TensorFlow学习笔记:构建多分类任务模型(未完)
任务描述
识别手势:

如上图所示,对于多分类任务,输出一个独热码矩阵:即仅有一个元素为1,其他元素均为0的列向量。
数据
训练集:0-5的手势图片各180张,像素为64*64。
测试集:0-5的手势图片各20张,像素为64*64。
载入数据
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()数据处理
# Flatten the training and test images
X_train_flatten = X_train_orig.reshape(X_train_orig.shape[0], -1).T
X_test_flatten = X_test_orig.reshape(X_test_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# Normalize image vectors
X_train = X_train_flatten/255.
X_test = X_test_flatten/255.
# Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6)
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6)构建模型
构建一个三层多分类模型,其中最后一层使用SOFTMAX激活函数:
LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX
创建placeholder
placeholder常用于等待样本X与标记Y输入:
def create_placeholders(n_x, n_y):
"""
Creates the placeholders for the tensorflow session.
Returns:
X -- placeholder for the data input, of shape [n_x, None] and dtype "float"
Y -- placeholder for the input labels, of shape [n_y, None] and dtype "float"
"""
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="X",shape=[n_x,None])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="Y",shape=[n_y,None])
return X, Y初始化参数
对于权重参数 W[i] 使用Xavier初始化(详见He初始化方法,两者类似),对于偏差参数 b[i] 使用零初始化:
def initialize_parameters():
tf.set_random_seed(1)
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1",[25,12288],initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b1 = tf.get_variable("b1", [25,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2",[12,25],initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b2 = tf.get_variable("b2", [12,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3",[6,12],initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b3 = tf.get_variable("b3", [6,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
"W3": W3,
"b3": b3}
return parameters前向传播
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
W3 = parameters['W3']
b3 = parameters['b3']
Z1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W1,X),b1)
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1)
Z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W2,A1),b2)
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2)
Z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W3,A2),b3)
return Z3tf.matmul()为矩阵乘法。注意到这里并没有计算A3,因为在tensorflow中最后一层的线性输出会被直接用于计算损失。
计算损失
tensorflow提供了计算交叉熵损失的函数tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = ..., labels = ...),不过需要注意它接受的参数矩阵形状必须为(样本个数,样本类目数)。
def compute_cost(Z3, Y):
# to fit the tensorflow requirement for tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(...,...)
logits = tf.transpose(Z3)
labels = tf.transpose(Y)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels))
return cost反向传播与参数更新
使用框架时,通常不需要考虑反向传播的具体过程,因为所有的反向传播与参数更新在框架中能用一行代码来实现。
在实现损失函数之后,创建一个“优化器”对象,在一个会话中同时运行“优化器”与损失函数,它会根据给定的损失来按照制定方法与学习率进行优化。
整合模型
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.0001,
num_epochs = 1500, minibatch_size = 32, print_cost = True):
"""
Implements a three-layer tensorflow neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SOFTMAX.
Arguments:
num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs
"""
ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables
tf.set_random_seed(1)
seed = 3
(n_x, m) = X_train.shape
n_y = Y_train.shape[0] # n_y : output size
costs = [] # To keep track of the cost
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_x,n_y)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
Z3 = forward_propagation(X,parameters)
cost = compute_cost(Z3,Y)
# Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer.
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
epoch_cost = 0. #每对整个样本进行一次训练称为一个epoch
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed)
for minibatch in minibatches:
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
# Run the session to execute the "optimizer" and the "cost"
_ , minibatch_cost = sess.run([optimizer,cost],feed_dict={X:minibatch_X,Y:minibatch_Y})
epoch_cost += minibatch_cost / num_minibatches #取均值
# Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, epoch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
costs.append(epoch_cost)
# plot the cost
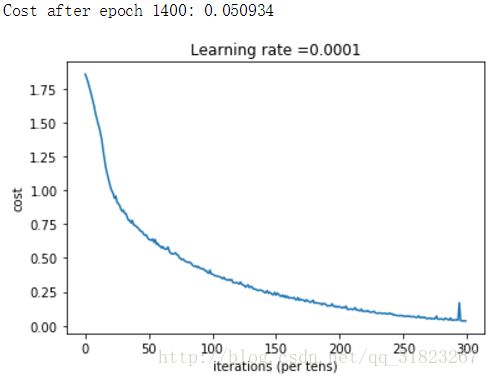
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
parameters = sess.run(parameters)
print ("Parameters have been trained!")
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(Z3), tf.argmax(Y))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print ("Train Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train}))
print ("Test Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test}))
return parameters训练模型
parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)