UI绘制的详细步骤
1. 测量performMeasure
->view.measure
->view.onMeasure
->view.setMeasuredDimension
->setMeasuredDimensionRaw
2. 布局performLayout
->view.layout
->view.onLayout
3. 绘制performDraw
->ViewRootImpl.draw(fullRedrawNeeded)
->ViewRootImpl.drawSoftware
->view.draw(Canvas)
1. 测量performMeasure:
先看ViewRootImpl.class源码中的performMeasure方法:
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
调用了View.class的measure方法
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
//读取缓存
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
...
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
//调用onMeasure
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
...
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
//设置缓存
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
代码逻辑还算是比较清晰的,调用步骤一如开头总结出来的,为了更好的理解View绘制的过程,我们再来理解一个类 MeasureSpec.class
了解MeasureSpec
View的布局参数 包含 模式 + 尺寸 的信息
而MeasureSpec 作为一个32位的int值,则记录了 模式 + 尺寸 这些信息
00 000000000000000000000000000000
【前2位代表模式SpecMode,后30位代表尺寸SpecSize】
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
3左移30位,转为二进制:
11 000000000000000000000000000000
~MODE_MASK 则为:
00 111111111111111111111111111111
- public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
0左移30位,转为二进制:
00 000000000000000000000000000000
父容器不对View做任何限制,一般系统内部使用
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
1左移30位,转为二进制:
01 000000000000000000000000000000
父容器检测出View的大小,View的大小就是SpecSize LayoutParams match_parent 以及 固定大小public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
2左移30位,转为二进制:
10 000000000000000000000000000000
父容器制定一个可用大小,View的大小不能超过这个值,LayoutParams wrap_content
如何生成一个MeasureSpec呢?Android已经给你提供方法了,传入一个mode,一个size,makeMeasureSpec方法就会返回一个MeasureSpec给你。而通过getMode和getSize就能从传入的MeasureSpec中取出mode和size。
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,
@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
View的测量-确定DecorView的MeasureSpec
DecorView的MeasureSpec由窗口大小和自身LayoutParams共同决定,遵循如下规则:
- LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT :精确模式,窗口大小
- LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT :最大模式,最大为窗口大小
- 固定大小:精确模式,大小为LayoutParams的大小
回想刚才的分析流程,performMeasure方法里执行了mView.measure方法,measure方法中又执行了onMeasure方法,而对于我们要探究的DecorView来说,我们就要看一下继承自FrameLayout的DecorView.class是否重写了onMeasure方法,而不是只看View.class中的实现了,不同View子类对于onMeasure、onLayout、onDraw的重写,是我们的学习重点。
DecorView的onMeasure方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
可以看到里面还调用了super.onMeasure,那我们再来看看DecorView父类FrameLayout的onMeasure实现:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
其中,在for循环中调用了ViewGroup.class的 measureChildWithMargins方法
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
在ViewGroup.class的 measureChildWithMargins方法之中,以及在FrameLayout.class的setMeasuredDimension方法之后,也都调用了ViewGroup.class的getChildMeasureSpec方法:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
for循环之后,调用了View.class的setMeasuredDimension方法,以及setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法:
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
- onMeasure方法传入的参数widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec就是当前容器的测量规格。
- for循环调用measureChildWithMargins,而这个方法就是测量FrameLayout中子控件的宽高,其中的getChildMeasureSpec方法就是获取子控件的测量规格。
getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension)这个方法有三个参数:
spec 表示父容器的测量规格,
padding 就不说了,
childDimension 子控件的布局参数(MarginLayoutParams)对应的尺寸。
方法中根据父容器的不同mode模式,给子控件的resultSize resultMode赋值。
最后通过MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode)方法将其打包。
- for循环不是把子View都测量了个遍么,然后调用了一个方法setMeasuredDimension,这个方法是设定父控件自身的宽高的,因为父控件的宽高可能是和子控件的宽高也有关系的。
阶段总结:
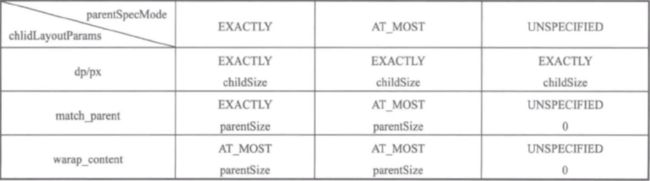
View的MeasureSpec由父容器的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams决定
- 子View长宽为固定,则无视父类模式,肯定为EXACTLY模式,且长宽都为childSize
- 子View长宽为match_parent,则跟随父类的模式,且长宽都为parentSize,UNSPECIFIED模式为0
- 子View长宽为wrap_content,则模式都为AT_MOST,且长宽都为暂定为parentSize
【注:parentSize都是父控件的剩余大小,减去padding之类的长度】
ViewGroup
->measure
->onMeasure【通过measureChildWithMargins方法测量子控件的宽高,调用子控件的measure】
->setMeasureDimension
->setMeasureDimensionRaw【保存自己的宽高】
View
->measure
->onMeasure
->setMeasureDimension() 【getDefaultSize() 】
->setMeasureDimensionRaw
注意View.class的setMeasureDimension
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
//子控件为wrap_content时
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
//子控件为match_parent时
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
//都赋值为父控件的specSize
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
实战技巧
自定义View时,如果不重写onMeasure,则match_parent和wrap_content的效果一样。 此时需要视情况决定是否重写onMeasure方法,另需注意,当自定义类型为容器ViewGroup时,重写onMeasure方法要测量子View宽高后再设置自身宽高,非ViewGroup的View则不需测量子View。
