GitChat 《Spring Data JPA 实战》笔记
开篇:
课程介绍
Spring Data JPA课程介绍:
“现在的开发人员是站在巨人的肩上,弯道超车”
课程详细介绍:
本课的内容分为基础、进阶和深入,对 Spring Data JPA 的使用、手册、实战、源码分析等进行全面的讲解
所选的技术版本都是基于 Spring Boot 2.0 来讲解的,选择学习本课程内容,你已经在大多数开发人员领先一步
作者介绍
曾经先后在驴妈妈、携程、要买车公司担任过 Java 高级工程师、架构师、开发主管、技术经理等职务
第01课:整体认识 JPA
“未来已经来临,只是尚未流行”
MyBatis 以灵活著称,但是要维护复杂的配置
Spring Data JPA 与 Spring Boot 配合起来使用具有天然的优势
你会发现越来越多的公司的招聘要用会有传统的 SSH、Spring、MyBatis 要求,逐步的变为 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud、Spring Data 等 Spring 全家桶的要求
市场上 ORM 框架比对
- MyBatis:缺点就是工作量比较大,需要各种配置文件的配置和 SQL 语句。
- Hibernate:上手来说比较难,比较适合企业级的应用系统开发
- Spring Data JPA:可以理解为 JPA 规范的再次封装抽象,底层还是使用了 Hibernate 的 JPA 技术实现。
由于 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 在市场上的流行,Spring Data JPA 也逐渐进入大家的视野。
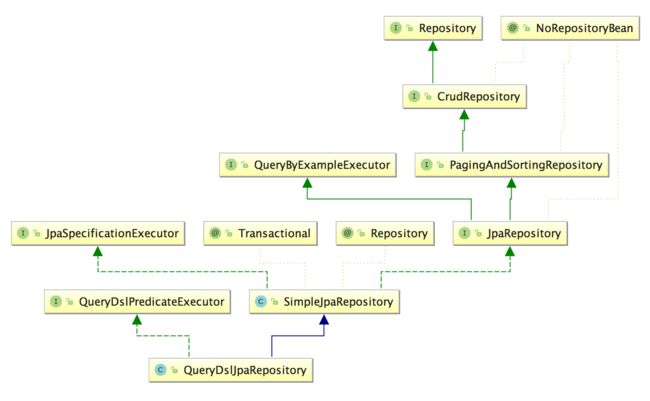
Spring Data JPA 的主要类及结构图
我们需要掌握和使用到的类
七个大 Repository 接口:
- Repository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- CrudRepository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- PagingAndSortingRepository(org.springframework.data.repository);
- JpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository);
- QueryByExampleExecutor(org.springframework.data.repository.query);
- JpaSpecificationExecutor(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository);
- QueryDslPredicateExecutor(org.springframework.data.querydsl)。
两大 Repository 实现类:
- SimpleJpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support);
- QueryDslJpaRepository(org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support)。
类的结构关系图如图所示
需要了解到的类,真正的 JPA 的底层封装类
- EntityManager(javax.persistence);
- EntityManagerImpl(org.hibernate.jpa.internal)。
MySQL 的快速开始实例
Repository
package com.example.example1;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;(或JpaRepository)
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository {
} Controller
package com.example.example1;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/demo")(或@RequestMapping("/demo"))
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping(path = "/add")
public void addNewUser(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam String email) {
User n = new User();
n.setName(name);
n.setEmail(email);
userRepository.save(n);
}
@GetMapping(path = "/all")
@ResponseBody
public Iterable getAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
} 第02课:JPA 基础查询方法 JpaRepository 详解
CrudRepository 方法详解
通过上面类关系图可以看到 CrudRepository 提供了公共的通用的 CRUD 方法。
CrudRepository interface 内容
package org.springframework.data.repository;
import java.util.Optional;
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository extends Repository {
S save(S entity);(1)
Iterable saveAll(Iterable entities);(2)
Optional findById(ID id);(3)
boolean existsById(ID id);(4)
Iterable findAll();(5)
Iterable findAllById(Iterable ids);(6)
long count();(7)
void deleteById(ID id);(8)
void delete(T entity);(9)
void deleteAll(Iterable entities);(10)
void deleteAll();(11)
}
第03课:定义查询方法(Defining Query Methods)
Spring Data JPA 的最大特色,利用方法名定义查询方法。
关键字列表
| 关键字 | 案例 | JPQL 表达 |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is,Equals | findByFirstname、findByFirstnameIs、findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age <= ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (参数增加前缀 %) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (参数增加后缀 %) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (参数被 % 包裹) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection |
… where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
| True | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| False | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
第04课:注解式查询方法
@Query 的分页
案例 4.7:直接用 Page 对象接受接口,参数直接用 Pageable 的实现类即可。
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository {
@Query(value = "select u from User u where u.lastname = ?1")
Page findByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
}
//调用者的写法
repository.findByFirstName("jackzhang",new PageRequest(1,10));
@Query 的优缺点与实战经验分享
| 分类 | 描述 |
| 优点 | (1)可以灵活快速的使用 JPQL 和 SQL |
| (2)对返回的结果和字段记性自定义 | |
| (3)支持连表查询和对象关联查询,可以组合出来复杂的 SQL 或者 JPQL | |
| (4)可以很好的表达你的查询思路 | |
| (5)灵活性非常强,快捷方便 | |
| 缺点 | (1)不支持动态查询条件,参数个数如果是不固定的不支持 |
| (2)有些读者会将返回结果用 Map 或者 Object[] 数组接收结果,会导致调用此方法的开发人员不知道返回结果里面到底有些什么数据 | |
| 实战经验 | (1)当出现很复杂的 SQL 或者 JPQL 的时候建议用视图 |
| (2)返回结果一定要用对象接收,最好每个对象里面的字段和你返回的结果一一对应 | |
| (3)动态的 Query Param 会在后面的章节中讲到 | |
| (4)能用 JPQL 的就不要用 SQL |
第05课:@Entity 实例里面常用注解详解
第06课:JpaRepository 扩展之 QueryByExampleExecutor
第07课:JpaRepository 扩展之 JpaSpecificationExecutor
第08课:JpaRepository 扩展之自定义 Repository
第09课:Auditing 与 @Version
第10课:对 MVCWeb 的支持分页和排序的支持
第11课:Spring Data JPA 的配置之 SpringBoot 2.0 加载详解
第12课:DataSource 的配置与事务详解、多数据源
第13课:Spring Data JPA 之 QueryDSL 支持
感谢张振华老师的达人课教程,本篇博客只是筛选了部分自己觉得重要的章节内容来学习。具体可以查看张振华老师的达人课。本篇博客为所做笔记,如果涉及到侵权行为,请告知,将立即删除。
原文链接:http://blog.maptoface.com/post/117