Qt容器类介绍,遍历容器
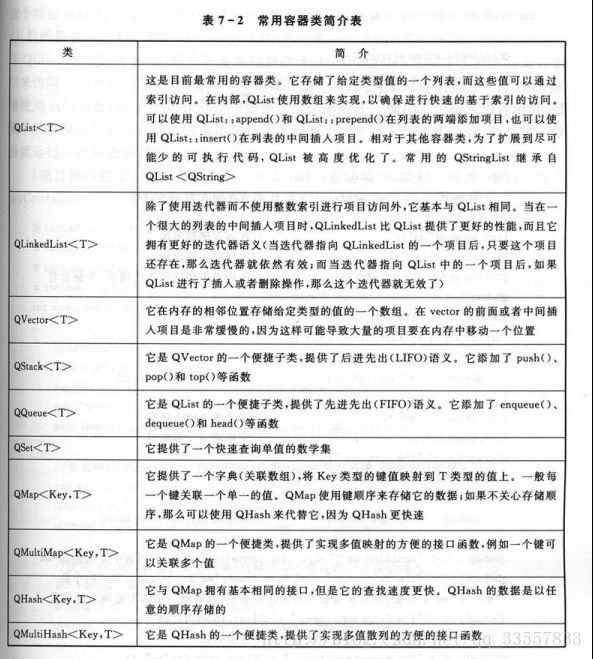
Qt容器:顺序容器、关联容器;
顺序容器:是指容器中的数据都为一个接一个的线性存储。如:QList、QLinkedList、QVector、QStack、QQueue;
关联容器:容器中数据以<键,值>模式存储。如:QMap、QMultiMap、QHash、QMultiHash、QSet;
例子:QMap
#include int>map;
//插入数据初始化
map["one"]=1;
map["three"] = 3;
//利用函数插入数据
map.insert("seven",7);
//获取键值,[]操作---------------》若map中无该键值,则自动插入
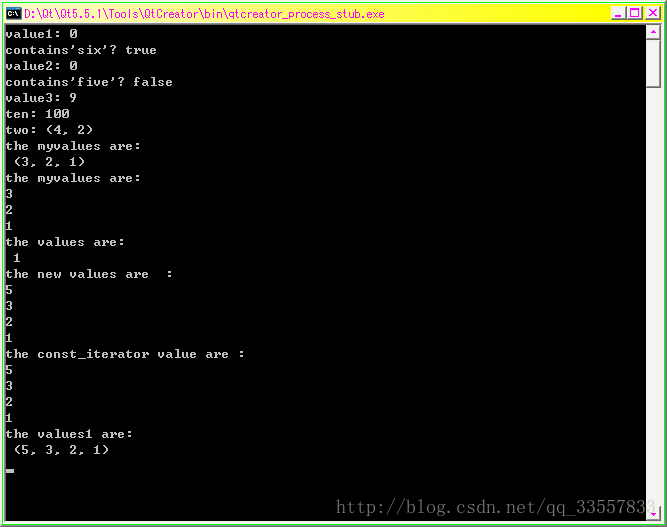
int value1=map["six"];
qDebug()<<"value1:"<"contains'six'?"<<map.contains("six");
//获取键值,value函数调用----------》若map中无该键值,则不会自动插入
int value2 = map.value("five");
qDebug()<<"value2:"<"contains'five'?"<<map.contains("five");
//当键不存在 value的返回值默认为0,亦可以自己设置,此处设为9
int value3 = map.value("nine",9);
qDebug()<<"value3:"<//map一键对应一值,若用insert函数给新键设值,旧值被覆盖掉
map.insert("ten",10);
map.insert("ten",100);
qDebug()<<"ten:"<<map.value("ten");
//用insertMulti函数实现一键多值,用values函数获取值列表
map.insertMulti("two",2);
map.insertMulti("two",4);
QList<int>values=map.values("two");
qDebug()<<"two:"<//用QMultiMap类实现一键多值
QMultiMapint>map1,map2,map3;
map1.insert("values",1);
map1.insert("values",2);
map2.insert("values",3);
//可进行相加,这样map3的“values”键将包含3,2,1三个值
map3 = map1+map2;
QList<int>myvalues=map3.values("values");
qDebug()<<"the myvalues are:\n"<"the myvalues are:";
for(int i=0;i"the values are:\n"<"values",1);
map3.insert("values",6);
map3.replace("values",5);//替换掉最新的值,即把6替换掉
//以下两种显示方式为迭代器方式在此仅供查询数据使用
qDebug()<<"the new values are :";
QMapint>::iterator i = map3.find("values");
while (i != map3.end() && i.key() == "values") {
qDebug() << i.value();
++i;
}
qDebug()<<"the const_iterator value are :";
QMapint>::const_iterator i1 = map3.find("values");
while (i1 != map3.end() && i1.key() == "values") {
