MyBatis之整合Spring(Dao和Mapper两种方式)
1. 基础环境搭建
首先环境肯定得有,环境嘛,除了Java环境和开发环境外,那就是jar包咯,关于mybatis和spring整合的jar包,我已经上传到下载频道了==>传送门
将这些jar包导入到lib文件夹中即可,然后就是工程中的一些文件了,配置文件啊,java文件啊等,先看一下整个工程的结构。 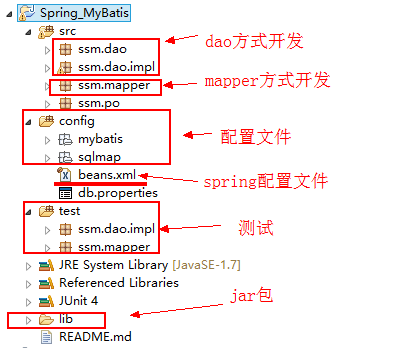
下面来完成所有的整合步骤。
2. 配置文件
在于spring整合之前,mybatis都是自己管理数据源的,然后sqlSessionFactory是我们自己去注入的,现在整合了,这些都要交给spring来管理了,来看一下beans.xml文件中的配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="${dataSource}" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="10" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="5" />
bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis/SqlMapConfig.xml" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
跟spring和hibernate整合的情况差不多,都是通过properties文件加载数据库连接信息,然后导入配置文件配置一下sessionFactory,下面看看db.properties和SqlMapConfig.xml文件。
#db.properties
dataSource=org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="ssm.po"/>
typeAliases>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml" />
<package name="ssm.mapper"/>
mappers>
configuration>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
3. dao方式开发的配置
在最开始我们提到,mybatis中有两种开发方式,一种dao开发方式,一种mapper开发方式,后者用的比较多,但是不排除没有使用dao方式的,所以两种我都总结一下,首先看dao方式开发的配置。
3.1 配置User.xml
在sqlMap包中有个User.xml,里面是针对用户的操作的一些配置,这里是整合,所以我就写了一个statement,如下:
<mapper namespace="test">
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="ssm.po.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
只是通过id查询用户,如果测试成功,说明整合成功,这里写完了后,别忘了在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载这个映射文件,但是上面已经加载过了,即
3.2 开发dao及其实现类
接下来就是开发dao及其实现类了,就一个方法,通过id查询用户,先来看下dao的方法:
public interface UserDao {
//根据用户id查询用户信息
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
再看下实现类:
public class UserDaoImpl extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements UserDao {
@Override
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception {
//继承SqlSessionDaoSupport,通过this.getSqlSession()就能得到sqlSession,因为SqlSessionDaoSupport中有该方法
SqlSession sqlSession = this.getSqlSession();
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", id);
return user;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
这里是重点:通过dao方式开发的话,dao的实现类在实现接口的同时,需要继承SqlSessionDaoSupport类,这个类中有获取SqlSession的方法,因为sqlSessionFactory已经在beans.xml文件中配置好了(下面有写),spring会自动注入进去,继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport类就可以直接通过getSqlSession()方法来获取sqlSession。然后就可以操作数据库了。
3.3 配置dao
上面也说了,要获取sqlSession必须得有sqlSessionFactory才行啊,这就需要spring来注入了,所以我们在beans.xml中配置一下该dao
<bean id="userDao" class="ssm.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
这样的话,dao开发方式就整合好了,下面来测试一下:
public class UserDaoImplTest {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:beans.xml");//得到spring容器
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() throws Exception {
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) applicationContext.getBean("userDao");//获取这个bean
User user = userDao.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4. mapper方式开发的配置
由前面的博文可知,mapper方法开发的话,mapper.xml和mapper.java文件要放在一个包下,这里主要放在ssm.mapper的包下了,下面看一下两个文件:
4.1 配置UserMapper.xml和UserMapper.java
<mapper namespace="ssm.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="user">
select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
//mapper接口,相当于dao接口
public interface UserMapper {
//根据id查询用户信息
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception;
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
这个和之前的都一样,没什么难度,注意xml中的namespace要写成对应的java文件的完全限定名即可。
4.2 配置beans.xml
上面已经配置好了mapper的映射和接口了,那么如何由spring来产生一个代理对象呢?spring是通过MapperFactoryBean来创建代理对象的,看下面的配置:
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="ssm.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
从配置中可以看出,使用MapperFactoryBean来产生mapper的代理对象,首先要配置一个mapperInterface,即你要spring产生哪个mapper接口对应的代理对象,所以肯定要把我们刚刚写好的mapper接口的完全限定名给传进去,spring就知道要创建对应的代理对象了。当然,sqlSessionFactory是必不可少的,否则怎么产生sqlSession呢?
测试程序就不写了,把上面的测试程序改一下,获取”userMapper”这个bean即可。
但是问题来了,如果有很多个mapper接口咋整?那beans.xml中难道要写很多个这样的bean么?答案肯定不是这样,我们可以在beans.xml中通过扫描包即可,即告诉spring,你把指定的包中所有的mapper接口都给我生成一个代理对象出来,如下:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="ssm.mapper" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
从上面的配置中可以看出,spring使用MapperScannerConfiger来进行mapper扫描的。要想扫描成功,必须遵循之前说的规范:即mapper.xml和mapper.java两个文件名必须保持一致,且在同一个目录下。这样的话,自动扫描出来的mapper的bean的id就为mapper类名的首字母小写。所以上面的bean没有id属性,因为这个是根据具体的mapper接口来的。basePackage是用来指定要扫描的包。这样就可以批量扫描mapper接口了。
测试程序和上面的一样,就不写了。到这里,spring和mybatis就整合好了,这里只是简单整合一下,主要是了解这个整合的过程以及方法,并没有用到spring的aop和事务等配置。