmin(loc_data[start_idx + c * 4]); //预测的边界框左上角x坐标
label_bbox[label][p].set_ymin(loc_data[start_idx + c * 4 + 1]); //预测的边界框左上角y坐标
label_bbox[label][p].set_xmax(loc_data[start_idx + c * 4 + 2]); //预测的边界框右下角x坐标
label_bbox[label][p].set_ymax(loc_data[start_idx + c * 4 + 3]); //预测的边界框右下角y坐标
}
}
loc_data += num_preds_per_class * num_loc_classes * 4;
}
}
其中LabelBBox的定义如下:
typedef map > LabelBBox; 这里的map中的关键字也是int型,表示的是代码中的label,当share_location = true时,均为-1,即只有一个关键字;当为false时,表示按类别存储。(注:由于loc_preds是vector,故不同输入图像和预测框间的对应是按顺序来的,即(*loc_preds)[0]中的所有预测框对应于batch中的第一张图像)
且loc_preds[i]->first表示类别(即如果共享则为-1,如果不共享则为类别);loc_preds[i]->second存储着预测框信息,且预测框数目均为num_preds_per_class(严格上应该用迭代器的形式引用first和second,此处只是为了说明方便)。
从上述代码中能够看出每个预测框在loc_data中占4位,例如:
loc_data[0]:对应于label = 0的第一个预测框中心坐标中的x坐标编码后的值(如果不共享的话)
loc_data[1]:对应于label = 0的第一个预测框中心坐标中的y坐标编码后的值(如果不共享的话)
loc_data[2]:对应于label = 0的第一个预测框宽度编码后的值(如果不共享的话)
loc_data[3]:对应于label = 0的第一个预测框高度编码后的值(如果不共享的话)
同时也能看出,在默认共享的情况下,预测框的数目是默认框数目的batch size倍(batch size即输入图像批量数)。SSD是默认共享的,即默认每一个边界框只预测一个目标。
MatchBBox
函数申明如下:
// Match prediction bboxes with ground truth bboxes.
void MatchBBox(const vector& gt,
const vector& pred_bboxes, const int label,
const MatchType match_type, const float overlap_threshold,
const bool ignore_cross_boundary_bbox,
vector* match_indices, vector* match_overlaps);
函数定义如下:
//匹配预测框
/*
参数gt_bboxes:地面实况框
参数pred_bboxes:预测框
参数label:当share_loaction为真时,label为-1;否则为目标类别(即为真时,所有目标类别共享一组预测框,而为假时,每种目标都有一组预测框)
参数match_type:匹配模式
参数overlap_threshold:交并比IOU阈值,用来判断是否匹配
参数ignore_cross_boundary_bbox:是否忽略那些超出输入图像范围的预测框
参数match_indices:输出参数,存储预测框匹配上的地面实况框索引号
参数match_overlaps:输出参数,存储匹配上的预测框与地面实况框之间的IOU
*/
void MatchBBox(const vector& gt_bboxes,
const vector& pred_bboxes, const int label,
const MatchType match_type, const float overlap_threshold,
const bool ignore_cross_boundary_bbox,
vector* match_indices, vector* match_overlaps) {
int num_pred = pred_bboxes.size(); //预测框数目
match_indices->clear();
match_indices->resize(num_pred, -1); //重新调整大小,并用-1赋值
match_overlaps->clear();
match_overlaps->resize(num_pred, 0.); //重新调整大小,并用0赋值
int num_gt = 0;
vector gt_indices;
if (label == -1) {
// label -1 means comparing against all ground truth. 标签-1表示与所有地面实况框进行比较(看是否匹配)
num_gt = gt_bboxes.size();
for (int i = 0; i < num_gt; ++i) {
gt_indices.push_back(i);
}
} else {
// Count number of ground truth boxes which has the desired label. 统计具有label类目标的地面实况框数量
for (int i = 0; i < gt_bboxes.size(); ++i) {
if (gt_bboxes[i].label() == label) {
num_gt++;
gt_indices.push_back(i);
}
}
}
if (num_gt == 0) {
return; //没有该label类的地面实况框,则直接返回
}
// Store the positive overlap between predictions and ground truth.
map > overlaps;
for (int i = 0; i < num_pred; ++i) { //遍历所有预测框
if (ignore_cross_boundary_bbox && IsCrossBoundaryBBox(pred_bboxes[i])) {
(*match_indices)[i] = -2; //忽略超出输入图像的预测框
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < num_gt; ++j) { //遍历所有选出的地面实况框
float overlap = JaccardOverlap(pred_bboxes[i], gt_bboxes[gt_indices[j]]);//计算交并比IOU
if (overlap > 1e-6) {
(*match_overlaps)[i] = std::max((*match_overlaps)[i], overlap); //保留最大的交并比(此句语句似乎没啥用)
overlaps[i][j] = overlap; //存储所有有交集的预测框与地面实况框对的交并比
}
}
}
// Bipartite matching. 二分匹配(即每个地面实况框匹配一个交并比最大的预测框,且一旦一个预测框匹配给了某一地面实况框,
//就不会再匹配给其他地面实况框,即使对于另一地面实况框而言,他们间的交并比也是最大的)
vector gt_pool;
for (int i = 0; i < num_gt; ++i) {
gt_pool.push_back(i);
}
while (gt_pool.size() > 0) { //循环所有选出的地面实况框,找到与其最匹配的预测框
// Find the most overlapped gt and cooresponding predictions.
