笔记参考:http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-conditional-statements.html
Python3条件控制
Python条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(结果是True或者False)来决定执行的代码块。
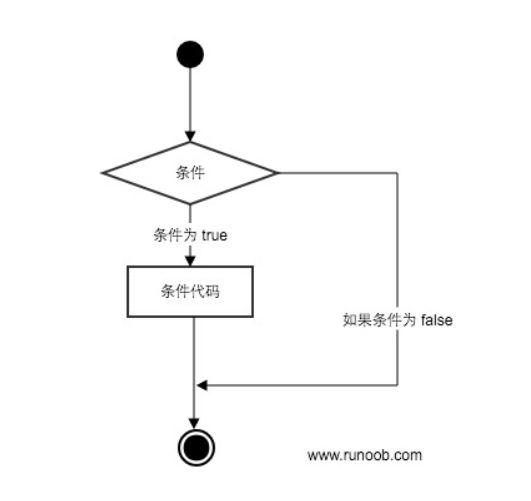
可以通过下图来简单了解条件语句的执行过程:
if 语句
Python中if语句的一般形式如下所示:
if condition_1:
statement_block_1
elif condition_2:
statement_block_2
else:
statement_block_3
#切记冒号不能丢!
- 如果 "condition_1" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_1" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_1" 为False,将判断 "condition_2"
- 如果"condition_2" 为 True 将执行 "statement_block_2" 块语句
- 如果 "condition_2" 为False,将执行"statement_block_3"块语句
- Python 中用 elif 代替了 else if,所以if语句的关键字为:if – elif – else。
注意: - 每个条件后面要使用冒号 :,表示接下来是满足条件后要执行的语句块。
- 使用缩进来划分语句块,相同缩进数的语句在一起组成一个语句块。
- 在Python中没有switch – case语句。
我们不妨举个小例子:
num_1 = 2
if num_1:
print('我想要小姐姐')
print(num_1)
num_2 = 0
if num_2:
print("屌丝洗洗睡吧")
print(num_2)
print('今天是个好日子')
输出结果如下:
我想要小姐姐
2
今天是个好日子
在这里我们又可以复习一下曾经学过的知识了,0在布尔值中代表False,1,2,3......在布尔值中代表True。
所以上述程序只执行了num_1下边的语句块,并未执行num_2下边的语句块。
我们再举一个例子:
score = int(input('请输入你的分数:'))
if score > 90:
print('优秀')
elif score > 80 and score <= 90:
print('良好')
elif score > 60 and score <= 80:
print('及格')
else:
print("滚犊子")
输出为:
请输入你的分数:78
及格
以下为if中常用的操作运算符:
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| < | 小于 |
| <= | 小于或等于 |
| > | 大于 |
| >= | 大于或等于 |
| == | 等于,比较两个值是否相等 |
| != | 不等于 |
举个小例子:
x, y, z = 3, 4, 5
if x>y:
print("今天中午吃卤菜")
elif y输出如下:
今天中午吃披萨
python大法好
最后我们玩一个猜数字的游戏吧,然后愉快的结束本节,小小小小白今天要去新街口浪:
print('小姐姐我们来玩一个猜数字大小的游戏吧')
num = 7
guess = 5
while guess != num:
guess = int(input('请输入一个数字:'))
if guess > num:
print('猜大了哦')
elif guess < num:
print('猜小了哦')
else:
print('你她娘的真是个人才!')
输出:
小姐姐我们来玩一个猜数字大小的游戏吧
请输入一个数字:5
猜小了哦
请输入一个数字:6
猜小了哦
请输入一个数字:7
你她娘的真是个人才!
今天先到这里,祝大家周末愉快。