本篇博客只是分析一下基本的服装均衡策略,com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule接口的一些实现。
负载均衡策略
负载均衡接口com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule
com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule
负载均衡策略的抽象类,在该抽象类中定义了负载均衡器ILoadBalancer对象,该对象能够在具体实现选择服务策略时,获取到一些负载均衡器中一些维护的信息来作为分配的依据,并以此设计一些算法来实现针对特定场景的高效率策略。
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalancerRule implements IRule, IClientConfigAware {
private ILoadBalancer lb;
@Override
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb){
this.lb = lb;
}
@Override
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(){
return lb;
}
}
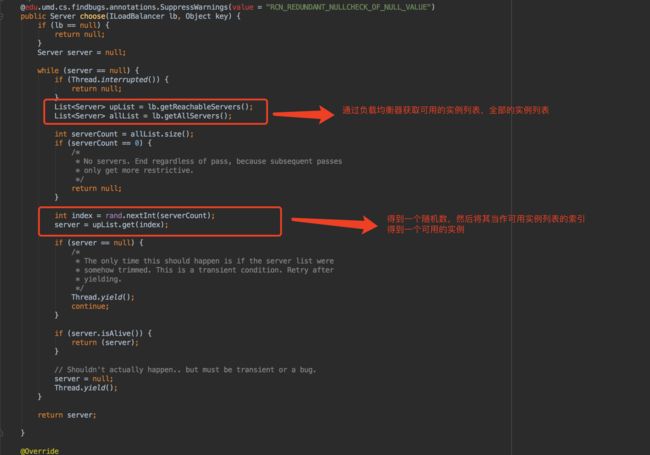
com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
该策略实现了从服务清单中随机选择一个服务实例的功能。
节选了部分源码,也是通过负载均衡器:
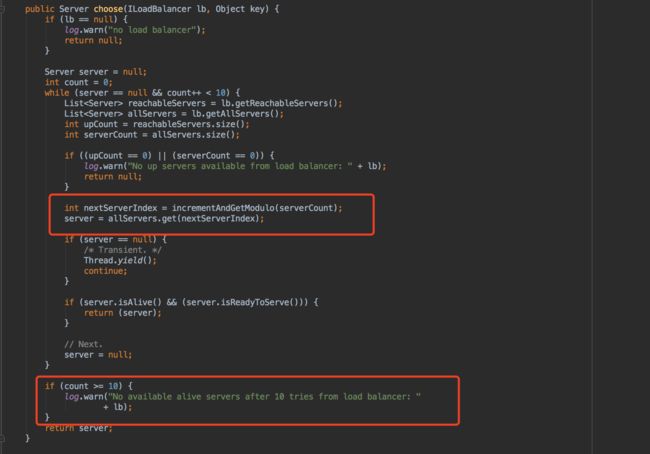
com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule
该策略实现按照线性轮询的方式依次选择实例的功能。它的具体实现如下,在循环中增加了一个count计数变量,该变量会在每次轮询之后累加,如果轮询次数Server超过10次,选择不到实例的话,会报警告信息。
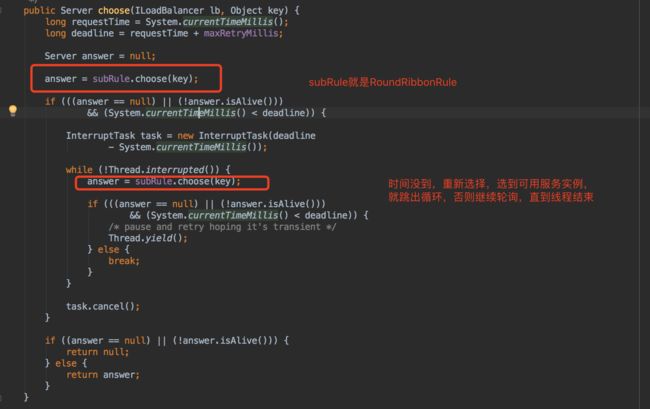
com.netflix.loadbalancer.RetryRule
该策略实现了一个具备重试机制的实例选择功能。具有RoundRobinRule实例的一个引用。也就是在一段时间内通过RoundRobinRule选择服务实例,一段时间内没有选择出服务则线程终止。
com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule
该策略是对RoundRobinRule的扩展,增加了根据实例的运行情况来计算权重,并根据权重来挑选实例,以达到更优的分配效果,增加了三个核心的内容:
会在启动的时候启动一个定时任务,去计算每个实例的权重,默认30s执行一次
void initialize(ILoadBalancer lb) {
if (serverWeightTimer != null) {
serverWeightTimer.cancel();
}
serverWeightTimer = new Timer("NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-"
+ name, true);
serverWeightTimer.schedule(new DynamicServerWeightTask(), 0,
serverWeightTaskTimerInterval);
// do a initial run
ServerWeight sw = new ServerWeight();
sw.maintainWeights();
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
logger
.info("Stopping NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-"
+ name);
serverWeightTimer.cancel();
}
}));
}
具体计算权重的算法
class DynamicServerWeightTask extends TimerTask {
public void run() {
ServerWeight serverWeight = new ServerWeight();
try {
//具体计算权重的方法
serverWeight.maintainWeights();
}catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error(
