fabric多节点集群部署(4+1)详解
fabric多节点集群部署(4+1)详解
本文也是在参考前人的资料下开始进行搭建并成功的,部署这个之前需要已经了解并成功部署过单节点。
前期工作:下载fabric代码,下载go,docker,docker-compose,并实现了单节点部署。
本文主要任务是在5台linux系统的电脑或虚拟机中完成fabric的集群部署。
机器相关配置:
| 名称 | 节点名字 | 组织 | ip地址 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computer1 | orderer.example.com | Orderer | 192.168.44.129 |
| Computer2 | peer0.org1.example.com | Org1 | 192.168.44.132 |
| Computer3 | peer1.org1.example.com | Org1 | 192.168.44.133 |
| Computer4 | peer0.org2.example.com | Org2 | 192.168.44.134 |
| Computer5 | peer1.org2.example.com | Org2 | 192.168.44.135 |
一 生成公私钥,证书等信息
生成相关信息我们只需要在一台机器上生成,然后通过ssh复制到其他机器相应的位置就行
方法一:直接通过系统脚本一键生成
注:我的fabric代码存放地址:home/ckt/go_code/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
进入项目:
cd go_code/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/e2e_cli/
生成公私钥,证书,创世区块等信息:
./generateArtifacts.sh mychannel方法二:手动一步步的生成
其实手动的步骤只是把generateArtifacts.sh这个脚本中的步骤拆分来,不过这样能对整个业务逻辑更熟悉
1.1 编译生成cryptogen
make -C ../.. release1.2 配置crypto-config.yaml
这个暂时不用配置,默认就行。
1.3 生成证书
../../release/linux-amd64/bin/cryptogen generate --config=./crypto-config.yaml代码执行后会在当前目录生成crypto-config目录,里面含有crypto-config.yaml刚刚配置好的组织及成员证书
二 生成创世区块和Channel配置区块
方法一:直接通过系统脚本一键生成
在一中采用脚本自动生成公私钥和证书时,已经把创世区块和channel配置一并生成完毕了,不需要在额外生成。
方法二:手动一步步的生成
2.1 编译生成configtxgen
make -C ../.. release2.2 配置configtx.yaml
官方提供的examples/e2e_cli/configtx.yaml这个文件里面配置了由2个Org参与的Orderer共识配置TwoOrgsOrdererGenesis,以及由2个Org参与的Channel配置:TwoOrgsChannel。Orderer可以设置共识的算法是Solo还是Kafka,以及共识时区块大小,超时时间等,我们使用默认值即可,不用更改。而Peer节点的配置包含了MSP的配置,锚节点的配置。如果我们有更多的Org,或者有更多的Channel,那么就可以根据模板进行对应的修改。
2.3 生成创世区块
../../release/linux-amd64/bin/configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsOrdererGenesis -outputBlock ./channel-artifacts/genesis.block执行后会生成genesis.block区块并保存到本地channel-artifacts文件夹中
2.4 生成Channel配置区块
../../release/linux-amd64/bin/configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputCreateChannelTx ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx -channelID mychannel2.5 更新锚节点
../../release/linux-amd64/bin/configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputAnchorPeersUpdate ./channel-artifacts/Org1MSPanchors.tx -channelID mychannel -asOrg Org1MSP../../release/linux-amd64/bin/configtxgen -profile TwoOrgsChannel -outputAnchorPeersUpdate ./channel-artifacts/Org2MSPanchors.tx -channelID $mychannel -asOrg Org2MSP最终,我们在channel-artifacts文件夹中,应该是能够看到4个文件。