qDebug() << i1.value();
++i1;
}
//将values的值存储在定义myvalues的Qlis容器中
QList<int>myvalues1=map3.values("values");
qDebug()<<"the values1 are:\n"<return a.exec();
} 注意数据的排列顺序;
遍历容器
迭代器提供一个统一的方法来访问容器中的项目。
迭代器:Jave风格、STL(标准模板库(Standard Template Library))风格;
两者比较:
Jave较STL使用方便,但性能上较弱与后者。
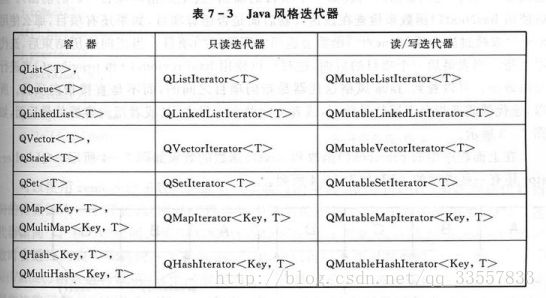
Jave风格迭代器:只读访问、读写访问;
例子:
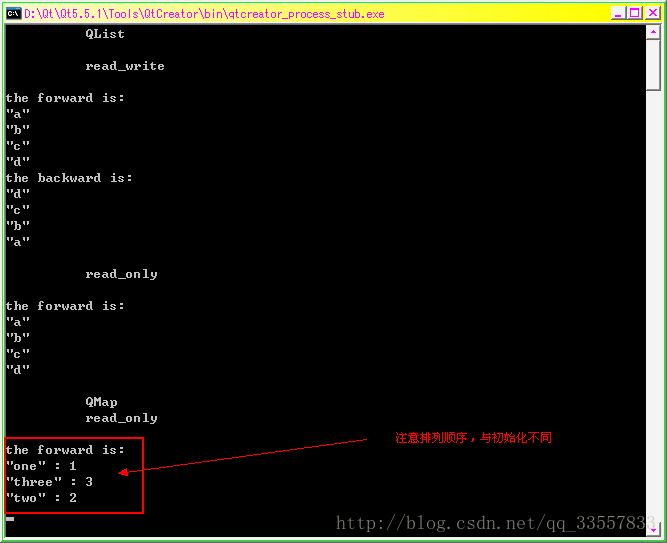
QList:
#include list; //容器list初始化
list<<"A"<<"B"<<"C"<<"D";
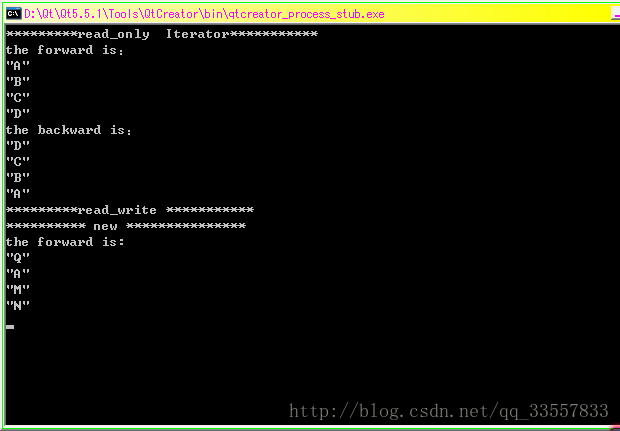
//只读模式:读取到的数据不可修改read_only
qDebug()<<"*********read_only Iterator***********";
QListIterator//移到最前面
i.toBack();//移到最后面
qDebug()<<"the backward is:";//反向遍历列表 D C B A
while(i.hasPrevious())
qDebug()<//读写模式
qDebug()<<"*********read_write ***********";
QMutableListIteratorj(list);
j.toBack();
while(j.hasPrevious())
{
QString str = j.previous();
if(str == "B")j.remove();//删除值为“B”的项目
}
j.insert("Q");//在列表最前面插入“Q”
j.toBack();//移到最后面
if(j.hasPrevious())j.previous()="N";//直接赋值
j.previous();
j.setValue("M");//函数赋值
j.toFront();//移到最前面
qDebug()<<"********** new ***************";
qDebug()<<"the forward is:";
while(j.hasNext())
{
qDebug()<return a.exec();
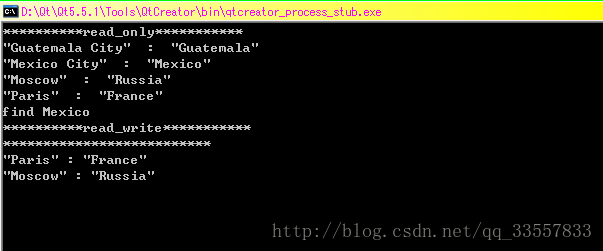
} QMap
代码如下:
#include map;
map.insert("Paris","France");
map.insert("Guatemala City","Guatemala");
map.insert("Mexico City","Mexico");
map.insert("Moscow","Russia");
//只读
qDebug()<<"**********read_only***********";
QMapIteratori(map);
i.toFront();
while(i.hasNext())
{
i.next();
qDebug()<.key()<<" : "<.value();
}
if(i.findPrevious("Mexico"))
qDebug()<<"find Mexico";
//读写
qDebug()<<"**********read_write***********";
QMutableMapIteratorj(map);
j.toFront();
