从零基础认识后台cms搭建
CMS系统搭建
D:
public List getCategoryList(long parentId) {
//根据parentId查询节点列表
TbContentCategoryExample example = new TbContentCategoryExample();
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andParentIdEqualTo(parentId);
//执行查询
List list = contentCategoryMapper.selectByExample(example);
List resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (TbContentCategory tbContentCategory : list) {
//创建节点
EUTreeNode node = new EUTreeNode();
node.setId(tbContentCategory.getId());
node.setText(tbContentCategory.getName());
node.setState(tbContentCategory.getIsParent()?"closed":"open");
resultList.add(node);
}
return resultList;
} M:List查询到的list是什么东西?
Z:Service层
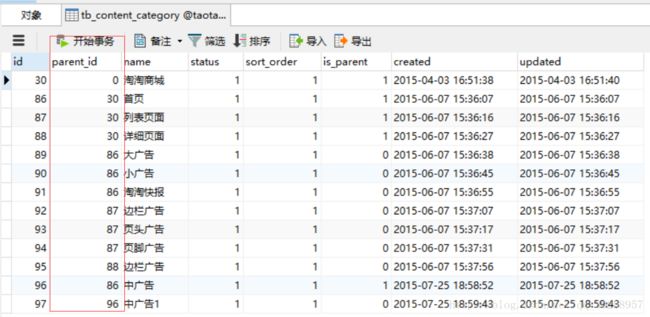
M:也就是说,如果parentId = 30,我可能会查到 首页,列表页面,详细页面 三个模块 。那这三个模块同一个parentId是有什么共同处呢?
D:这需要结合Controller来看:
@RequestMapping("/list")
@ResponseBody
public List getContentCatList(@RequestParam(value="id",defaultValue="0")Long parentId){
List list = contentCategoryService.getCategoryList(parentId);
return list;
} Z:@RequestParam(value="id",defaultValue="0")Long parentId
- 通过@PathVariable,例如/blogs/1
- 通过@RequestParam,例如blogs?blogId=1
当前台传来的与参数列表相同,为parentId,可以不用@RequestParam注解。而RequestParam注解还可以添加默认值。
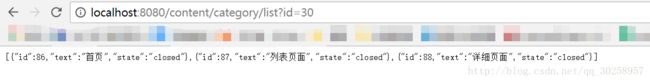
M:所以说,它第一次默认为parentId=0,根据数据库可以知道取到 淘淘商城 这个节点,而当点击 淘淘商城 时,它的id=30就作为parentId传到Controller,从而获得 首页 ,列表页面 ,详细页面 三个节点,以此类推构成以下动态加载的树状图。
M:那它是怎么以json的形式返回前端的呢?
Z:EUTreeNode是专门为了eTree而准备的model,这个model组成一个List,只要配合@ResponseBody的使用,就能返回为json数据。
【ResponseBody】一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用@RequestMapping后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,加上@Responsebody后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中。比如异步获取json数据,加上@responsebody后,会直接返回json数据。
D:
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.taotao.pojo.TbContentCategory">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="long" order="AFTER" useGeneratedKeys="true">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
selectKey>
insert into tb_content_category
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides="," >
<if test="id != null" >
id,
if>
<if test="parentId != null" >
parent_id,
if>
... public TaotaoResult insertContentCategory(long parentId, String name) {
//创建pojo
TbContentCategory contentCategory = new TbContentCategory();
contentCategory.setName(name); //设置主键返回
contentCategory.setIsParent(false); //新的叶子节点
contentCategory.setStatus(1); //1 正常 2 删除
contentCategory.setParentId(parentId);
contentCategory.setSortOrder(1);
contentCategory.setCreated(new Date());
contentCategory.setUpdated(new Date());
//添加记录到数据库中
contentCategoryMapper.insert(contentCategory);
//查看父节点的isParent是否为true
TbContentCategory parentCat = contentCategoryMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(parentId);
//判断是否为true
if(!parentCat.getIsParent()){
parentCat.setIsParent(true);
//更新父节点
contentCategoryMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(parentCat);
}
return TaotaoResult.ok(contentCategory);
}M:
"id" resultType="long" order="AFTER">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
这个是用来干嘛的?
