Qt之自绘制饼图
文章目录
- 1、说明
- 2、效果展示
- 3、思路分析
- 4、源码解说
- 5、测试代码
- 6、示例下载
1、说明
最近在搞绘图方面的工作,说实话C++的第三方绘图库并不算多,总之我了解的有:qtcharts、ChartDirector、qwt、kdchart和QCustomPlot。这几个库各有利弊。
- qtcharts:qt5.7之后才开源的模块,支持绘制各种图标,并且功能相当丰富,但是可扩展性差,如果自己想高度定制,比较困难,主要是和qt的源码风格有决定性的关系。
- ChartDirector:开源的第三方绘图库,使用方便,推荐使用
- qwt:主要绘制仪表盘类似的东西(这个库可以编译后加入qt帮助文档)
- kdchart:不仅可以绘制图表,而且可以绘制甘特图,功能也都挺好使,我个人之前在qt4.7的时候使用过
- QCustomPlot:简答的绘图库,因为只有两个文件,如果想高度定制我个人推荐这个靠谱,毕竟理解起来容易些
2、效果展示
下边是绘制的饼图展示效果,当然了不能满足大多数人的需要,我主要是在这里提供一种思路,如果需要在绘制上有所调整的小伙伴可以下载demo自行修改。
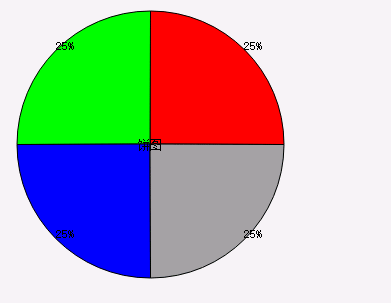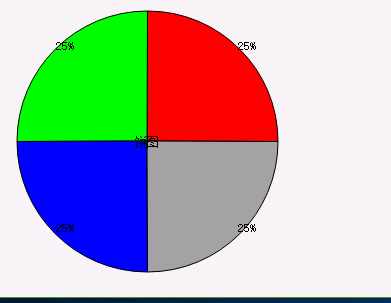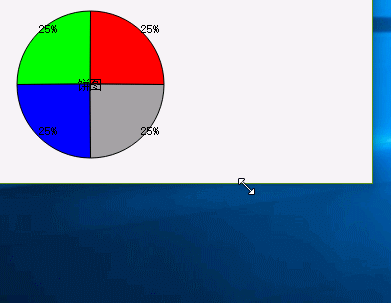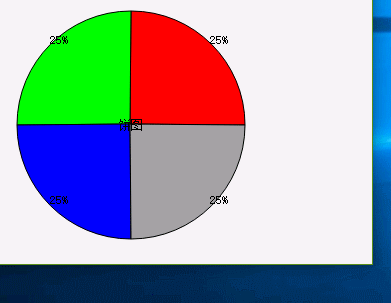
图1 展示图1
图2 展示2
图3 展示图3
3、思路分析
上边三张展示图,如果要说从理解难以成都来说,展示图3是比较容易理解。下边我就几个需要注意的细节描述下:
- 图表矩形距离边框距离,影响图表绘制矩形的因素
- 图表绘制方向,默认是逆时针
- 图表文本描述位置
- legend描述位置,demo中已经提供了接口,可以支持不同legend的展现形式
- 箭头长短
- 空心饼图(圆环图)
饼图绘制关键步骤:
- 添加数据项->构造数据缓存->绘制图表
- 窗口大小变化->构造数据项矩形->构造数据缓存->绘制图表
4、源码解说
首先来看两个结构体,主要是用来缓存数据,PieItemPrivate存储的是每一个item项的内容,包括item的legend,文本、颜色、值和一些辅助的结构体;PieChartPrivate结构是饼图类的私有数据存储结构,具体含义看注释
struct PieItemPrivate
{
PieItem item;//用户插入数据时的结构,包括注释、值和颜色
QPainterPath path;//项绘制时区域
QPoint labelPos;//文本位置
QRect m_LegendRect;//legend的矩形
};
struct PieChartPrivate
{
bool m_bLegendVisible = false;//是否显示图例
int m_Minx = 25;//左右最小边距
int m_Miny = 25;//上下最小边距
int m_MinDiameter = 130;//饼图最小直径
int m_RingWidth = 0;//如果是环,环的宽度
int m_StartRotationAngle = 0;//绘制item项的时候,其实角度
int m_LegendWidth = 100;//图表宽度 可以在插入新数据项的时候更新,计算展示legend所需要的最小尺寸
int m_LegendHeight = 30;//图例高度 可以在插入新数据项的时候更新,计算展示legend所需要的最小尺寸
double m_SumValue = 0;//所有item的value和
QRect m_PieRect;//饼图绘制矩形
QColor m_LabelColor = QColor(0, 0, 0);//百分比文字颜色
QString m_RingLabel = QStringLiteral("饼图");//图表中心文字描述
QVector m_Items;//图表项
};
1、当有新数据或者窗口大小发生变化时,计算数据缓存
void PieChart::ConstructData()
{
int pos = d_ptr->m_StartRotationAngle;
int angle;
QPainterPath subPath;
subPath.addEllipse(d_ptr->m_PieRect.adjusted(d_ptr->m_RingWidth, d_ptr->m_RingWidth, -d_ptr->m_RingWidth, -d_ptr->m_RingWidth));
for (auto iter = d_ptr->m_Items.begin(); iter != d_ptr->m_Items.end(); ++iter)
{
angle = 16 * iter->item.value / d_ptr->m_SumValue * 360;
QPainterPath path;
path.moveTo(d_ptr->m_PieRect.center());
path.arcTo(d_ptr->m_PieRect.x(), d_ptr->m_PieRect.y(), d_ptr->m_PieRect.width(), d_ptr->m_PieRect.height(), pos / 16.0, angle / 16.0);
path.closeSubpath();