while(j.hasNext())
{
#if 0
j.next();
qDebug()<.key()<<"::"<.value();
if(j.key().endsWith("City"))
j.remove();
#endif
#if 1 //等同于上面
//endWith()为QString类函数
//删除含City结尾的键的项目
if(j.next().key().endsWith("City"))
j.remove();
#endif
}
qDebug()<<"**************************";
j.toBack();
while(j.hasPrevious())//剩下的map
{
j.previous();
qDebug()<.key()<<":"<.value();
}
return a.exec();
}
STL风格迭代器:只读访问、读写访问;
其兼容Qt与STL的通用算法,在速度上进行优化;
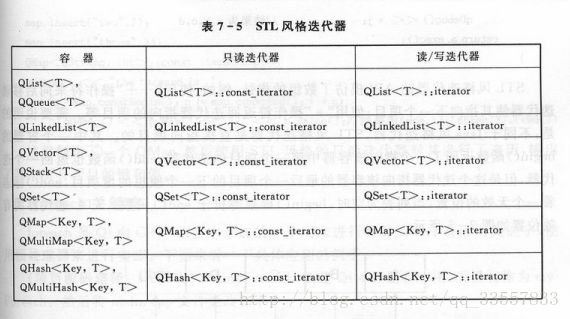

例子:
#include list;
list<<"A"<<"B"<<"C"<<"D";
//读写迭代器
qDebug()<<" read_write \n";
QList::const_iterator j;
qDebug()<<"the forward is:";
for(j=list.constBegin();j!=list.constEnd();++j)
{
qDebug()<<*j;
}
// QMap
qDebug()<<"\n QMap\n read_only \n";
QMapint>map;
map.insert("one",1);
map.insert("two",2);
map.insert("three",3);
QMapint>::const_iterator p;
qDebug()<<"the forward is:";
//注意输出的排列顺序是以字母的先后顺序排列的
for(p=map.constBegin();p!=map.constEnd();++p)
{
qDebug()<":"<return a.exec();
} foreach:是Qt向C++语言中添加的一个用来进行容器的顺序遍历的关键字,使用预处理器来进行实施。
例子:
#include list;
list.insert(0,"A");
list.insert(1,"B");
list.insert(2,"C");
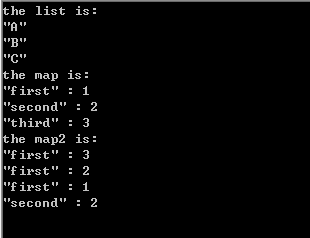
qDebug()<<"the list is:";
foreach (QString str,list) {
qDebug()<int>map;
map.insert("first",1);
map.insert("second",2);
map.insert("third",3);
qDebug()<<"the map is:";
foreach(QString str,map.keys())
qDebug()<":"<<map.value(str);
QMultiMapint>map2;
map2.insert("first",1);
map2.insert("first",2);
map2.insert("first",3);
map2.insert("second",2);
qDebug()<<"the map2 is:";
QListkeys = map2.uniqueKeys();
foreach(QString str,keys)
{
foreach (int i,map2.values(str)) {
qDebug()<":"<return a.exec();
} 不够完善请谅解,以后会慢慢添加的!
转:2种类型的迭代器的部分函数使用方式