Python爬虫与数据可视化
之前写过篇爬取前程无忧职位信息并保存到Excel的博客,
这里仔细的讲讲并且增加可视化内容
文章目录
- 1.数据挖掘
- 2.数据清洗
- 3.数据可视化
- 这里特别强调,pyecharts包千万别装新版的,我这里装的是0.5.9版的
- 其次如果要做地理坐标图,热力图啥的,必须安装地图包,比如世界地图包,中国地图包,城市地图包啥的
1.数据挖掘
代码所需包
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib.request
import xlwt
import re
import urllib.parse
from lxml import etree
import requests
进入前程无忧官网
我这里以搜索大数据职位信息

打开开发者模式
Request Headers 里面是我们用浏览器访问网站的信息,有了信息后就能模拟浏览器访问
这也是为了防止网站封禁IP,不过前程无忧一般是不会封IP的。

模拟浏览器
header={
'Host':'search.51job.com',
'Referer':'https://mkt.51job.com/tg/sem/pz_2018.html?from=baidupz',
'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests':'1',
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) 37abc/2.0.6.16 Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36'
}
这些基本数据都可以爬取:
为了实现交互型爬取,我写了一个能够实现输入想了解的职位就能爬取相关内容的函数
item = input()
def getfront(page,item): #page是页数,item是输入的字符串
result = urllib.parse.quote(item) #先把字符串转成十六进制编码
ur1 = result+',2,'+ str(page)+'.html'
ur2 = 'http://search.51job.com/list/000000,000000,0000,00,9,99,'
res = ur2+ur1 #拼接网址
a = urllib.request.urlopen(res)
html = a.read().decode('gbk') # 读取源代码并转为unicode
return html
def getInformation(html):
reg = re.compile(r'class="t1 ">.*? (.*?).*?(.*?).*?(.*?).*?',re.S)#匹配换行符
items=re.findall(reg,html)
return items
这里我除了爬取图上信息外,还把职位超链接后的网址,以及公司超链接的网址爬取下来了。
这里先不讲,后面后面会说到,
接下来就需要储存信息,这里使用Excel,虽然比较麻烦,不过胜在清晰直观
excel1 = xlwt.Workbook()
# 设置单元格
sheet1 = excel1.add_sheet('Job', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
sheet1.write(0, 0, '序号')
sheet1.write(0, 1, '职位')
sheet1.write(0, 2, '公司名称')
sheet1.write(0, 3, '公司地点')
sheet1.write(0, 4, '公司性质')
sheet1.write(0, 5, '薪资')
sheet1.write(0, 6, '学历要求')
sheet1.write(0, 7, '工作经验')
sheet1.write(0, 8, '公司规模')
sheet1.write(0, 9, '公司类型')
sheet1.write(0, 10,'公司福利')
sheet1.write(0, 11,'发布时间')
sheet1.write(0, 12,'任职要求')
爬取代码如下,这里就能利用双层循环来实现换页爬取与换行输出
number = 1
item = input()
for j in range(1,1000):
try:
print("正在爬取第"+str(j)+"页数据...")
html = getfront(j,item) #调用获取网页原码
for i in getInformation(html):
try:
url1 = i[1] #职位网址
url2 = i[3] #公司网址
res1 = requests.get(url1).text
res2 = requests.get(url2).text
s1 = etree.HTML(res1) # 将源码转化为能被 XPath 匹配的格式
s2 = etree.HTML(res2)
persons = s2.xpath('/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[2]/div/p[1]/text()')[1].strip()
comyany_avlue = s2.xpath('/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[2]/div/p[1]/text()')[0].strip()
experience = s1.xpath('/html/body/div[3]/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/p[2]/text()')[1].strip()
education = s1.xpath('/html/body/div[3]/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/p[2]/text()')[2].strip()