channel-artifacts/
├── channel.tx
├── genesis.block
├── Org1MSPanchors.tx
└── Org2MSPanchors.tx
三 配置相关的docker-compose文件
3.1 配置docker-compose-orderer
先把docker-compose-cli.yaml复制一份并命名docker-compose-orderer.yaml
cp ./docker-compose-cli.yaml ./docker-compose-orderer.yaml然后打开并编辑docker-compose-orderer.yaml,去掉peer和cli的代码部分,只留下orderer相关代码
生成后大概如下
# Copyright IBM Corp. All Rights Reserved.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
#
version: '2'
services:
orderer.example.com:
extends:
file: base/docker-compose-base.yaml
service: orderer.example.com
container_name: orderer.example.com
3.2 配置docker-compose-peer
先把docker-compose-cli.yaml复制一份并命名docker-compose-peer.yaml
cp ./docker-compose-cli.yaml ./docker-compose-peer.yaml然后打开并编辑docker-compose-peer.yaml,去掉orderer的代码部分,去掉其他多余peer部分(编辑peer0.org1时,删掉其他三个peer代码部分),只留下一个peer和cli相关代码。
接下来再进行部分代码修改(以peer0.org1为例):
peer节点部分添加extra_hosts,添加后代码如下:
peer0.org1.example.com:
container_name: peer0.org1.example.com
extends:
file: base/docker-compose-base.yaml
service: peer0.org1.example.com
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.44.129"cli中将command那一行代码前加#注释掉,或者删除该行代码
删除多余depend_on,添加extra_hosts,最后cli中部分代码如下:
depends_on:
- peer0.org1.example.com
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.44.129"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.44.132"
- "peer1.org1.example.com:192.168.44.133"
- "peer0.org2.example.com:192.168.44.134"
- "peer1.org2.example.com:192.168.44.135"
以上就将peer节点配置成功了,但是有一个小细节,在peer1.org1主机中配置时,还需要在extra_hosts中加入peer0.org1的信息(同理在配置peer1.org2时需要加入peer0.org2的信息),具体代码如下:
peer0.org1.example.com:
container_name: peer0.org1.example.com
extends:
file: base/docker-compose-base.yaml
service: peer0.org1.example.com
extra_hosts:
- "orderer.example.com:192.168.44.129"
- "peer0.org1.example.com:192.168.44.132"3.2 配置base/docker-compose-base.yaml
将base/docker-compose-base.yaml中所有peer的端口映射都改为相同的:
ports:
- 7051:7051
- 7052:7052
- 7053:7053四 启动fabric环境
4.1 启动peer和orderer
在peer节点主机上输入如下命令启动peer和orderer:
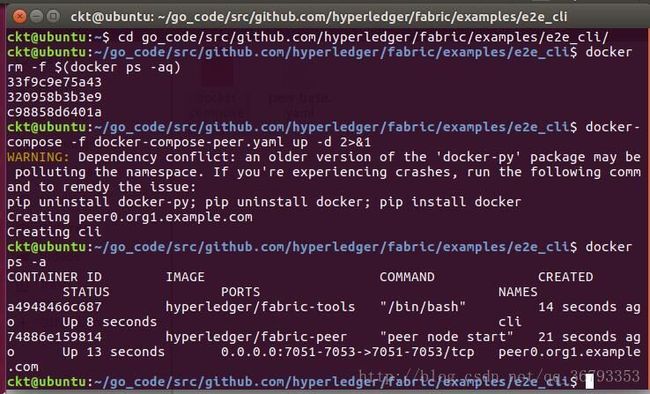