int max_idx = -1;
int max_gt_idx = -1;
float max_overlap = -1;
for (map >::iterator it = overlaps.begin();
it != overlaps.end(); ++it) {
int i = it->first; //预测框索引
if ((*match_indices)[i] != -1) {
// The prediction already has matched ground truth or is ignored. 该预测框和地面实况框对(i,j)已经匹配上了(无需再匹配)或者是被忽略的预测框
continue;
}
//遍历所剩下的所有地面实况框,寻找与当前预测框的交并比最大的地面实况框
for (int p = 0; p < gt_pool.size(); ++p) {
int j = gt_pool[p];
if (it->second.find(j) == it->second.end()) {
// No overlap between the i-th prediction and j-th ground truth. 第i个预测框与第j个地面实况框间并没有交集
continue;
}
// Find the maximum overlapped pair.
if (it->second[j] > max_overlap) { //更新
// If the prediction has not been matched to any ground truth,
// and the overlap is larger than maximum overlap, update.
max_idx = i;
max_gt_idx = j;
max_overlap = it->second[j];
}
}
}
if (max_idx == -1) {
// Cannot find good match. 此情况下说明所设计的默认框并没有完全覆盖所有的地面实况框
break;
} else { //将对应匹配数据写入对应变量中
CHECK_EQ((*match_indices)[max_idx], -1);
(*match_indices)[max_idx] = gt_indices[max_gt_idx];
(*match_overlaps)[max_idx] = max_overlap;
// Erase the ground truth.
gt_pool.erase(std::find(gt_pool.begin(), gt_pool.end(), max_gt_idx)); //若匹配上,则清除该地面实况框索引
}
}
switch (match_type) {
case MultiBoxLossParameter_MatchType_BIPARTITE:
// Already done. 上述过程已经完成二分匹配
break;
case MultiBoxLossParameter_MatchType_PER_PREDICTION: //SSD论文中的匹配方法(详见论文2.2节),是在上述二分匹配的基础上进一步匹配
// Get most overlaped for the rest prediction bboxes.
for (map >::iterator it = overlaps.begin();
it != overlaps.end(); ++it) { //重新遍历所有的有交集的预测框和地面实况框对
int i = it->first;
if ((*match_indices)[i] != -1) {
// The prediction already has matched ground truth or is ignored. 该预测框和地面实况框对(i,j)已经匹配上了(无需再匹配)或者是被忽略的预测框
continue;
}
int max_gt_idx = -1;
float max_overlap = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < num_gt; ++j) {
if (it->second.find(j) == it->second.end()) {
// No overlap between the i-th prediction and j-th ground truth. 第i个预测框与第j个地面实况框间并没有交集
continue;
}
// Find the maximum overlapped pair.
float overlap = it->second[j];
//原因在于一个预测框只能对应一个地面实况框,但根据SSD,一个地面实况框可以对应多个IOU大于设置阈值的预测框
if (overlap >= overlap_threshold && overlap > max_overlap) { //即为了满足预测框只对应一个地面实况框这一约束
// If the prediction has not been matched to any ground truth,
// and the overlap is larger than maximum overlap, update.
max_gt_idx = j;
max_overlap = overlap;
}
}
if (max_gt_idx != -1) { //将对应匹配数据写入对应变量中
// Found a matched ground truth.
CHECK_EQ((*match_indices)[i], -1);
(*match_indices)[i] = gt_indices[max_gt_idx];
(*match_overlaps)[i] = max_overlap;
}
}
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown matching type.";
break;
}
return;
} MatchBBox()此函数可以说是这么多函数里面较难理解的一个函数了,主要是有部分其实我们并不需要,因为SSD所使用的匹配方法是PER_PREDICTION,而不是BIPARTITE(二分法),当然这里写了一大堆二分法的,个人感觉是借鉴了其他作者的代码(其他作者用的二分法,但没有PER_PREDICTION这种方法),然后在那基础上修改而来的(加上了PER_PREDICTION)。
此函数关于PER_PREDICTION这种匹配模式的原理其实就是SSD论文2.2节中很简略的一句话:
Unlike MultiBox, we then match default boxes to any ground truth with jaccard overlap higher than a threshold(0.5).
