kail端口扫描
全连接扫描,根据三次握手的完整性来判断端口是否存在
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
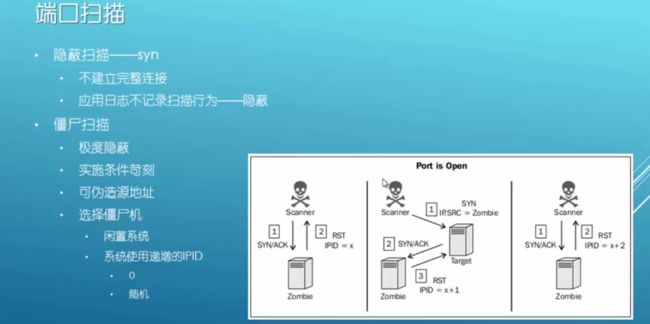
┃隐蔽端口扫描 ┃
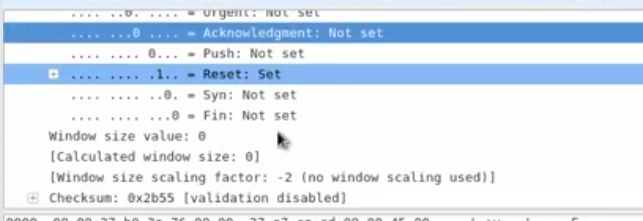
┃Syn—–syn/ack—–rst ┃
┃Scapy ┃
┃ sr1(IP(dst=”192.168.60.3”)/TCP(dport=80),timeout=1,verbose=1) ┃
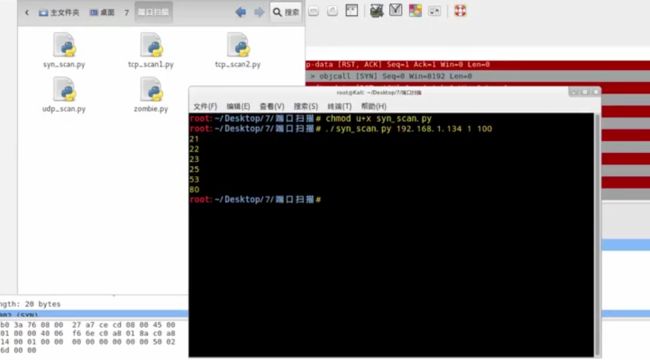
┃ ./syn_scan.py ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
Scapy Scapy是一个可以让用户发送、侦听和解析并伪装网络报文的Python程序。
首先进入scapy
然后构造包
![]()
先不要发送,因为是实验,所以打开wireshark来监听
然后
a.display()root@kali:~# scapy
WARNING: No route found for IPv6 destination :: (no default route?)
Welcome to Scapy (2.2.0)
>>> a=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.1.134")/TCP(dport=80),timeout=1,verbose=1)
>>>a.display
>>> a=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.1.134")/TCP(flags="S"dport=22),timeout=1)
>>> a=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.1.134")/TCP(flags="S"dport=2222),timeout=1)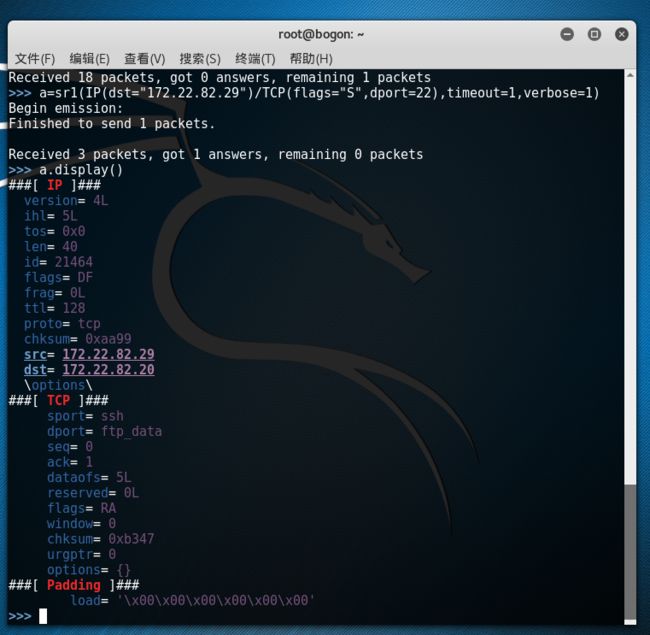
操作系统会认为这是一个没来由的sYn,ack;返回rst.我们没有建立握手,你莫名其妙给我发syn,拒绝
我们可以使用python脚本来扫描一个ip的端口
[syn_scan.py]
#!/usr/bin/python
import loggging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
import sys
if len(sys.argv)!=4;
print "Usage - ./syn_scan.py [Target.IP] [First Port] [Las Port]"
print "Example - ./syn_scan.py 1.1.1.5 1 100"
print "Example will TCP SYN port 1 thorough 100 om 10.0.0.5"
sys.exit()
ip=sys.argv[1]
start=int(sys.argv[2])
end=int(sys.argv[3]
for port in range(start,end);
a=str(IP(dst=ip)/UDP(dport=prot),timeout=1,verbose=0)
if a==None;
pass
else;
if(int(a(TCP),flags)==18;
print port
else
pass╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃隐蔽端口扫描 ┃
┃nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p 80,21,25,110,443 ┃
┃nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p 1-65535 --open ┃
┃nmap -sS 1.1.1.1 -p- --open ┃
┃nmap -sS -iL iplist.txt -p 80 ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
root@kali:~# nmap 192.168.1.134 -p1-100
Starting Nmap 6.49BETA5 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2015-10-01 23:01 CST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.134
Host is up (0.00068s latency).