docker-compose -f docker-compose-peer.yaml up -d在orderer节点主机上输入:
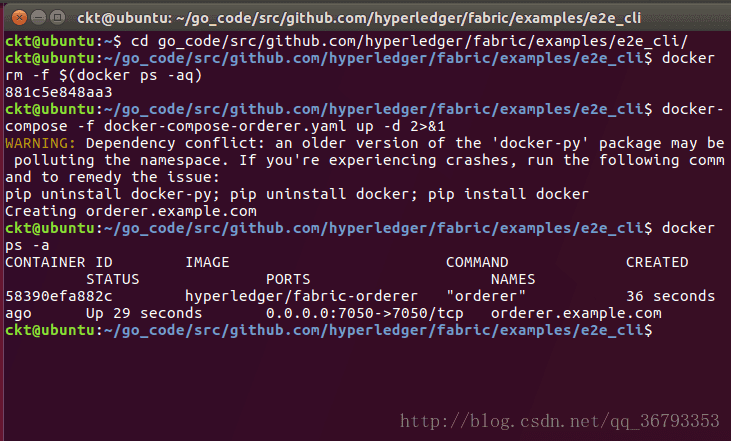
docker-compose -f docker-compose-orderer.yaml up -d4.2 查看启动情况:
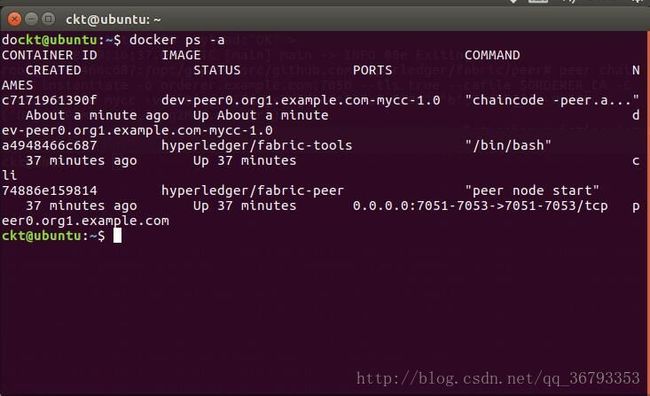
docker ps -a可以看到peer节点下有peer和cli容器,orderer中有orderer,则表示成功。
4.3 进入cli
这里我们以在peer0.org1中示范进入
docker exec -it cli bash当显示:root@81aebc129d03:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer# 的时候表示成功进入cli。
快速启动
接下来步骤可以直接通过快速启动来操作,也可以一步步的来添加,快速启动代码:
./script/script.sh mychannel4.4 创建Channel
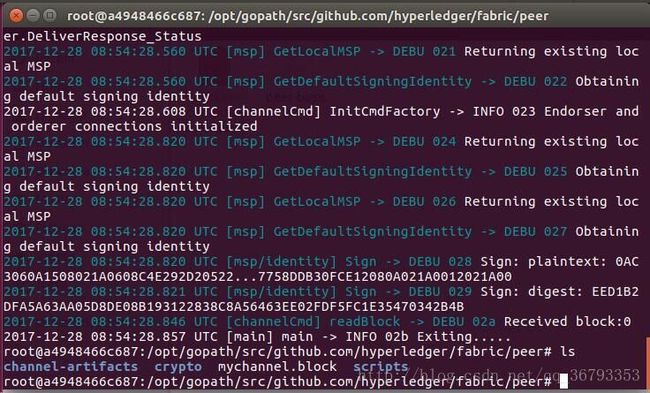
ORDERER_CA=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem
peer channel create -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx --tls true --cafile $ORDERER_CA创建完成后ls可以看到原来的目录下多了一个mychannel.block文件
4.5 各个Peer加入Channel
CLI默认连接的是peer0.org1,那么我们要将这个Peer加入mychannel就很简单,只需要运行如下命令:
peer channel join -b mychannel.block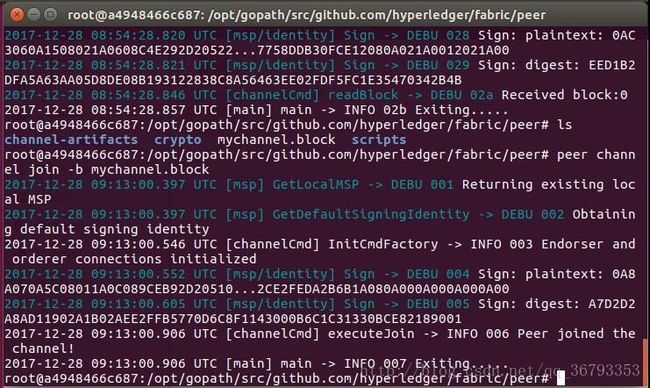
其他几个Peer又该怎么加入Channel呢?这里就需要修改CLI的环境变量,使其指向另外的Peer。比如我们要把peer1.org1加入mychannel,那么命令是:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org1MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org1.example.com:7051peer channel join -b mychannel.block系统会返回成功加入Channel的消息。
同样的方法,将peer0.org2加入mychannel:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org2MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7051peer channel join -b mychannel.block最后把peer1.org2加入mychannel:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org2MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer1.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org2.example.com:7051peer channel join -b mychannel.block
4.6 更新锚节点
对于Org1来说,peer0.org1是锚节点,我们需要连接上它并更新锚节点:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org1MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051peer channel update -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/Org1MSPanchors.tx --tls true --cafile $ORDERER_CA对于Org2,peer0.org2是锚节点,对应的更新代码是:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org2MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7051peer channel update -o orderer.example.com:7050 -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/Org2MSPanchors.tx --tls true --cafile $ORDERER_CA整个Fabric网络和Channel都准备完毕。
五 链上代码的安装与运行