意思就是一个地面实况框可以对应多个默认框(或预测框),但要满足两者间的IOU阈值大于0.5,但一个默认框(或预测框)只能对应一个地面实况框,即两者并不是一一对应关系(二分法是一一对应关系)。后半句话虽然在上面这一行英文中没有说明,但其实很重要(因为一个预测框至多预测一个目标,所以才有这样的关系)。
当然PER_PREDICTION可以在BIPARTITE上进一步挑选匹配对,因为BIPARTITE匹配模式寻找的是和地面实况框最为重叠的默认框,只要这默认框和该地面实况框的IOU大于上述阈值,那就可以成为PER_PREDICTION模式中的一对。
所以函数本身先执行一遍BIPARTITE匹配模式(默认最重叠的情况下,IOU肯定大于设定的阈值),采用的是while循环(直到所有地面实况框都匹配上了默认框,才退出此循环),利用while循环遍历每一个地面实况框,去匹配所有默认框的好处在于能够保证两者之前匹配上的一一对应关系。
然后执行PER_PREDICTION模式,采用for循环遍历每一个默认框,去匹配所有的地面实况框,只要满足该预测框与某一地面实况框的IOU相对于该预测框与其余地面实况框间的IOU最大且大于所设定的IOU阈值,则认为两者匹配。采用这样的for循环方式的好处是可以保证一个地面实况框对应多个默认框,而一个默认框只对应一个地面实况框。
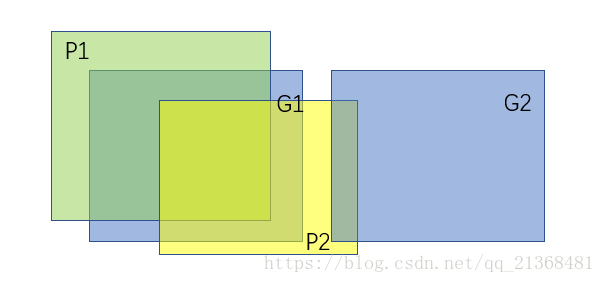
举个例子,如下图所示:
执行完 BIPARTITE后,默认框P1和地面实况框G1匹配上;在此基础上运行完PER_PREDICTION后,默认框P1也与G1匹配上(虽然P2与地面实况框G2之间也有交集,但与G1的IOU更大,且大于设定的阈值0.5)。
FindMatches
函数声明如下:
// Find matches between prediction bboxes and ground truth bboxes.
// all_loc_preds: stores the location prediction, where each item contains
// location prediction for an image.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth bboxes for the batch.
// prior_bboxes: stores all the prior bboxes in the format of NormalizedBBox.
// prior_variances: stores all the variances needed by prior bboxes.
// multibox_loss_param: stores the parameters for MultiBoxLossLayer.
// all_match_overlaps: stores jaccard overlaps between predictions and gt.
// all_match_indices: stores mapping between predictions and ground truth.
void FindMatches(const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
vector > >* all_match_overlaps,
vector > >* all_match_indices); 函数定义如下:
//寻找与地面实况框匹配的预测框
/*
参数all_loc_preds:预测框
参数all_gt_bboxes:地面实况框
参数prior_bboxes:默认框
参数prior_variances:默认框坐标的variance
参数multibox_loss_param:multibox_loss层的设置参数
参数all_match_overlaps:输出参数,保存所有匹配上的预测框和地面实况框的重合率
参数all_match_indices:输出参数,保存所有匹配对
*/
void FindMatches(const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
vector > >* all_match_overlaps,
vector > >* all_match_indices) {
// all_match_overlaps->clear();
// all_match_indices->clear();
// Get parameters.
CHECK(multibox_loss_param.has_num_classes()) << "Must provide num_classes.";
const int num_classes = multibox_loss_param.num_classes();
CHECK_GE(num_classes, 1) << "num_classes should not be less than 1.";
const bool share_location = multibox_loss_param.share_location(); //各种目标类间是否共享定位预测(共享的话说明每个边框最后的检测结果至多为一类目标)
const int loc_classes = share_location ? 1 : num_classes;
const MatchType match_type = multibox_loss_param.match_type(); //匹配类型
const float overlap_threshold = multibox_loss_param.overlap_threshold(); //重叠阈值
const bool use_prior_for_matching =
multibox_loss_param.use_prior_for_matching(); //获取判断是否使用默认框来进行匹配
const int background_label_id = multibox_loss_param.background_label_id(); //背景的标签类
const CodeType code_type = multibox_loss_param.code_type(); //编码方式
const bool encode_variance_in_target =
multibox_loss_param.encode_variance_in_target(); //获取判断是否在定位损失目标中编码默认框的variance参数
const bool ignore_cross_boundary_bbox =
multibox_loss_param.ignore_cross_boundary_bbox(); //获取判断是否忽略交叉框(即有部分超出图像所在坐标的边界框)参数
// Find the matches.
int num = all_loc_preds.size(); //batch size大小,即该输入批量的图像数
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
map > match_indices;
map > match_overlaps;
// Check if there is ground truth for current image.
if (all_gt_bboxes.find(i) == all_gt_bboxes.end()) { //all_gt_bboxes是按图像存储的,即map >中的int表示第几张图,同一张图的地面实况框存储在一个vector中
// There is no gt for current image. All predictions are negative. 当前输入图像上没有地面实况框
all_match_indices->push_back(match_indices);
all_match_overlaps->push_back(match_overlaps);
continue;
}
// Find match between predictions and ground truth.
const vector& gt_bboxes = all_gt_bboxes.find(i)->second;
if (!use_prior_for_matching) { //不使用默认框进行匹配(即使用解码后的预测框进行匹配)
for (int c = 0; c < loc_classes; ++c) {
int label = share_location ? -1 : c;
if (!share_location && label == background_label_id) {
// Ignore background loc predictions. 忽略背景类的定位预测
continue;
}
// Decode the prediction into bbox first.
vector loc_bboxes;
bool clip_bbox = false; //不进行裁剪
//解码预测框
DecodeBBoxes(prior_bboxes, prior_variances,
code_type, encode_variance_in_target, clip_bbox,
all_loc_preds[i].find(label)->second, &loc_bboxes);
//匹配地面实况框和预测框
MatchBBox(gt_bboxes, loc_bboxes, label, match_type,
overlap_threshold, ignore_cross_boundary_bbox,
&match_indices[label], &match_overlaps[label]);
}
} else { //使用默认框进行匹配
// Use prior bboxes to match against all ground truth.