comyany_type = s2.xpath('/html/body/div[2]/div[2]/div[2]/div/p/a/text()')
welface = re.findall(re.compile(r'(.*?)',re.S),res1)
requir = s1.xpath('/html/body/div[3]/div[2]/div[3]/div[1]/div/p/text()')
print(i[0],i[2],i[4],i[5],comyany_avlue,experience,education,persons,comyany_type,welface,i[6])
sheet1.write(number,0,number)
sheet1.write(number,1,i[0])
sheet1.write(number,2,i[2])
sheet1.write(number,3,i[4])
sheet1.write(number,4,comyany_avlue)
sheet1.write(number,5,i[5])
sheet1.write(number,6,education)
sheet1.write(number,7,experience)
sheet1.write(number,8,persons)
sheet1.write(number,9,comyany_type)
sheet1.write(number,10,(" ".join(str(i) for i in welface)))
sheet1.write(number,11,i[6])
sheet1.write(number,12,requir)
number+=1;
excel1.save("51job2.xls")
except:
pass
except:
pass
2.数据清洗
首先要打开文件
#coding:utf-8
import pandas as pd
import re
data = pd.read_excel(r'51job.xls',sheet_name='Job')
result = pd.DataFrame(data)
清洗思路:
1、出现有空值(NAN)得信息,直接删除整行
a = result.dropna(axis=0,how='any')
pd.set_option('display.max_rows',None) #输出全部行,不省略
b = u'数据'
number = 1
li = a['职位']
for i in range(0,len(li)):
try:
if b in li[i]:
#print(number,li[i])
number+=1
else:
a = a.drop(i,axis=0)
except:
pass
b2= u'人'
li2 = a['学历要求']
for i in range(0,len(li2)):
try:
if b2 in li2[i]:
#print(number,li2[i])
number+=1
a = a.drop(i,axis=0)
except:
pass
4、转换薪资单位
如上图就出现单位不一致的情况
b3 =u'万/年'
b4 =u'千/月'
li3 = a['薪资']
for i in range(0,len(li3)):
try:
if b3 in li3[i]:
x = re.findall(r'\d*\.?\d+',li3[i])
#print(x)
min_ = format(float(x[0])/12,'.2f') #转换成浮点型并保留两位小数
max_ = format(float(x[1])/12,'.2f')
li3[i] = str(min_+'-'+max_+'万/月')
if b4 in li3[i]:
x = re.findall(r'\d*\.?\d+',li3[i])
#print(x)
min_ = format(float(x[0])/10,'.2f')
max_ = format(float(x[1])/10,'.2f')
li3[i] = str(min_+'-'+max_+'万/月')
print(i,li3[i])
except:
pass
保存到另一个Excel文件
a.to_excel('51job2.xls', sheet_name='Job', index=False)
这里只是简单的介绍了一些数据清理的思路,并不是说只要清理这些就行了
有时候有的公司网页并不是前程无忧类型的,而是他们公司自己做的网页,这也很容易出错
不过只要有了基本思路,这些都不难清理
3.数据可视化
数据可视化可以说是很重要的环节,如果只是爬取数据而不去可视化处理,那么可以说数据的价值根本没有发挥
可视化处理能使数据更加直观,更有利于分析
甚至可以说可视化是数据挖掘最重要的内容
同样的我们先看代码需要的包
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
import re
from pyecharts import Funnel,Pie,Geo
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
这里特别强调,pyecharts包千万别装新版的,我这里装的是0.5.9版的
其次如果要做地理坐标图,热力图啥的,必须安装地图包,比如世界地图包,中国地图包,城市地图包啥的
file = pd.read_excel(r'51job2.xls',sheet_name='Job')
f = pd.DataFrame(file)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows',None)
1、创建多个列表来单独存放【‘薪资’】【‘工作经验’】【‘学历要求’】【‘公司地点’】等信息
add = f['公司地点']
sly = f['薪资']
edu = f['学历要求']
exp = f['工作经验']
address =[]
salary = []
education = []