安装和运行ChainCode,以系统给的Example02为例。该例子定义了a,b两个账户,两者相互之间可以转账。
5.1 Install ChainCode–安装链上代码
仍然是保持在CLI的命令行下,我们先切换到peer0.org1这个节点:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org1MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051使用peer chaincode install命令可以安装指定的ChainCode并对其命名:
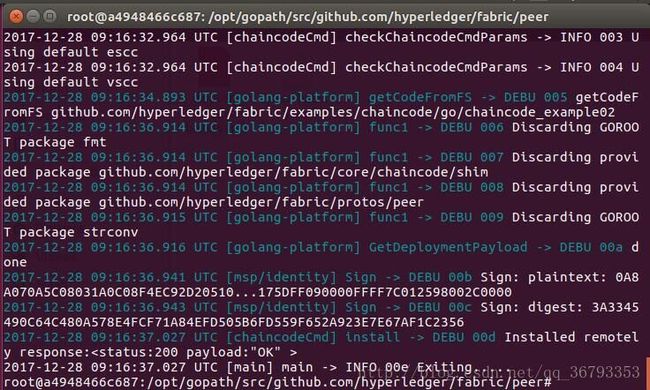
peer chaincode install -n mycc -v 1.0 -p github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02安装的过程其实就是对CLI中指定的代码进行编译打包,并把打包好的文件发送到Peer,等待接下来的实例化。
其他节点由于暂时还没使用到,我们可以先不安装,等到了步骤5.4的时候再安装。
5.2 Instantiate ChainCode–实例化链上代码
实例化链上代码主要是在Peer所在的机器上对前面安装好的链上代码进行包装,生成对应Channel的Docker镜像和Docker容器。并且在实例化时我们可以指定背书策略。我们运行以下命令完成实例化:
peer chaincode instantiate -o orderer.example.com:7050 --tls true --cafile $ORDERER_CA -C mychannel -n mycc -v 1.0 -c '{"Args":["init","a","100","b","200"]}' -P "OR ('Org1MSP.member','Org2MSP.member')"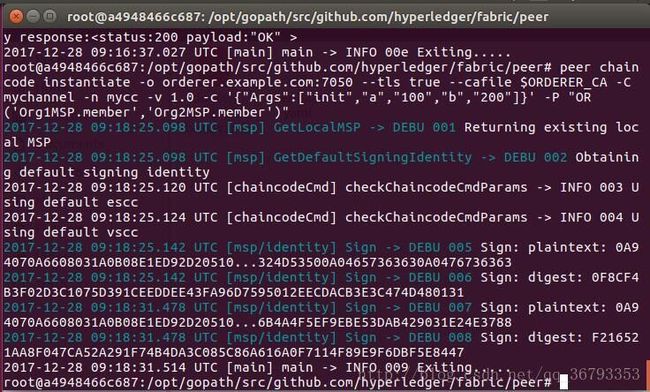
如果我们新开一个Ubuntu终端,去查看peer0.org1上的日志,那么就可以知道整个实例化的过程到底干了什么:
docker logs -f peer0.org1.example.com5.3 在一个Peer上查询并发起交易
现在链上代码的实例也有了,并且在实例化的时候指定了a账户100,b账户200,我们可以试着调用ChainCode的查询代码,验证一下,在cli容器内执行:
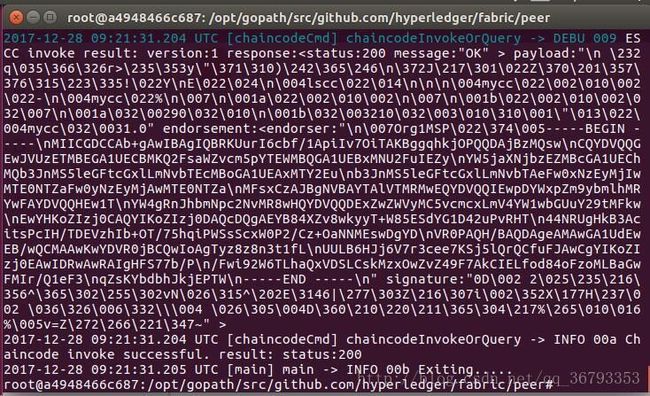
peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["query","a"]}'接下来我们可以试着把a账户的10元转给b。对应的代码:
ORDERER_CA=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.example.com:7050 --tls true --cafile $ORDERER_CA -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["invoke","a","b","10"]}'5.4 在另一个节点上查询交易
前面的操作都是在org1下面做的,那么处于同一个区块链(同一个Channel下)的org2,是否会看org1的更改呢?我们试着给peer0.org2安装链上代码:
CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID="Org2MSP"
CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer0.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt
CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp
CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org2.example.com:7051peer chaincode install -n mycc -v 1.0 -p github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02由于mycc已经在前面org1的时候实例化了,也就是说对应的区块已经生成了,所以在org2不能再次初始化。我们直接运行查询命令:
peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["query","a"]}'这个时候我们发现运行该命令后要等很久(我这里花了40秒)才返回结果:
Query Result: 90
这是因为peer0.org2也需要生成Docker镜像,创建对应的容器,才能通过容器返回结果。我们到peer0.org2机器的Ubuntu终端,执行docker ps,可以看到原本的容器中又多了一个容器
以上就是多节点集群部署的全部过程,如有错误,欢迎提出改正。