vector temp_match_indices;
vector temp_match_overlaps;
const int label = -1;
//匹配地面实况框和默认框
MatchBBox(gt_bboxes, prior_bboxes, label, match_type, overlap_threshold,
ignore_cross_boundary_bbox, &temp_match_indices,
&temp_match_overlaps);
if (share_location) {
match_indices[label] = temp_match_indices;
match_overlaps[label] = temp_match_overlaps;
} else {
// Get ground truth label for each ground truth bbox.
vector gt_labels;
for (int g = 0; g < gt_bboxes.size(); ++g) {
gt_labels.push_back(gt_bboxes[g].label());
}
// Distribute the matching results to different loc_class.
for (int c = 0; c < loc_classes; ++c) {
if (c == background_label_id) {
// Ignore background loc predictions. 忽略背景的定位预测
continue;
}
match_indices[c].resize(temp_match_indices.size(), -1);
match_overlaps[c] = temp_match_overlaps;
for (int m = 0; m < temp_match_indices.size(); ++m) {
if (temp_match_indices[m] > -1) {
const int gt_idx = temp_match_indices[m];
CHECK_LT(gt_idx, gt_labels.size()); //判断gt_idx是否小于地面实况框数目(一个默认框至多匹配一个地面实况框)
if (c == gt_labels[gt_idx]) {
match_indices[c][m] = gt_idx;
}
}
}
}
}
}
all_match_indices->push_back(match_indices);
all_match_overlaps->push_back(match_overlaps);
}
} 此函数调用MatchBBox()函数来实现地面实况框与预测框之间的匹配关系,如果采用预测框本身来进行匹配,则需要先对预测框进行解码(原因在解码函数那已经说明),然后调用MatchBBox()函数完成匹配;如果采用默认框进行匹配(SSD采用此方法),则直接调用MatchBBox()函数完成匹配,然后在此基础上完成预测框与地面实况框之间的匹配(预测框本身是和默认框一一对应的,所以可以采用默认框进行匹配)。
MineHardExamples
函数申明如下:
// Mine the hard examples from the batch.
// conf_blob: stores the confidence prediction.
// all_loc_preds: stores the location prediction, where each item contains
// location prediction for an image.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth bboxes for the batch.
// prior_bboxes: stores all the prior bboxes in the format of NormalizedBBox.
// prior_variances: stores all the variances needed by prior bboxes.
// all_match_overlaps: stores jaccard overlap between predictions and gt.
// multibox_loss_param: stores the parameters for MultiBoxLossLayer.
// all_match_indices: stores mapping between predictions and ground truth.
// all_loc_loss: stores the confidence loss per location for each image.
template
void MineHardExamples(const Blob& conf_blob,
const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const vector > >& all_match_overlaps,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
int* num_matches, int* num_negs,
vector > >* all_match_indices,
vector >* all_neg_indices); 函数定义如下:
//挖掘硬样本(负样本)
/*
参数conf_blob:置信度blob
参数all_loc_preds:输入图像上的定位预测
参数all_gt_bboxes:地面实况框
参数prior_bboxes:默认框
参数prior_variances:默认框坐标variance
参数all_match_overlap:存储着预测框与地面实况框之间的交并比(注:SSD使用默认框与地面实况框之间的交并比)
参数multibox_loss_param:multibox_loss层的设置参数
参数num_matches:输出参数,总的匹配对数
参数num_negs:输出参数,表示所有输入图像上总的负样本数目
参数all_match_indices:存储预测框与地面实况框之间的匹配对(既是输入也是输出,且只有在挖掘类型为HARD_EXAMPLE下会改变其值)
参数all_neg_indices:存储所有负样本索引
*/
template
void MineHardExamples(const Blob& conf_blob,
const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const vector > >& all_match_overlaps,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
int* num_matches, int* num_negs,
vector > >* all_match_indices,
vector >* all_neg_indices) {
int num = all_loc_preds.size(); //batch size(即输入的图像数目)
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_match_overlaps.size());
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_match_indices->size());
// all_neg_indices->clear();
*num_matches = CountNumMatches(*all_match_indices, num); //统计总的匹配上的对数
*num_negs = 0;
int num_priors = prior_bboxes.size(); //默认框数目
CHECK_EQ(num_priors, prior_variances.size());
// Get parameters. 得到multibox_loss层所设置的一系列参数
CHECK(multibox_loss_param.has_num_classes()) << "Must provide num_classes.";
const int num_classes = multibox_loss_param.num_classes(); //类别数目
CHECK_GE(num_classes, 1) << "num_classes should not be less than 1.";
const int background_label_id = multibox_loss_param.background_label_id(); //背景的label
const bool use_prior_for_nms = multibox_loss_param.use_prior_for_nms(); //是否使用默认框进行非极大值抑制(NMS)(默认为false)
const ConfLossType conf_loss_type = multibox_loss_param.conf_loss_type(); //置信度损失类型
const MiningType mining_type = multibox_loss_param.mining_type(); //挖掘类型
if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_NONE) { //如果挖掘类型为NONE,则不需要后续的操作,直接拿所有负样本训练
return;
}
const LocLossType loc_loss_type = multibox_loss_param.loc_loss_type(); //定位损失类型
const float neg_pos_ratio = multibox_loss_param.neg_pos_ratio(); //负样本和正样本数目比值
const float neg_overlap = multibox_loss_param.neg_overlap(); //不匹配预测的重叠上限
const CodeType code_type = multibox_loss_param.code_type(); //编码/解码类型
const bool encode_variance_in_target =
multibox_loss_param.encode_variance_in_target(); //是否在目标函数中编码variance(默认为false)
const bool has_nms_param = multibox_loss_param.has_nms_param(); //是否设置了NMS参数
float nms_threshold = 0;
int top_k = -1;
if (has_nms_param) {
nms_threshold = multibox_loss_param.nms_param().nms_threshold();
top_k = multibox_loss_param.nms_param().top_k();
}
const int sample_size = multibox_loss_param.sample_size(); //默认为64(在挖掘类型为HARD_EXAMPLE时有用)
// Compute confidence losses based on matching results.