Not shown: 94 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp open telnet
25/tcp open smtb
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
MAC Address: 80:00:27:B0:3A:76(Cadmus Computer Systems)
Nmap done: 1 IP address(1 host up) scanned in 5.72 seconds
root@kali:~# nmap 192.168.1.134 -p1-100 --open首先会解析主机名


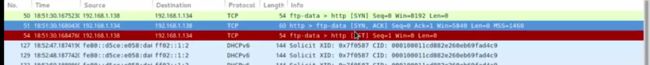
-S表示用syn扫描,没有像nmap进行dns解析,直接发包
-c发十个包,–spoof 伪造源地址,回包会回给伪造的源地址,所以wireshock抓不到包
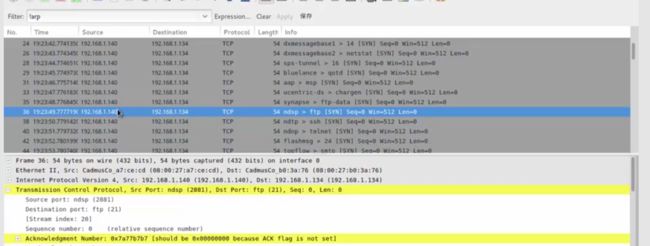 ,可以交换机做镜像端口来查看
,可以交换机做镜像端口来查看
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃隐蔽端口扫描 ┃
┃hping3 ┃
┃hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 80 -S ┃
┃hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 80,21,25,443 -S ┃
┃hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 0-65535 ┃
┃hping3 -c 10 -S --spoof 1.1.1.2 -p ++1 1.1.1.3 ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
root@kali:~# hping3 192.168.1.134 --scan 1-100 -S
Scanning 192.168.1.134 (192.168.1.134), port 1-100
100 ports to scan, use -V to see all the replies
+----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+
|port| serv name | flags |ttl| id | win | len |
+----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+
21 ftp : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
22 ssh : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
23 telnet : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
25 smtp : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
53 domain : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
80 http : .S..A... 64 0 5840 46
All replies received Done.
Not responding ports:
root@kali:~# hping3 -c 10 -S --spoof 1.1.1.2 -p ++1 1.1.1.3
HPING 1.1.1.3 (eth0 1.1.1.3): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes
--- 1.1.1.3 hping statistic ---
10 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 0.0/0.0/0.0 ms
root@kali:~# hping3 -c 10 -S --spoof 192.168.1.140 -p ++1 192.168.1.134
HPING 192.168.1.134 (eth0 192.168.1.134): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes
--- 192.168.1.134 hping statistic ---
10 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 0.0/0.0/0.0 ms
root@kali:~# hping3 -c 100 -S --spoof 192.168.1.140 -p ++1 192.168.1.134
HPING 192.168.1.134 (eth0 192.168.1.134): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes
--- 192.168.1.134 hping statistic ---
100 packets transmitted, 0 packets received, 100% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 0.0/0.0/0.0 ms╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃全连接端口扫描 ┃
┃Scapy ┃
┃ Syn扫描不需要raw packets ┃
┃ 内核认为syn/ack是非法包,直接发rst终端连接 ┃
┃ 全连接扫描对scapy比较困难 ┃
┃sr1(IP(dst=”192.168.20.2”)/TCP(dport=22,flags=’S’)) ┃
┃./tcp_scan1.py ┃
┃./tcp_scan2.py ┃
┃iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp –tcp-flags RST RST -d 192.168.20.2 -j DROP ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋

[tcp_scan1.py]
#!/usr/bin/python
import loggging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
response=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.60.4")/TCP(dport=80,flags='S'))
reply=sr1(IP(dst="192.168.60.4")/TCP(dport=80,flags='A',ack(response[TCP].seq+1)))[tcp_scan2.py]
#!/usr/bin/python
import loggging
logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
from scapy.all import *
SYN=IP(dst="192.168.1.134")/TCP(dport=25,flags='S')
print"-- SENT --"
SYN.display()
print"\n\n-- RECEIVED --"
response=sr1(SYN,timeout=1,verbose=0)
response.display()
if int(response[TCP].flags)==18;
print"\n\n-- SENT --"
A=IP(dst="192.168.1.134")/TCP(dport=25flags='A',ack(response[TCP].seq+1))
A.display()
print"\n\n-- RECEIVED --"
response2=sr1(A,timeout=1,verbose=0)
response2.display()
else;
print"SYN-ACK not returned"root@kali:~# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags RST RST -d 192.168.1.134 -j DROP把接收方发送的RST包DROP掉
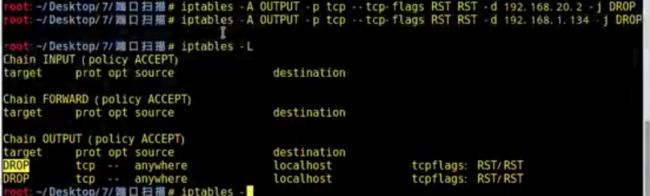
重新运行脚本测试,succeful
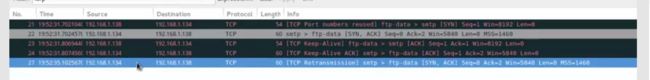
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃全连接端口扫描 ┃
┃nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 80 ┃
┃nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 80,21,25 ┃
┃nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 80-2000 ┃
┃nmap -sT -iL iplist.txt -p 80 ┃
┃默认1000个常用端口 ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
root@kali:~# nmap -sT 192.168.1.134 -p1-100
T表示全连接,速度慢
不指定端口,会扫描一千个常用端口
Starting Nmap 6.49BETA5 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2015-10-02 13:56 CSTn
Nmap scan report for localhost(192.168.1.134)
Host is up (0.0020s latency).
