Python文件处理
慕课网上《Python文件处理》课程个人总结笔记,侵删。
慕课网视频课程链接:https://www.imooc.com/learn/416
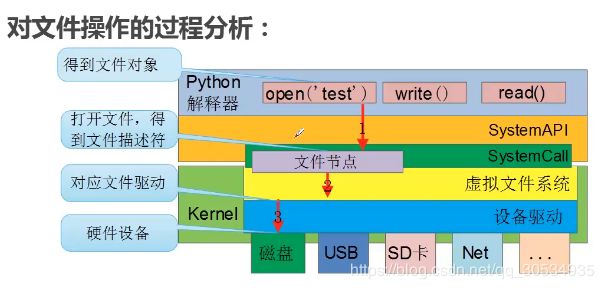
一、文件简介
1.1 课程简介和基本概念
文件:Python中文件是对象
linux文件:一切设备都可以是文件
文件属性:用户,读、写、执行权限
二、Python文件基础操作
2.1 python文件操作之文件打开方式
open(name,mode,buf)
name:文件路径
mode:打开方式
buf:缓冲区大小
文件打开方式:
r 只读方式打开 文件必须存在
w 只写方式打开 文件不存在则创建文件,存在则清空文件内容
a 追加方式打开 文件不存在则创建文件
r+/w+ 读写方式打开 r+从开始处覆盖,w+清空内容后写入
a+ 追加和读写方式打开
rb/wb/ab/rb+/wb+/ab+ 二进制方式打开,可用于读图片
可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37471638/article/details/82460732
2.2 python文件操作之文件读取方式
文件读取方式:
read(size): 读取文件size个字节
readline(size): 读取一行,每行读取size个字节
readlines(size_t): 读取满buf,返回每一行所组成的列表
iter: 使用迭代器读取文件,可以读完全部文件
默认size_t=8192*size,可用io.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE查看
代码示例:
//每次读取前需要close并重新open
f = open("imooc.txt")
c = f.read()
c = f.read(10)
c = f.readlines()
c = f.readlines(10)
c = f.readlines()
print(c)
f.close()
f = open("imooc.txt")
iter_r = iter(f)
for line in iter_r:
print(line)
f.close()
2.3 python文件操作之文件写入与写缓存
文件写入方式:
write(str): 将字符串写入文件
writelines(sequence_of_strings): 写多行到文件,参数为可迭代对象
代码示例:
//每次读取前需要close并重新open
f = open('imooc.txt','r’)
f.write('123456')
f.writelines(('1','2','3'))
f.writelines(['1','2','3'])
注意:写缓存机制,close后才会写入到文件中
python写磁盘时机:
1、主动调用close()或者flush方法,写缓存同步到磁盘
2、写入数据量大于或者等于写缓存,写缓存同步到磁盘
2.4 python文件操作之文件关闭
python文件为什么要关闭:
1、将写缓存同步到磁盘
2、linux系统中每个进程打开文件的个数是有限的
3、如果打开文件数到达系统限制,再次打开就会失败
查看:
# linux下
ps
cat /proc/20384/
limits
Max open files = 1024/4096
尝试示例:
#file.fileno 查看打开文件数目
list_f = []
for i in range(1025):
list_f.append(open('imooc.txt','w'))
print ("%d:%d" % (i,list_f[i].fileno())
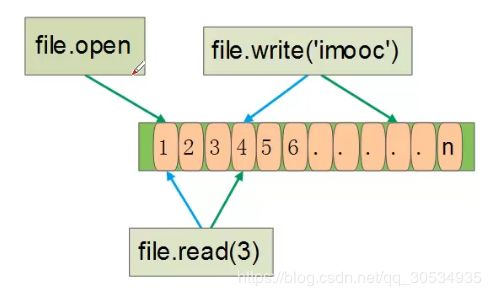
2.5 python文件操作之文件指针
python写入和读取问题:
1、写入文件后,必须打开才能读取写入内容
2、读取文件后,无法重新再次读取度过的内容
python文件指针操作:
seek(offset,whence)
offeset: 偏移量
whence: 偏移相对位置方式
python文件指针定位方式:
os.SEEK_SET: 相对文件起始位置 0
os.SEEK_CUR: 相对文件当前位置 1
os.SEEK_END: 相对文件结尾位置 2
代码示例:
#源文件为0123456789abcdef
f = open('imooc.txt','r+') //windows中用rb模式打开
import os
f.tell()
f.read(3)
f.seek(0,os.SEEK_SET)
f.tell()
f.read(3)
f.seek(0,os.SEEK_END) //windows中比其小1(因为linux中有\n)
f.tell()
f.seek(-5,os.SEEK_CUR)
f.tell()
f.read()
f.tell()
f.seek(0,os.SEEK_END) //报错,超出范围
f.seek(-17,os.SEEK_CUR)
三、文件属性及OS模块
3.1 python文件属性编码格式
python文件属性:
file.fileno(): 文件描述符
file.mode: 文件打开权限
file.encoding: 文件编码格式
file.closed: 文件是否关闭
python标准文件:
文件标准输入:sys.stdin
文件标准输出:sys.stdout
文件标准错误:sys.stderr
import sys
sys.stdout = print
python文件命令行参数:
根据参数不同完成不同功能
sys模块提供sys.argv属性,通过该属性可以得到命令航参数
sys.argv:字符串组成的列表
import sys
if __name__ == '__main__':
print (len(sys.argv))
for arg in sys.argv:
print (arg)
运行:python argv.py 0 1 2 3
python文件编码方式:
将unicode转换为utf-8 //python3中不需要转码
f = open('imooc.txt','w+')
a = unicode.encode(u'慕课','utf-8')