vector > all_conf_loss;
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
//利用CPU版的函数计算置信度损失
ComputeConfLoss(conf_blob.cpu_data(), num, num_priors, num_classes,
background_label_id, conf_loss_type, *all_match_indices, all_gt_bboxes,
&all_conf_loss);
#else
//利用GPU版的函数计算置信度损失
ComputeConfLossGPU(conf_blob, num, num_priors, num_classes,
background_label_id, conf_loss_type, *all_match_indices, all_gt_bboxes,
&all_conf_loss);
#endif
vector > all_loc_loss;
if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_HARD_EXAMPLE) { //如果挖掘类型为HARD_EXAMPLE
// Compute localization losses based on matching results. 在匹配的基础上计算定位误差
Blob loc_pred, loc_gt;
if (*num_matches != 0) {
vector loc_shape(2, 1);
loc_shape[1] = *num_matches * 4;
loc_pred.Reshape(loc_shape);
loc_gt.Reshape(loc_shape);
Dtype* loc_pred_data = loc_pred.mutable_cpu_data(); //存储每一匹配对中的预测框信息
Dtype* loc_gt_data = loc_gt.mutable_cpu_data(); //存储每一匹配对中的编码后的地面实况框信息
//得到编码后的预测框和地面实况框匹配对(用于后续计算定位损失)
EncodeLocPrediction(all_loc_preds, all_gt_bboxes, *all_match_indices,
prior_bboxes, prior_variances, multibox_loss_param,
loc_pred_data, loc_gt_data);
}
//计算定位损失
ComputeLocLoss(loc_pred, loc_gt, *all_match_indices, num,
num_priors, loc_loss_type, &all_loc_loss);
} else {
// No localization loss. 其余挖掘类型暂时不需要计算定位损失
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
vector loc_loss(num_priors, 0.f);
all_loc_loss.push_back(loc_loss);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { //循环遍历每一张输入图像
map >& match_indices = (*all_match_indices)[i];
const map >& match_overlaps = all_match_overlaps[i];
// loc + conf loss.
const vector& conf_loss = all_conf_loss[i];
const vector& loc_loss = all_loc_loss[i];
vector loss;
std::transform(conf_loss.begin(), conf_loss.end(), loc_loss.begin(),
std::back_inserter(loss), std::plus());
// Pick negatives or hard examples based on loss. 以下基于上面计算好的loss选择负样本/硬例子
//set中每个元素只包含一个关键字,set支持高效的关键字查询操作——检查一个给定关键字是否在set中
set sel_indices; //sel_indices用于存储最终选出来的负样本索引号(不按预测框原有顺序排列,基于NMS或loss从高到低排列)
vector neg_indices; //用于存储最终选出来的负样本索引号(按预测框原有顺序排列)
for (map >::iterator it = match_indices.begin();
it != match_indices.end(); ++it) { //循环遍历所有类别
const int label = it->first;
int num_sel = 0;
// Get potential indices and loss pairs. 获取所有潜在的负样本(形成损失-索引对)
vector > loss_indices; //存储潜在负样本的损失及其索引(即第几个预测框)
for (int m = 0; m < match_indices[label].size(); ++m) { //循环遍历所有预测框
if (IsEligibleMining(mining_type, match_indices[label][m],
match_overlaps.find(label)->second[m], neg_overlap)) { //如果当前预测框无匹配的地面实况框且IOU小于设定阈值,则加入潜在负样本队列中
loss_indices.push_back(std::make_pair(loss[m], m)); //成对
++num_sel;
}
}
//以下根据不同的挖掘类型,计算相应所需的负样本数目
if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_MAX_NEGATIVE) { //如果挖掘类型为MAX_NEGATIVE(SSD使用此类型)
int num_pos = 0;
for (int m = 0; m < match_indices[label].size(); ++m) { //循环遍历所有预测框,计算正样本(即匹配上地面实况框的预测框)数目,用于限制负样本数量
if (match_indices[label][m] > -1) {
++num_pos;
}
}
num_sel = std::min(static_cast(num_pos * neg_pos_ratio), num_sel); //计算所需的负样本数量
} else if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_HARD_EXAMPLE) { //如果挖掘类型为HARD_EXAMPLE
CHECK_GT(sample_size, 0);
num_sel = std::min(sample_size, num_sel); //负样本数量由sample_size决定
}
// Select samples.