2. 布局performLayout
先看ViewRootImpl.class源码中的performLayout方法:
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
mLayoutRequested = false;
mScrollMayChange = true;
mInLayout = true;
//这个mView就是顶层View
final View host = mView;
if (host == null) {
return;
}
try {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
...
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
mInLayout = false;
}
看见 host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());,追踪一下View.class的layout方法:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
...
}
...
}
可以看到有一处调用setFrame方法,就是对mLeft,mTop,mBottom,mRight进行赋值,确定了这四个值,View的位置可以说就固定下来了。然后调用了onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b),但是点进去发现View.class的onLayout方法是空方法,也就是说是留给子类重写的。如果我们自定义的是容器类型的,则需在onLayout里摆放子View的位置,如果我们自定义的是View,则无需重写。
距离FrameLayout:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */);
}
//遍历子控件对子控件进行摆放,并调用子View的layout方法,形成递归操作
void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) {
final int count = getChildCount();
final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground();
final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground();
final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground();
final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int childLeft;
int childTop;
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity == -1) {
gravity = DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY;
}
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection);
final int verticalGravity = gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 +
lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
if (!forceLeftGravity) {
childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin;
break;
}
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin;
}
switch (verticalGravity) {
case Gravity.TOP:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
break;
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
childTop = parentTop + (parentBottom - parentTop - height) / 2 +
lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
childTop = parentBottom - height - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
default:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
}
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
}
}
}
阶段总结
ViewGroup
->layout【确定自己的位置,4个点的位置】
->onLayout【负责子View的布局,自定义时需要重写】**View
->layout【确定自己的位置,4个点的位置】
3. 绘制performDraw
先看ViewRootImpl.class源码
private void performDraw() {
...
try {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if (usingAsyncReport && !canUseAsync) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.setFrameCompleteCallback(null);
usingAsyncReport = false;
}
} finally {
mIsDrawing = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
...
}
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
...
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset,
scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) {
return false;
}
...
}
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) {
...
mView.draw(canvas);
...
}
这时候,代码追踪draw方法来到了View.class,通过观察注释即可得知draw的绘制步骤
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Step 7, draw the default focus highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (debugDraw()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
...
}
因为涉及到子View的绘制,我们看一下ViewGroup.class中对dispatchDraw的实现
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
...
//遍历子控件,通过drawChild绘制子控件
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
while (transientIndex >= 0 && mTransientIndices.get(transientIndex) == i) {
final View transientChild = mTransientViews.get(transientIndex);
if ((transientChild.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE ||
transientChild.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime);
}
transientIndex++;
if (transientIndex >= transientCount) {
transientIndex = -1;
}
}
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(preorderedList, children, childIndex);
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
...
}
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
阶段总结
ViewGroup
->绘制背景drawBackground(Canvas)
-> 绘制自己onDraw(Canvas)【自定义时需重写】
-> 绘制子View dispatchDraw(Canvas)
-> 绘制前景,滚动条等装饰 onDrawForeground(Canvas)View
->绘制背景drawBackground(Canvas)
-> 绘制自己onDraw(Canvas)【自定义时需重写】
-> 绘制前景,滚动条等装饰 onDrawForeground(Canvas)
总结
自定义View时
ViewGroup
-> onMeasure
-> onLayout
-> onDraw【可选,例如容器中装载的都是系统控件,则不用重写】View
-> onMeasure
-> onDraw【可选】