f.write(a)
f.close()
使用codecs模块提供方法创建指定编码格式文件
open(fname,mode,encoding,errors,buffering)
import codecs
f = codecs.open('test.txt','w','utf-8')
3.2 Linux文件系统简介
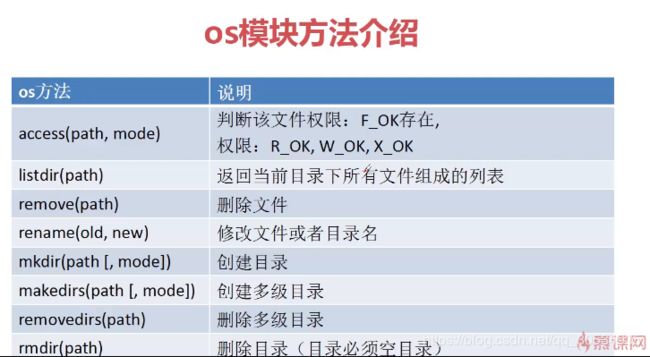
3.3 OS模块对文件和目录操作
使用os模块打开文件
open(filename,flag,mode)
flag:文件打开方式
os.O_CREAT 创建文件
os.O_RDONLY 只读方式打开
os.O_WRONLY 只写方式打开
os.O_RDWR 读写方式打开
使用os模块对文件进行操作(更加偏向于底层)
os.read(fd,buffersize): 读取文件
os.write(fd,string): 写入文件
os.lseek(fd,pos,how): 文件指针操作
os.close(fd): 关闭文件
fd为文件描述符
代码示例:
import os
fd = os.open('imooc.txt',os.O_CREAT|os.O_RDWR)
str = 'imooc'
str = str.encode()
n = os.write(fd,str)
l = os.lseek(fd,0,os.SEEK_SET)
s = os.read(fd,5)
f.close()
os.rename('imooc.txt','im.txt')
os.mkdir('test')
os.mkdir('te/rr/ttt/ee')
os.rmdir('test')
os.removedirs('te/rr/ttt/ee')
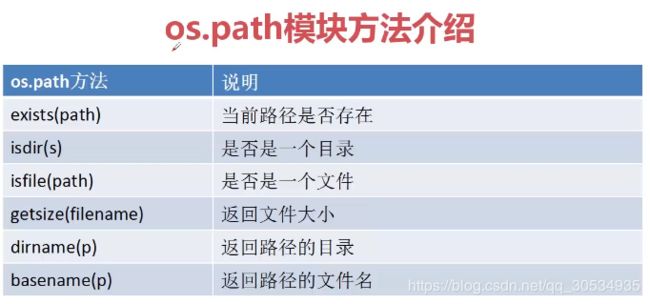
os.path.isdir('.')
os.path.isdir('im.txt')
os.path.isfile('im.txt')
os.path.getsize('im.txt')
os.path.basename('im.txt')
os.path.dirname('im.txt')
四、文件练习
4.1 文件练习
练习内容:
使用python管理ini文件,实现查询、添加、删除、保存
练习目的:
1、掌握文件基本操作
2、认识ini文件
3、了解configparse
ini配置文件格式:
节: [session]
参数(键=值): name=value
例子: [port]
port1 = 8000
port2 = 2001
代码示例1:
'''
# im.txt的内容
[userinfo]
name = zhangru
pwd = 123
[study]
python_base = 15
python_junior = 20
linux_base_ = 15
'''
import configparser
cfg = configparser.configparser()
cfg.read('im.txt')
cfg.sections()
for se in cfg.sections():
print (se)
print (cfg.items(se))
cfg.set('userinfo','pwd','`123456')
cfg.set('userinfo','email','userimooc.com')
for se in cfg.sections():
print (se)
print (cfg.items(se))
cfg.remove_option('userinfo','email')
for se in cfg.sections():
print (se)
print (cfg.items(se))
代码示例2:
'''
# im.txt的内容同示例1
1: dump ini
2: del section
3: del item
4: modify item
5: add section
6: save modify
'''
# _*_ coding:utf8 _*_
import configparser
class student_info(object):
def __init__(self,recordfile):
self.logfile = recordfile
self.cfg = configparser.ConfigParser()
def cfg_load(self):
self.cfg.read(self.logfile)
def cfg_dump(self):
se_list = self.cfg.sections()
print ('----------------->')
for se in se_list:
print (se)
print (self.cfg.items(se))
print ('<-----------------')
def delete_item(self,section,key):
self.cfg.remove_option(section,key)
def delete_section(self,section):
self.cfg.remove_section(section)
def add_section(self,section):
self.cfg.add_section(section)
def set_item(self,section,key,value):
self.cfg.set(section,key,value)
def save(self):
fp = open(self.logfile,'w')
self.cfg.write(fp)
fp.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
info = student_info('im.txt')
info.cfg_load()
info.cfg_dump()
info.set_item('userinfo','pwd','abc')
info.cfg_dump()
info.add_section('login')
info.set_item('login','2015-0511','20')
info.cfg_dump()
info.save()