if (has_nms_param && nms_threshold > 0) { //SSD采用MAX_NEGATIVE挖掘类型,不需要在此做非极大值抑制
// Do nms before selecting samples. 在挑选样本前先进行非极大值抑制
vector sel_loss;
vector sel_bboxes;
if (use_prior_for_nms) { //为true,则使用默认框做非极大值抑制
for (int m = 0; m < match_indices[label].size(); ++m) { //循环遍历所有默认框
if (IsEligibleMining(mining_type, match_indices[label][m],
match_overlaps.find(label)->second[m], neg_overlap)) {
sel_loss.push_back(loss[m]);
sel_bboxes.push_back(prior_bboxes[m]);
}
}
} else { //use_prior_for_nms = false时采用预测框做NMS,故需要先进行预测数据解码
// Decode the prediction into bbox first.
vector loc_bboxes;
bool clip_bbox = false;
DecodeBBoxes(prior_bboxes, prior_variances,
code_type, encode_variance_in_target, clip_bbox,
all_loc_preds[i].find(label)->second, &loc_bboxes);
for (int m = 0; m < match_indices[label].size(); ++m) { //循环遍历所有预测框
if (IsEligibleMining(mining_type, match_indices[label][m],
match_overlaps.find(label)->second[m], neg_overlap)) {
sel_loss.push_back(loss[m]);
sel_bboxes.push_back(loc_bboxes[m]);
}
}
}
// Do non-maximum suppression based on the loss.
vector nms_indices;
ApplyNMS(sel_bboxes, sel_loss, nms_threshold, top_k, &nms_indices);
if (nms_indices.size() < num_sel) {
LOG(INFO) << "not enough sample after nms: " << nms_indices.size();
}
// Pick top example indices after nms.
num_sel = std::min(static_cast(nms_indices.size()), num_sel);
for (int n = 0; n < num_sel; ++n) {
sel_indices.insert(loss_indices[nms_indices[n]].second);
}
} else { //不进行非极大值抑制,直接根据损失排序选择最终所需的负样本
// Pick top example indices based on loss.
std::sort(loss_indices.begin(), loss_indices.end(),
SortScorePairDescend); //根据损失降序排序
for (int n = 0; n < num_sel; ++n) {
sel_indices.insert(loss_indices[n].second);
}
}
// Update the match_indices and select neg_indices. 利用sel_indices更新match_indices和neg_indices
for (int m = 0; m < match_indices[label].size(); ++m) {//循环遍历所有预测框
if (match_indices[label][m] > -1) { //此部分没理解,应该是其他论文中定义了HARD_EXAMPLE类型的具体做法,SSD没使用此类型,暂不深究
if (mining_type == MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_HARD_EXAMPLE &&
sel_indices.find(m) == sel_indices.end()) {
match_indices[label][m] = -1;
*num_matches -= 1;
}
} else if (match_indices[label][m] == -1) {
if (sel_indices.find(m) != sel_indices.end()) {
neg_indices.push_back(m);
*num_negs += 1; //记录所有输入图像总的所挑选出的负样本数目
}
}
}
}
all_neg_indices->push_back(neg_indices); //将当前输入图像上的所有挑选出的负样本存放入all_neg_indices
}
}
阅读此函数真的需要很大的勇气和耐心。不过由于SSD用到的负样本挖掘模式是MAX_NEGATIVE,所以HARD_EXAMPLE模式部分可以不用看,即在此博客中,暂时忽略了计算定位损失的函数ComputeLocLoss()和用于非极大抑制的函数ApplyNMS(),感兴趣的同学可以自行研读。
此函数先是计算置信度损失,就是对全部预测框,计算其置信度损失,无论该预测框中的是目标还是背景,均按softmax损失函数计算损失值,然后根据正样本的数目以及规定的正负样本比例计算出所需要的负样本数目N(如果负样本数目本来就小于这个计算出来的值N,则全部当作负样本),然后按照损失从高到低排列,挑选出前N个当作负样本,写入负样本索引中。
详细的挖掘条件,可参见SSD论文2.2节部分的Hard negative mining部分。
EncodeLocPrediction
函数申明如下:
// Encode the localization prediction and ground truth for each matched prior.
// all_loc_preds: stores the location prediction, where each item contains
// location prediction for an image.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth bboxes for the batch.
// all_match_indices: stores mapping between predictions and ground truth.
// prior_bboxes: stores all the prior bboxes in the format of NormalizedBBox.
// prior_variances: stores all the variances needed by prior bboxes.
// multibox_loss_param: stores the parameters for MultiBoxLossLayer.
// loc_pred_data: stores the location prediction results.
// loc_gt_data: stores the encoded location ground truth.
template
void EncodeLocPrediction(const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
Dtype* loc_pred_data, Dtype* loc_gt_data); 函数定义如下:
//得到编码后的预测框和地面实况框匹配对(用于后续计算定位损失)
template
void EncodeLocPrediction(const vector& all_loc_preds,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const vector& prior_bboxes,
const vector >& prior_variances,
const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
Dtype* loc_pred_data, Dtype* loc_gt_data) {
int num = all_loc_preds.size(); //输入图像数目
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_match_indices.size());
// Get parameters.