Z:它可以做在 keyProperty=”id”列返回插入后生成的id值,order=”AFTER”表示在执行sql之后。
而他返回的id值不需要进行获取,会自动添加到contentCategoryMapper.insert(contentCategory);的contentCategory中。
M:那这一段的作用是什么?
//查看父节点的isParent是否为true
TbContentCategory parentCat = contentCategoryMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(parentId);
//判断是否为true
if(!parentCat.getIsParent()){
parentCat.setIsParent(true);
//更新父节点
contentCategoryMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(parentCat);
}Z:因为在一个叶子节点下一级添了一个叶子节点,所以原先的叶子节点就变成父节点,所以需要改变其父节点的IsParent为true,说明它是父节点。
M:那判断是不是父节点的作用无非就是节省updateByPrimaryKey的次数咯。
M:为什么每次都要返回生成的id呢?
D:Controller中
@RequestMapping("/create")
@ResponseBody
public TaotaoResult createContentCategory(Long parentId,String name){
TaotaoResult result = contentCategoryService.insertContentCategory(parentId, name);
return result;
}Z:因为他新增叶子节点调用Controller的时候需要传父id过来,还有新增的名字。而返回的id其实就会成为它子节点的parentId,拥有 父节点的id + 名字 就可以生成一个子节点了。
M:那SortOrder是干嘛用的?
Z:表示同级类目的展现次序,如数值相等则按名称次序排列。取值范围:大于零的整数。
D:
@Override
public TaotaoResult deleteByPrimaryKey(long id, long parentId) {
//删除记录
contentCategoryMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
//判断是否父节点是否变空
TbContentCategoryExample example = new TbContentCategoryExample();
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andParentIdEqualTo(parentId);
List list = contentCategoryMapper.selectByExample(example);
if(list.size()==0){ //子节点为空
TbContentCategory parentCat = contentCategoryMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(parentId);
parentCat.setIsParent(false);
}
return TaotaoResult.ok();
} M:能解释下获取值的过程吗?
TbContentCategoryExample example = new TbContentCategoryExample();
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andParentIdEqualTo(parentId);
List list = contentCategoryMapper.selectByExample(example); Z:这是该逆向工程数据库的查询过程。
工具:首先需要一个example,通过example创建一个criteria,注入一个mapper对象。
过程:criteria用来存值,example作为mapper对象方法的值。
M:为什么删除旧的树节点时,传过来的parentId为空,而数据库却已有该字段?
Z:这个涉及到eTree创建的方式,到时再研究,目前还是不知道,有其他人知道吗?
D:eTree配合Dategrid显示,这里主要是pageHelper的使用。
public EUDataDridResult getContentList(int page, int rows, long categoryId) {
TbContentExample example = new TbContentExample();
//分页处理
PageHelper.startPage(page, rows);
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andCategoryIdEqualTo(categoryId);
List list = contentMapper.selectByExample(example);
//创建返回值对象
EUDataDridResult result = new EUDataDridResult();
result.setRows(list);
//取分页信息
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(list);
result.setTotal(pageInfo.getTotal());
return result;
} M:PageHelper.startPage(page, rows);在这里的作用是什么?
Z:这是分页插件的方法
PageHelper.startPage(page, rows);告诉插件查询第几页,多少条数据.- 则获取当前的总条数
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(list);
result.setTotal(pageInfo.getTotal()); M:那为什么要把数据放进EUDataDridResult里呢?
D:EUDataDridResult 的pojo
public class EUDataDridResult {
private long total;
private List rows;
...Z:EUDataDridResult存放的是 列信息 和 数据的长度,当它返回给datagrid的时候,datagrid就会根据该pojo将数据进行显示。
M:那long categoryId的作用是?