"Throwable caught while running DynamicServerWeightTask for "
+ name, t);
}
}
}
权重算法
public void maintainWeights() {
ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer();
if (lb == null) {
return;
}
if (serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.get()) {
return; // Ping in progress - nothing to do
} else {
serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(true);
}
try {
logger.info("Weight adjusting job started");
AbstractLoadBalancer nlb = (AbstractLoadBalancer) lb;
LoadBalancerStats stats = nlb.getLoadBalancerStats();
if (stats == null) {
// no statistics, nothing to do
return;
}
double totalResponseTime = 0;
// find maximal 95% response time
for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) {
// this will automatically load the stats if not in cache
ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server);
totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg();
}
// weight for each server is (sum of responseTime of all servers - responseTime)
// so that the longer the response time, the less the weight and the less likely to be chosen
Double weightSoFar = 0.0;
// create new list and hot swap the reference
List finalWeights = new ArrayList();
for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) {
ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server);
double weight = totalResponseTime - ss.getResponseTimeAvg();
weightSoFar += weight;
finalWeights.add(weightSoFar);
}
setWeights(finalWeights);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception while dynamically calculating server weights", t);
} finally {
serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
举个简单的列子,就是4个实例,A,B,C,D平均响应时间为10,40,80,100,所以总响应时间是10+40+80+100=230,每个实例权重为总响应时间与实际自身的平均响应时间的差的累积所得,所以A,B,C,D的权重分别如下:
实例A: 230-10=220
实例B:220+(230-40)=410
实例C:410+(230-80)=560
实例D:560+(230-100)=690
所以实例A:[0.220]
实例B:(220,410]
实例C:(410,560]
实例D:(560,690)
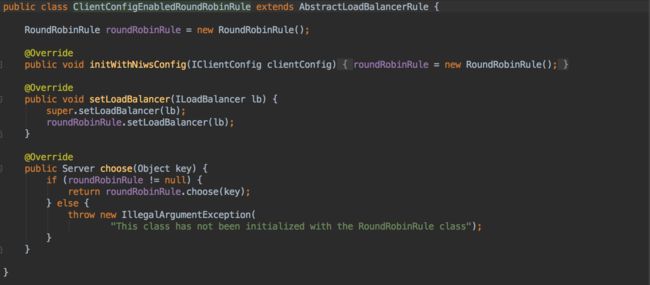
com.netflix.loadbalancer.ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule
该策略较为特殊,一般不直接使用,本身没有实现什么特殊的逻辑,内部也定义了一个RoundRobinRule策略,而choose函数的实现也正是使用了RoundRobinRule的线性轮询机制,所以它实现的功能实际上与RoundRobinRule相同。在子类中做一些高级策略时通常有可能会存在一些无法实施的情况,使用父类的实现作为备选。