experience = []
for i in range(0,len(f)):
try:
a = add[i].split('-')
address.append(a[0])
#print(address[i])
s = re.findall(r'\d*\.?\d+',sly[i])
s1= float(s[0])
s2 =float(s[1])
salary.append([s1,s2])
#print(salary[i])
education.append(edu[i])
#print(education[i])
experience.append(exp[i])
#print(experience[i])
except:
pass
2、matploblib库生成 工作经验—薪资图 与 学历—薪资图
min_s=[] #定义存放最低薪资的列表
max_s=[] #定义存放最高薪资的列表
for i in range(0,len(experience)):
min_s.append(salary[i][0])
max_s.append(salary[i][0])
my_df = pd.DataFrame({'experience':experience, 'min_salay' : min_s, 'max_salay' : max_s}) #关联工作经验与薪资
data1 = my_df.groupby('experience').mean()['min_salay'].plot(kind='line')
plt.show()
my_df2 = pd.DataFrame({'education':education, 'min_salay' : min_s, 'max_salay' : max_s}) #关联学历与薪资
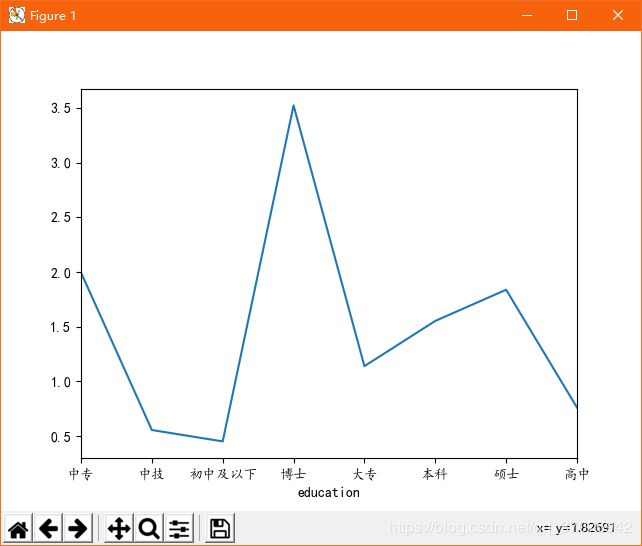
data2 = my_df2.groupby('education').mean()['min_salay'].plot(kind='line')
plt.show()
def get_edu(list):
education2 = {}
for i in set(list):
education2[i] = list.count(i)
return education2
dir1 = get_edu(education)
# print(dir1)
attr= dir1.keys()
value = dir1.values()
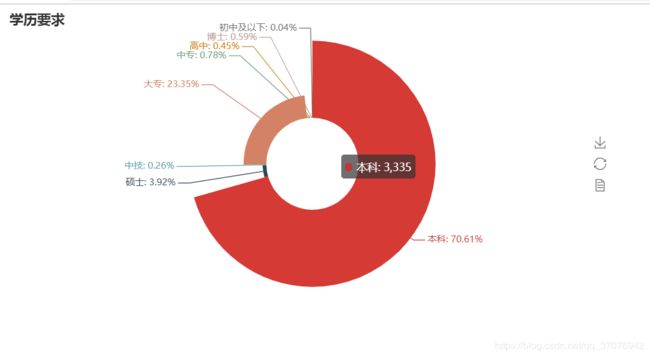
pie = Pie("学历要求")
pie.add("", attr, value, center=[50, 50], is_random=False, radius=[30, 75], rosetype='radius',
is_legend_show=False, is_label_show=True,legend_orient='vertical')
pie.render('学历要求玫瑰图.html')
def get_address(list):
address2 = {}
for i in set(list):
address2[i] = list.count(i)
address2.pop('异地招聘')
address2.pop('山东省')
address2.pop('怒江')
address2.pop('池州')
return address2
dir2 = get_address(address)
#print(dir2)
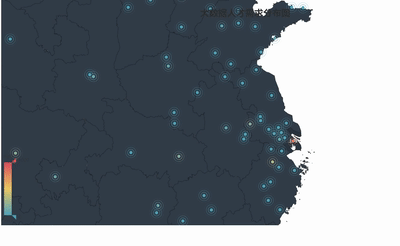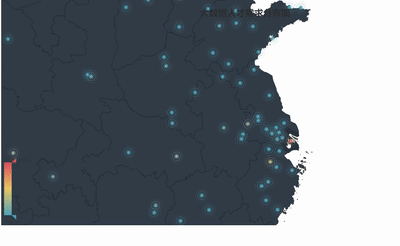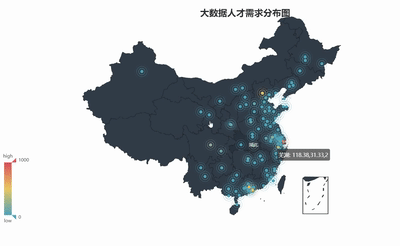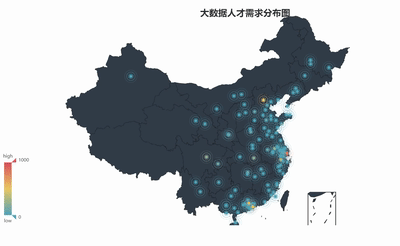
geo = Geo("大数据人才需求分布图", title_color="#2E2E2E",
title_text_size=24,title_top=20,title_pos="center", width=1300,height=600)
attr2 = dir2.keys()
value2 = dir2.values()
geo.add("",attr2, value2, type="effectScatter", is_random=True, visual_range=[0, 1000], maptype='china',symbol_size=8, effect_scale=5, is_visualmap=True)
geo.render('大数据城市需求分布图.html')
def get_experience(list):
experience2 = {}
for i in set(list):
experience2[i] = list.count(i)
return experience2
dir3 = get_experience(experience)
#print(dir3)
attr3= dir3.keys()
value3 = dir3.values()
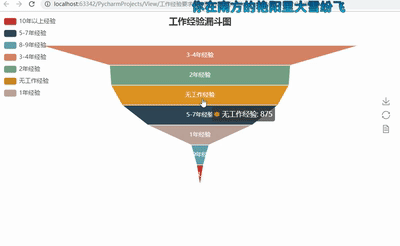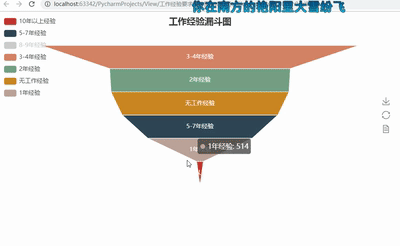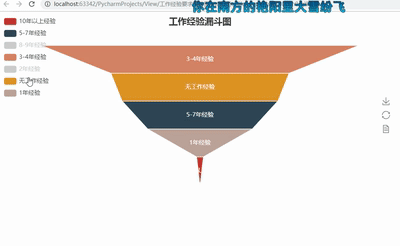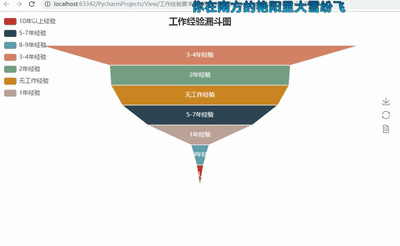
funnel = Funnel("工作经验漏斗图",title_pos='center')
funnel.add("", attr3, value3,is_label_show=True,label_pos="inside", label_text_color="#fff",legend_orient='vertical',legend_pos='left')
funnel.render('工作经验要求漏斗图.html')