Z:因为是树节点,eTree每点击一下就会把categoryId作为参数传给Controller。
D:返回状态处理Controller
@RequestMapping("/list/{contentCategoryId}")
@ResponseBody
public TaotaoResult getContentList(@PathVariable Long contentCategoryId){
try {
List list = contentService.getContentList(contentCategoryId);
return TaotaoResult.ok(list);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return TaotaoResult
.build(500, ExceptionUtil.getStackTrace(e)); //出错状态码,错误消息
}
} M:为什么要包try…catch
Z:获取可能失败,所以要对过程捕捉异常处理。
M:那return TaotaoResult.ok(list);的list作用是什么?
D:ok()方法
public static TaotaoResult ok(Object data) {
return new TaotaoResult(data);
}
public TaotaoResult(Object data) {
this.status = 200;
this.msg = "OK";
this.data = data;
}Z:当我们返回ok方法时,他就会将 list + 状态码 + 状态信息 进行返回
M:那build方法return TaotaoResult.build(500, ExceptionUtil.getStackTrace(e)); 呢?
D:build()方法
public static TaotaoResult build(Integer status, String msg) {
return new TaotaoResult(status, msg, null);
}Z:与ok()方法相似, 区别就是build()方法的状态码和状态信息由自己手动添加。
M:但是状态信息要怎么写呢,状态码对应的状态信息我也不清楚呢?
Z:所以这里提供了工具类ExceptionUtil,用来返回状态信息:ExceptionUtil.getStackTrace(e)。
D:其实也不过是控制台的信息toString返回而已
public static String getStackTrace(Throwable t) {
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw);
try {
t.printStackTrace(pw);
return sw.toString();
} finally {
pw.close();
}
}M:怎么让轮播图显示呢?
D:protal工程的Service文件
@Value("${REST_BASE_URL}")
private String REST_BASE_URL;
@Value("${REST_INDEX_AD_URL}")
private String REST_INDEX_AD_URL;
@Override
public String getContentList() {
//调用服务层的服务
String result = HttpClientUtil.doGet(REST_BASE_URL + REST_INDEX_AD_URL);
//把字符串转化为TaotaoResult
try{
TaotaoResult taotaoResult = TaotaoResult.formatToList(result, TbContent.class);
//取内容列表
List list = (List)taotaoResult.getData();
List M:这个注入代码是干嘛用的呢?
@Value("${REST_BASE_URL}")
private String REST_BASE_URL;D:properties文件
#服务层属性定义
#基础url
REST_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8081/rest
#首页大广告Url
REST_INDEX_AD_URL=/content/list/89Z:这就是读取配置文件的信息,注入到变量中,由于该信息可能经常变动,所以使用配置文件存起来。
M:String result = HttpClientUtil.doGet(REST_BASE_URL + REST_INDEX_AD_URL);这段代码是干嘛用的呢?