const CodeType code_type = multibox_loss_param.code_type(); //编码/解码类型
const bool encode_variance_in_target =
multibox_loss_param.encode_variance_in_target(); //是否在目标函数中编码(默认为false)
const bool bp_inside = multibox_loss_param.bp_inside(); //如果为true,则当encode_type为CORNER或CORNER_SIZE时,仅在图像区域内的corner上反向传播(默认为false)
const bool use_prior_for_matching =
multibox_loss_param.use_prior_for_matching(); //是否使用默认框进行匹配
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { //遍历所有输入图像
for (map >::const_iterator
it = all_match_indices[i].begin();
it != all_match_indices[i].end(); ++it) { //遍历所有类别
const int label = it->first;
const vector& match_index = it->second;
CHECK(all_loc_preds[i].find(label) != all_loc_preds[i].end());
const vector& loc_pred =
all_loc_preds[i].find(label)->second;
for (int j = 0; j < match_index.size(); ++j) { //遍历所有的预测框
if (match_index[j] <= -1) { //如果没有匹配对象,直接跳过
continue;
}
// Store encoded ground truth. 存储编码后的地面实况
const int gt_idx = match_index[j];
CHECK(all_gt_bboxes.find(i) != all_gt_bboxes.end());
CHECK_LT(gt_idx, all_gt_bboxes.find(i)->second.size());
const NormalizedBBox& gt_bbox = all_gt_bboxes.find(i)->second[gt_idx];
NormalizedBBox gt_encode;
CHECK_LT(j, prior_bboxes.size());
//编码地面实况框(对应于论文2.2节,类似与Fast R-CNN)
EncodeBBox(prior_bboxes[j], prior_variances[j], code_type,
encode_variance_in_target, gt_bbox, >_encode); //此函数实际上是把地面实况框的左上角和右下角模式编码为中心坐标加长宽模式
loc_gt_data[count * 4] = gt_encode.xmin();
loc_gt_data[count * 4 + 1] = gt_encode.ymin();
loc_gt_data[count * 4 + 2] = gt_encode.xmax();
loc_gt_data[count * 4 + 3] = gt_encode.ymax();
// Store location prediction. 存储定位预测
CHECK_LT(j, loc_pred.size());
if (bp_inside) { //为真时,只对在图像区域内的预测框进行反向传播,即利用地面实况框来模拟不在范围内的预测框的0梯度
NormalizedBBox match_bbox = prior_bboxes[j]; //如果use_prior_for_matching = true,则match_bbox就为相应的默认框
if (!use_prior_for_matching) {//否则需要先进行解码,得到真正的预测框信息(原始的预测信息是编码后的,需要转化为相应的左上角和右下角坐标),再进行判断是否在图像区域内
const bool clip_bbox = false;
//解码
DecodeBBox(prior_bboxes[j], prior_variances[j], code_type,
encode_variance_in_target, clip_bbox, loc_pred[j],
&match_bbox);
}
// When a dimension of match_bbox is outside of image region, use
// gt_encode to simulate zero gradient. 当match_bbox的维度在图像区域之外时,使用gt_encode来模拟零梯度
loc_pred_data[count * 4] =
(match_bbox.xmin() < 0 || match_bbox.xmin() > 1) ?
gt_encode.xmin() : loc_pred[j].xmin();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 1] =
(match_bbox.ymin() < 0 || match_bbox.ymin() > 1) ?
gt_encode.ymin() : loc_pred[j].ymin();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 2] =
(match_bbox.xmax() < 0 || match_bbox.xmax() > 1) ?
gt_encode.xmax() : loc_pred[j].xmax();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 3] =
(match_bbox.ymax() < 0 || match_bbox.ymax() > 1) ?
gt_encode.ymax() : loc_pred[j].ymax();
} else { //都需要进行反向传播
loc_pred_data[count * 4] = loc_pred[j].xmin();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 1] = loc_pred[j].ymin();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 2] = loc_pred[j].xmax();
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + 3] = loc_pred[j].ymax();
}
if (encode_variance_in_target) { //这里就不是很清楚为何这么做了(不过SSD使用直接在bbox中编码)
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
CHECK_GT(prior_variances[j][k], 0);
loc_pred_data[count * 4 + k] /= prior_variances[j][k];
loc_gt_data[count * 4 + k] /= prior_variances[j][k];
}
}
++count;
}
}
}
}
此函数实际上是为了方便后续调用caffe中的损失函数层计算前向传播用的,基本思想就是为匹配上地面实况框的预测框分配对应的地面实况框编码后的数据,方便损失函数中一一对应计算损失值(一一对应就是索引对齐的意思)。注意一个地面实况框可以对应多个预测框,但一个预测框只对应一个地面实况框。
相应的编码过程参见函数EncodeBBox()。
EncodeConfPrediction
函数申明如下:
// Encode the confidence predictions and ground truth for each matched prior.
// conf_data: num x num_priors * num_classes blob.
// num: number of images.
// num_priors: number of priors (predictions) per image.
// multibox_loss_param: stores the parameters for MultiBoxLossLayer.
// all_match_indices: stores mapping between predictions and ground truth.
// all_neg_indices: stores the indices for negative samples.
// all_gt_bboxes: stores ground truth bboxes for the batch.
// conf_pred_data: stores the confidence prediction results.