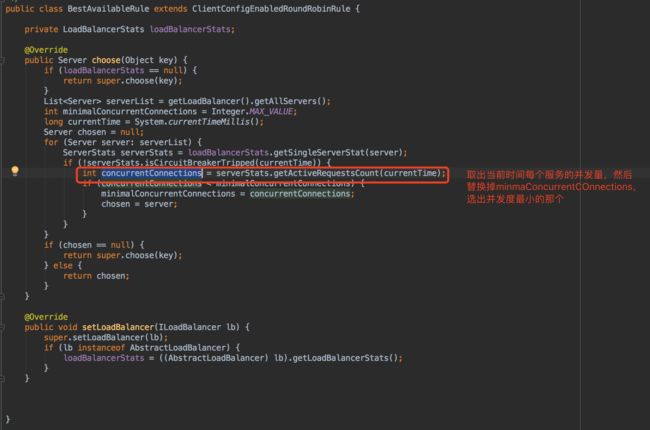
com.netflix.loadbalancer.BestAvailableRule
该策略继承ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule,在实现中它注入了负载均衡的统计对象LoadBalancerStats,同时在具体的choose算法中利用LoadBalancerStats保存的实例统计信息来选择满足要求的实例。它通过遍历负载均衡器中的维护的所有实例,会过滤掉故障的实例,并找出并发请求数最小的一个,所以该策略的特性时可选出最空闲的实例。
同时,该算法核心依赖与LoadBalancerStats,当其为空时候,策略是无法执行,执行父类的线性轮询机制。
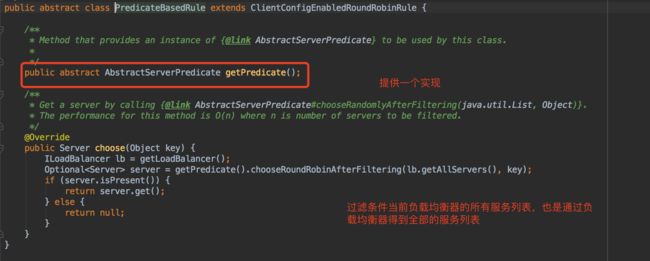
com.netflix.loadbalancer.PredicateBasedRule
这是个抽象策略,他也继承了ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule,这是一个基于Predicate实现的策略,Predicate是Google Guava Collection工具对集合进行过滤的条件接口(java8也引入了这个概念)
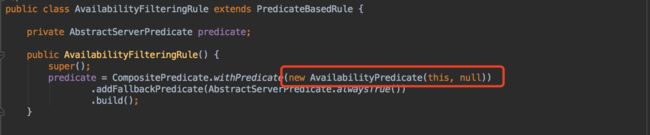
com.netflix.loadbalancer.AvailabilityFilteringRule
继承PredicateBasedRule类,过滤逻辑是AvailabilityPredicate类。
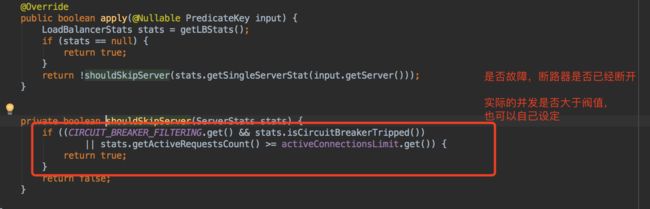
AvailabilityPredicate的过滤逻辑:
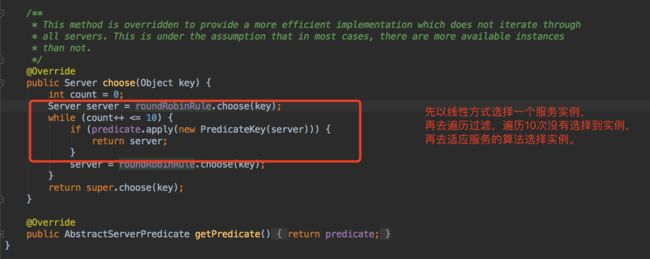
AvailabilityFilteringRule的轮询算法:
com.netflix.loadbalancer.ZoneAvoidanceRule
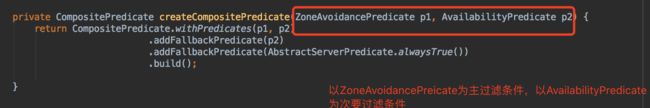
该策略是com.netflix.loadbalancer.PredicateBasedRule的具体实现类。它使用了CompositePredicate来进行服务实例清单的过滤。这是一个组合过滤条件,在其构造函数中,它以ZoneAvoidancePredicate为主要过滤条件,AvailabilityPredicate为次要过滤条件初始化了组合过滤条件的实例。
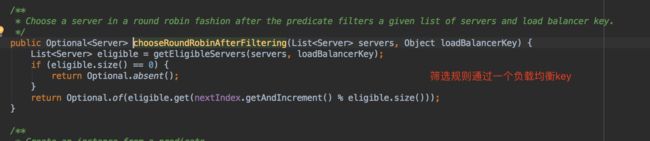
ZoneAvoidanceRule并没有重写choose方法,完全遵循了父类的过滤主逻辑:“先过滤清单,再轮询选择”。
public class CompositePredicate extends AbstractServerPredicate {
private AbstractServerPredicate delegate;
private List fallbacks = Lists.newArrayList();
@Override
public List getEligibleServers(List servers, Object loadBalancerKey) {
List result = super.getEligibleServers(servers, loadBalancerKey);
Iterator i = fallbacks.iterator();
while (!(result.size() >= minimalFilteredServers && result.size() > (int) (servers.size() * minimalFilteredPercentage))
&& i.hasNext()) {
AbstractServerPredicate predicate = i.next();
result = predicate.getEligibleServers(servers, loadBalancerKey);
}
return result;
}
}
在获取过滤结果的实现函数getEligibleServers中,处理逻辑如下:
- 使用主过滤条件对所有实例过滤并返回过滤后的实例清单。
- 依次使用过滤条件进行过滤
- 每次过滤后都去判断二个条件:过滤后的实例总数 >=最小过滤实例数(minimalFilteredServers,默认值是1),过滤后的实例比例 > 最小过滤百分比(minimalFilteredPercentage,默认值为0)