if (d_ptr->m_RingWidth > 0 && d_ptr->m_RingWidth <= d_ptr->m_PieRect.width() / 2)
{
path -= subPath;
}
iter->path = path;
double labelAngle = (pos + angle / 2) / 16;
double tx = (d_ptr->m_PieRect.width() - d_ptr->m_RingWidth) / 2 * qCos(labelAngle / 360 * 2 * 3.1415926);
double ty = -(d_ptr->m_PieRect.width() - d_ptr->m_RingWidth) / 2 * qSin(labelAngle / 360 * 2 * 3.1415926);
iter->labelPos = QPoint(tx, ty) + d_ptr->m_PieRect.center();
pos += angle;
}
}
2、当窗口大小发生变化时,重新计算各项所在矩形,ConstructRect方式是用来计算各子项矩形区域的,内部调用ConstructCornerLayout方法是生产制定的布局,有兴趣的小伙伴可以写自己的矩形区域计算方式,开达到不同的绘制效果。
void PieChart::ConstructRect(const QSize & size)
{
switch (d_ptr->m_Items.size())
{
case 4:
ConstructCornerLayout(size);
default:
break;
}
}
//该方法是针对4个legend,并且在四角的位置所计算的布局方式,小伙伴也可以实现自己的布局计算,然后在ConstructRect接口中调用
void PieChart::ConstructCornerLayout(const QSize & size)
{
int currentR = d_ptr->m_MinDiameter;
int diameter;
int horiWidth = size.width();
if (d_ptr->m_bLegendVisible)
{
horiWidth -= d_ptr->m_LegendWidth * 2;
}
if (horiWidth > size.height())
{
diameter = size.height();
}
else
{
diameter = horiWidth;
}
int x, y;
int r = diameter - d_ptr->m_Minx * 2;
currentR = r > currentR ? r : currentR;
if (d_ptr->m_bLegendVisible)
{
x = d_ptr->m_Minx + d_ptr->m_LegendWidth;
y = (size.height() - currentR) / 2;
//计算4个legend位置
d_ptr->m_Items[1].m_LegendRect = QRect(d_ptr->m_Minx, d_ptr->m_Miny, d_ptr->m_LegendWidth, d_ptr->m_LegendHeight);
d_ptr->m_Items[0].m_LegendRect = QRect(x + r, d_ptr->m_Miny, d_ptr->m_LegendWidth, d_ptr->m_LegendHeight);
d_ptr->m_Items[3].m_LegendRect = QRect(x + r, size.height() - d_ptr->m_Miny - 30, d_ptr->m_LegendWidth, d_ptr->m_LegendHeight);
d_ptr->m_Items[2].m_LegendRect = QRect(d_ptr->m_Minx, size.height() - d_ptr->m_Miny - 30, d_ptr->m_LegendWidth, d_ptr->m_LegendHeight);
}
else
{
x = d_ptr->m_Minx;
y = d_ptr->m_Miny;
}
d_ptr->m_PieRect = QRect(x, y, currentR, currentR);//计算饼图位置
}
5、测试代码
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
PieChart w;
w.AddData(100, Qt::red, "red");
w.AddData(100, Qt::green, "green");
w.AddData(100, Qt::blue, "blue");
w.AddData(100, Qt::gray, "gray");
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
6、示例下载
Qt之自绘制饼图
如果您觉得文章不错,不妨给个
打赏,写作不易,感谢各位的支持。您的支持是我最大的动力,谢谢!!!
很重要–转载声明
-
本站文章无特别说明,皆为原创,版权所有,转载时请用链接的方式,给出原文出处。同时写上原作者:朝十晚八 or Twowords
-
如要转载,请原文转载,如在转载时修改本文,请事先告知,谢绝在转载时通过修改本文达到有利于转载者的目的。