Z:HttpClientUtil是封装HttpClient的一个工具类,通过这个工具类能访问到指定url的数据,可以使用GET请求或者POST请求。
D:doGet的源码
public static String doGet(String url) {
return doGet(url, null);
}
public static String doGet(String url, Map param) {
// 创建Httpclient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
String resultString = "";
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 创建uri
URIBuilder builder = new URIBuilder(url);
if (param != null) {
for (String key : param.keySet()) {
builder.addParameter(key, param.get(key));
}
}
URI uri = builder.build();
// 创建http GET请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
// 执行请求
response = httpclient.execute(httpGet);
// 判断返回状态是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
resultString = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
httpclient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return resultString;
} Z:当前请求的param为null,而当添加map作为参数的时候,就可以执行带参数GET请求。
M:虽然没什么作用,但我想知道HttpClient对象是怎么创建来的。CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
Z:这个有点偏题, 我们只要知道它可以创建HttpClient实例即可。
M:那创建uri又是怎么实现的呢?URIBuilder builder = new URIBuilder(url);
D: URIBuilder.class的构造方法
public URIBuilder(final String string) throws URISyntaxException {
super();
digestURI(new URI(string));
}Z:它这里调用了super()方法,该方法是调用父类的构造函数,其父类为Object,
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}从上面的代码中看到Object类定义了一个静态初始化块,我们知道当创建Java对象时,系统总是先调用静态初始化块,静态初始化块中调用了registerNatives()方法,在Java中使用 native 关键字修饰的方法,说明此方法并不是由Java中完成的,而是通过C/C++来完成的,并被编译成.dll,之后才由Java调用。方法的具体实现是在dll文件中,当然对于不同平台实现的细节也有所不同,以上registerNatives()方法主要作用就是将C/C++中的方法映射到Java中的native方法,实现方法命名的解耦。(来源)
而digestURI(new URI(String))的方法则执行了以下多个方法,这里将不深入做研究了,关于一些源码,大概知道既可以了:
private void digestURI(final URI uri) {
this.scheme = uri.getScheme();
this.encodedSchemeSpecificPart = uri.getRawSchemeSpecificPart();
this.encodedAuthority = uri.getRawAuthority();
this.host = uri.getHost();
this.port = uri.getPort();
this.encodedUserInfo = uri.getRawUserInfo();
this.userInfo = uri.getUserInfo();
this.encodedPath = uri.getRawPath();
this.path = uri.getPath();
this.encodedQuery = uri.getRawQuery();
this.queryParams = parseQuery(uri.getRawQuery(), Consts.UTF_8);
this.encodedFragment = uri.getRawFragment();
this.fragment = uri.getFragment();
}M:那代码TaotaoResult taotaoResult = TaotaoResult.formatToList(result, TbContent.class);是用来干嘛的呢?
D:TaotaoResult.java里的formatToList()方法
/**
* Object是集合转化
* @param jsonData json数据
* @param clazz 集合中的类型
* @return
*/
public static TaotaoResult formatToList(String jsonData, Class clazz) {
try {
JsonNode jsonNode = MAPPER.readTree(jsonData);
JsonNode data = jsonNode.get("data");
Object obj = null;
if (data.isArray() && data.size() > 0) {
obj = MAPPER.readValue(data.traverse(),
MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructCollectionType(List.class, clazz));
}
return build(jsonNode.get("status").intValue(), jsonNode.get("msg").asText(), obj);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}Z:jsonData是传过来的json数据,而clazz是指定的pojo,该方法会将json数据根据pojo将其转化为pojo对象。
M:for里面的数据应该是给属性赋值吧,但是在前端是怎么使用这些属性的呢?
for (TbContent tbContent : list) {
Map map =new HashMap<>();
map.put("src", tbContent.getPic());
map.put("height", 240);
map.put("width", 670);
map.put("srcB", tbContent.getPic2());
map.put("widthB", 550);
map.put("heightB", 240);
map.put("href", tbContent.getUrl());
map.put("alt", tbContent.getSubTitle());
resultList.add(map);
}Z:它在下面把map数据转化为json字符串之后,它就会返回给Controller页面,最后到达index.jsp页面。index.jsp页面会将数据逐个提取出来,拼接成标签进行显示:
;(function(cfg, doc) {
if ( !cfg.DATA_MSlide ) {
cfg.DATA_MSlide=[];
}
var data = ${ad1};
cfg.DATA_MSlide = data;
// 初始化一个广告信息
if ( cfg.DATA_MSlide.length > 1 ) {
var first = pageConfig.FN_GetCompatibleData( cfg.DATA_MSlide[0] );
var TPL = ''
+'
+''
+''" target="_blank" title="'+ first.alt +'">'
+' '" width="'+ first.width +'" height="'+ first.height +'" >'
+''
+''
+'';
doc.write(TPL);
}
})(pageConfig, document);;
'" width="'+ first.width +'" height="'+ first.height +'" >'
+''
+''
+'';
doc.write(TPL);
}
})(pageConfig, document);;M:原来是这样实现轮播图管理的。