// conf_gt_data: stores the confidence ground truth.
template
void EncodeConfPrediction(const Dtype* conf_data, const int num,
const int num_priors, const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const vector >& all_neg_indices,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
Dtype* conf_pred_data, Dtype* conf_gt_data); 函数定义如下:
//解码所需要的置信度数据和地面实况
/*
参数conf_data:存储着所有的置信度数据
参数num:输入的图像数目
参数num_priors:默认框数目
参数multibox_loss_param:存储着multibox_loss层的设置参数
参数all_match_indices:存储着所有预测框和地面实况框的匹配对
参数all_neg_indices:存储着所有的负样本索引号
参数all_gt_bboxes:存储着所有地面实况框信息
参数conf_pred_data:输出参数,保存所需要的置信度数据
参数conf_gt_data:输出参数,保存所需要的地面实况数据(就是目标的标签信息)
*/
template
void EncodeConfPrediction(const Dtype* conf_data, const int num,
const int num_priors, const MultiBoxLossParameter& multibox_loss_param,
const vector > >& all_match_indices,
const vector >& all_neg_indices,
const map >& all_gt_bboxes,
Dtype* conf_pred_data, Dtype* conf_gt_data) {
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_match_indices.size());
// CHECK_EQ(num, all_neg_indices.size());
// Retrieve parameters.
CHECK(multibox_loss_param.has_num_classes()) << "Must provide num_classes.";
const int num_classes = multibox_loss_param.num_classes(); //类别数目
CHECK_GE(num_classes, 1) << "num_classes should not be less than 1.";
const int background_label_id = multibox_loss_param.background_label_id(); //背景类标签
const bool map_object_to_agnostic =
multibox_loss_param.map_object_to_agnostic(); //如果为true,则将所有目标类映射到不可知的类。它对于学习目标检测器很有用(默认为false)
if (map_object_to_agnostic) {
if (background_label_id >= 0) {
CHECK_EQ(num_classes, 2);
} else {
CHECK_EQ(num_classes, 1);
}
}
const MiningType mining_type = multibox_loss_param.mining_type(); //负样本挖掘类型
bool do_neg_mining;
if (multibox_loss_param.has_do_neg_mining()) {
LOG(WARNING) << "do_neg_mining is deprecated, use mining_type instead.";
do_neg_mining = multibox_loss_param.do_neg_mining();
CHECK_EQ(do_neg_mining,
mining_type != MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_NONE);
}
do_neg_mining = mining_type != MultiBoxLossParameter_MiningType_NONE;
const ConfLossType conf_loss_type = multibox_loss_param.conf_loss_type(); //加载置信度损失类型
int count = 0; //用于指针的索引
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { //循环遍历所有的输入图像
if (all_gt_bboxes.find(i) != all_gt_bboxes.end()) {
// Save matched (positive) bboxes scores and labels.
//以下保存正样本的置信度预测和标签
const map >& match_indices = all_match_indices[i];
for (map >::const_iterator it =
match_indices.begin(); it != match_indices.end(); ++it) { //循环遍历所有目标类别
const vector& match_index = it->second;
CHECK_EQ(match_index.size(), num_priors); //检查是否与默认框数目一致
for (int j = 0; j < num_priors; ++j) { //循环遍历所有的预测框
if (match_index[j] <= -1) { //无匹配对象的直接跳过
continue;
}
const int gt_label = map_object_to_agnostic ?
background_label_id + 1 :
all_gt_bboxes.find(i)->second[match_index[j]].label(); //获取与当前预测框匹配的地面实况框中目标的类别标签
int idx = do_neg_mining ? count : j;
//根据不同的置信度损失类型设置不同的地面实况
switch (conf_loss_type) {
case MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_SOFTMAX:
conf_gt_data[idx] = gt_label;
break;
case MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_LOGISTIC:
conf_gt_data[idx * num_classes + gt_label] = 1;
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown conf loss type.";
}
if (do_neg_mining) {
// Copy scores for matched bboxes.
caffe_copy(num_classes, conf_data + j * num_classes,
conf_pred_data + count * num_classes); //调用caffe_copy将相应的正样本置信度预测数据拷贝到conf_pred_data相应位置
++count;
}
}
}
//以下保存负样本的置信度预测和标签
if (do_neg_mining) {
// Save negative bboxes scores and labels.
for (int n = 0; n < all_neg_indices[i].size(); ++n) {
int j = all_neg_indices[i][n];
CHECK_LT(j, num_priors);
caffe_copy(num_classes, conf_data + j * num_classes,
conf_pred_data + count * num_classes); //调用caffe_copy将相应的负样本置信度预测数据拷贝到conf_pred_data相应位置
switch (conf_loss_type) {
case MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_SOFTMAX:
conf_gt_data[count] = background_label_id; //负样本的标签均为背景类
break;
case MultiBoxLossParameter_ConfLossType_LOGISTIC:
if (background_label_id >= 0 &&
background_label_id < num_classes) {
conf_gt_data[count * num_classes + background_label_id] = 1;
}
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown conf loss type.";
}
++count;
}
}
}
if (do_neg_mining) {
conf_data += num_priors * num_classes; //如果设置了负样本挖掘,则更新conf_data指针到下一张图(不需要挖掘的话,在进入此函数前就已经设置好conf_data了)
} else {
conf_gt_data += num_priors; //如果没设置负样本挖掘,则需要更新conf_gt_data指针到下一张图(挖掘的情况下,用count来索引,所以无需更新指针索引)
}
}
} 此函数实际上是为了方便后续调用caffe中的损失函数层计算前向传播用的,基本思想就是将挑选出的正负样本的类别置信度数据和地面实况中的类别标签对应上(负样本中的目标背景类,对应的标签为背景类标签)。