Not shown 94 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp open telnet
25/tcp open smtb
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
MAC Address: 80:00:27:B0:3A:76(Cadmus Computer Systems)
Nmap done: 1 IP address(1 host up) scanned in 5.72 seconds╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃全连接端口扫描 ┃
┃dmitry ┃
┃ 功能简单,但使用简便 ┃
┃ 默认150个最常用的端口 ┃
┃dmitry -p 172.16.36.135 ┃
┃dmitry -p 172.16.36.135 -o output ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
root@kali:~# dmitry -p 192.168.1.134
Deepmagic Information Gathering Tool
"There be some deep magic going on"
ERROR: Unable to locate Host Name for 192.168.1.134
Continuing with limited modules
HostIP:192.168.1.134
HostName:
Gathered TCP Port information for 192.168.1.134
---------------------------------
Port State
21/tcp open
22/tcp open
23/tcp open
25/tcp open
53/tcp open
80/tcp open
111/tcp open
139/tcp open
Portscan Finished: Scanned 150 ports, 141 ports were in state closed
All scans completed, exiting查看帮助
root@kali:~# dmitry -h
Deepmagic Information Gathering Tool
"There be some deep magic going on"
dmitry: invalid option -- 'h'
Usage: dmitry [-winsepfb] [-t 0-9] [-o %host.txt] host
-o Save output to %host.txt or to file specified by -o file
-i Perform a whois lookup on the IP address of a host
-w Perform a whois lookup on the domain name of a host
-n Retrieve Netcraft.com information on a host
-s Perform a search for possible subdomains
-e Perform a search for possible email addresses
-p Perform a TCP port scan on a host
* -f Perform a TCP port scan on a host showing output reporting filtered ports
* -b Read in the banner received from the scanned port
* -t 0-9 Set the TTL in seconds when scanning a TCP port ( Default 2 )
*Requires the -p flagged to be passed
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
┃全连接端口扫描 ┃
┃nc -nv -w 1 -z 192.168.60.4 1-100 ┃
┃for x in (seq2030);donc−nv−w1−z1.1.1.1 x;done | grep open ┃
┃for x in (seq2030);donc−nv−w1−z1.1.1. x;done ┃
╋━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╋
w超时时间
root@kali:~# nc -h
[v1.10-41]
connect to somewhere: nc [-options] hostname port[s] [ports] …
listen for inbound: nc -l -p port [-options] [hostname] [port]
options:
-c shell commands as `-e’; use /bin/sh to exec [dangerous!!]
-e filename program to exec after connect [dangerous!!]
-b allow broadcasts
-g gateway source-routing hop point[s], up to 8
-G num source-routing pointer: 4, 8, 12, …
-h this cruft
-i secs delay interval for lines sent, ports scanned
-k set keepalive option on socket
-l listen mode, for inbound connects
-n numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS
-o file hex dump of traffic
-p port local port number
-r randomize local and remote ports
-q secs quit after EOF on stdin and delay of secs
-s addr local source address
-T tos set Type Of Service
-t answer TELNET negotiation
-u UDP mode
-v verbose [use twice to be more verbose]
-w secs timeout for connects and final net reads
-C Send CRLF as line-ending
-z zero-I/O mode [used for scanning]
port numbers can be individual or ranges: lo-hi [inclusive];
hyphens in port names must be backslash escaped (e.g. ‘ftp-data’).
root@kali:~# nc -nv -w 1 -z 192.168.1.134 1-100
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 80 (http) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 53 (domain) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 25 (smtp) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 23 (telnet) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 22 (ssh) open
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.1.134] 21 (ftp) open