HttpRequest
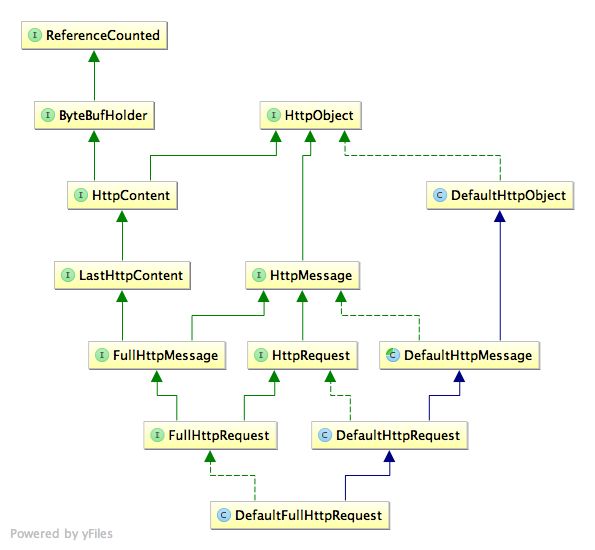
Netty中的httprequest类结构如下图所示
先来看DefaultFullHttpRequest,主要参数包括HttpVersion,HttpMethod,String,即Http版本,使用的Http方法,以及url
private final ByteBuf content;
private final HttpHeaders trailingHeader;
private final boolean validateHeaders;
public DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion httpVersion, HttpMethod method, String uri) {
this(httpVersion, method, uri, Unpooled.buffer(0));
}
public DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion httpVersion, HttpMethod method, String uri, ByteBuf content) {
this(httpVersion, method, uri, content, true);
}
public DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion httpVersion, HttpMethod method, String uri,
ByteBuf content, boolean validateHeaders) {
super(httpVersion, method, uri, validateHeaders);
if (content == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("content");
}
this.content = content;
trailingHeader = new DefaultHttpHeaders(validateHeaders);
this.validateHeaders = validateHeaders;
}
再到DefaultHttpMessage,这里封装了http的headers
private HttpVersion version;
private final HttpHeaders headers;
然后来看看DefaultHttpHeaders里面包含了一个headerEntry数组,headerEntry是一个键值对
private final HeaderEntry[] entries = new HeaderEntry[BUCKET_SIZE];
private final class HeaderEntry implements Map.Entry
HttpResponse
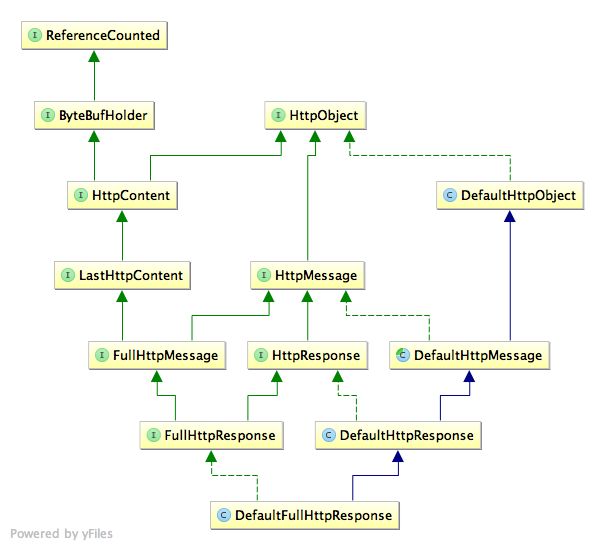
HttpResponse的类结构和Request基本一样,但其没有HttpMethod类型,只有一个HttpResponseStatus,所以我们一般抓到的包中协议以http开头的都是Response,有get等开头的是Request
private final ByteBuf content;
private final HttpHeaders trailingHeaders;
private final boolean validateHeaders;
public DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion version, HttpResponseStatus status) {
this(version, status, Unpooled.buffer(0));
}
public DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion version, HttpResponseStatus status, ByteBuf content) {
this(version, status, content, true);
}
public DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion version, HttpResponseStatus status,
ByteBuf content, boolean validateHeaders) {
super(version, status, validateHeaders);
if (content == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("content");
}
this.content = content;
trailingHeaders = new DefaultHttpHeaders(validateHeaders);
this.validateHeaders = validateHeaders;
}
HttpResponseEncoder和HttpRequestEncoder
这两个handler均继承与HttpObjectEncoder,编码方式也类似,代码如下
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List头部编码
@Override
protected void encodeInitialLine(ByteBuf buf, HttpRequest request) throws Exception {
request.getMethod().encode(buf);//编码方法
buf.writeByte(SP);//添加空格
// Add / as absolute path if no is present.
// See http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-5.1.2
String uri = request.getUri();
if (uri.length() == 0) {
uri += SLASH;
} else {//编码URL
int start = uri.indexOf("://");
if (start != -1 && uri.charAt(0) != SLASH) {
int startIndex = start + 3;
// Correctly handle query params.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2732
int index = uri.indexOf(QUESTION_MARK, startIndex);
if (index == -1) {
if (uri.lastIndexOf(SLASH) <= startIndex) {
uri += SLASH;
}
} else {
if (uri.lastIndexOf(SLASH, index) <= startIndex) {
int len = uri.length();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(len + 1);
sb.append(uri, 0, index)
.append(SLASH)
.append(uri, index, len);
uri = sb.toString();
}
}
}
}
buf.writeBytes(uri.getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
buf.writeByte(SP);
request.getProtocolVersion().encode(buf);//编码版本
buf.writeBytes(CRLF);
}
编码Headers
static void encode(HttpHeaders headers, ByteBuf buf) {
if (headers instanceof DefaultHttpHeaders) {
((DefaultHttpHeaders) headers).encode(buf);
} else {
for (Entry header: headers) {
encode(header.getKey(), header.getValue(), buf);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
static void encode(CharSequence key, CharSequence value, ByteBuf buf) {
if (!encodeAscii(key, buf)) {
buf.writeBytes(HEADER_SEPERATOR);
}
if (!encodeAscii(value, buf)) {
buf.writeBytes(CRLF);
}
}
HttpObjectDecoder
编码是从HttpObject转成bytebuf,而解码就是从bytebuf中读取HttpObject
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer, ListHttpContentCompressor
这个handler其实就是对Content进行了压缩,包含了压缩方式和压缩等级,这里有gzip和zlib两种压缩方式
@Override
protected Result beginEncode(HttpResponse headers, String acceptEncoding) throws Exception {
String contentEncoding = headers.headers().get(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_ENCODING);
if (contentEncoding != null &&
!HttpHeaders.Values.IDENTITY.equalsIgnoreCase(contentEncoding)) {
return null;
}
ZlibWrapper wrapper = determineWrapper(acceptEncoding);
if (wrapper == null) {
return null;
}
String targetContentEncoding;
switch (wrapper) {
case GZIP:
targetContentEncoding = "gzip";
break;
case ZLIB:
targetContentEncoding = "deflate";
break;
default:
throw new Error();
}
return new Result(
targetContentEncoding,
new EmbeddedChannel(ZlibCodecFactory.newZlibEncoder(
wrapper, compressionLevel, windowBits, memLevel)));
}