我们使用SQL查询不能只使用很简单、最基础的SELECT语句查询。如果想从多个表查询比较复杂的信息,就会使用高级查询实现。常见的高级查询包括多表连接查询、内连接查询、外连接查询与组合查询等
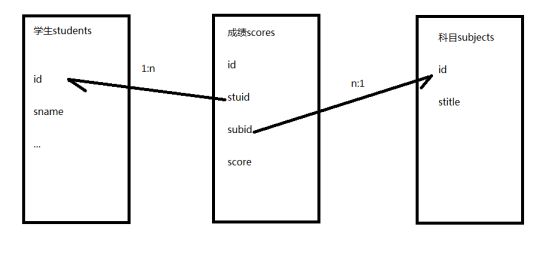
以一个简单的学生信息表(学生ID、学生姓名、学生性别)与一个科目表(科目ID、科目)还有学生成绩表(学生ID、科目ID、分数)为例子
创建表
create table scores(
id int auto_increment primary key,
stuid int,
subid int,
score decimal(5,2),
);
create table students(
id int auto_increment primary key,
sname varchar(20),
sex char(1)
);
create table subjects(
id int auto_increment primary key,
stitle varchar(20)
);
学生列的数据不是在这里新建的,而应该从学生表引用过来,关系也是一条数据;根据范式要求应该存储学生的编号,而不是学生的姓名等其它信息
同理,科目表也是关系列,引用科目表中的数据
外键
思考:怎么保证关系列数据的有效性呢?任何整数都可以吗?
答:必须是学生表中id列存在的数据,可以通过外键约束进行数据的有效性验证为stuid添加外键约束
alter table scores
add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id);
此时插入或者修改数据时,如果stuid的值在students表中不存在则会报错
在创建表时可以直接创建约束
外键的级联操作
- 在删除students表的数据时,如果这个id值在scores中已经存在,则会抛异常
- 推荐使用逻辑删除,还可以解决这个问题
- 可以创建表时指定级联操作,也可以在创建表后再修改外键的级联操作
alter table scores
add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id)
on delete cascade;
在创建表时可以直接创建约束,添加级联操作
create table scores(
id int auto_increment primary key,
stuid int,
subid int,
score decimal(5,2),
#这里我在创建表时直接创建约束,添加级联操作。后面就不用在添加了
foreign key(stuid) references students(id) on delete cascade,
foreign key(subid) references subjects(id) on delete cascade
);
级联操作的类型包括:
restrict(限制):默认值,抛异常
cascade(级联):如果主表的记录删掉,则从表中相关联的记录都将被删除
set null:将外键设置为空
no action:什么都不做
连接查询
-- 建表和数据S
create table students(
id int auto_increment primary key,
sname varchar(20)
);
create table subjects(
id int auto_increment primary key,
stitle varchar(20)
);
create table scores(
id int auto_increment primary key,
stuid int,
subid int,
score decimal(5,2),
foreign key(stuid) references students(id) on delete cascade,
foreign key(subid) references subjects(id) on delete cascade
);
insert into subjects(stitle) values('语文');
insert into subjects(stitle) values('数学');
insert into subjects(stitle) values('英语');
insert into students(sname,sex) values('小明','男');
insert into students(sname,sex) values('小美','女');
insert into students(sname,sex) values('小壮','男');
insert into students(sname,sex) values('小敏','女');
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(1,1,88);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(1,2,95);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(2,1,89);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(2,3,95);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(3,1,92);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(3,2,85);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(4,2,82);
insert into scores(stuid,subid,score) values(4,3,99);
/*查询学生的编号,姓名,科目的名称,成绩*/
select t1.id,t1.sname,t2.stitle,t3.score
from students t1,subjects t2,scores t3
where t3.stuid=t1.id and t3.subid=t2.id;
select t1.id,t1.sname,t2.stitle,t3.score
from scores t3
inner join students t1
on t3.stuid = t1.id
inner join subjects t2
on t3.subid = t2.id;
内连接(INNER JOIN)
INNER JOIN ...表 ON ...条件
-- 查询学生的姓名、平均分
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
group by students.sname;
/*查询学生的编号,姓名,科目的名称,成绩*/
-- 方法一
select t1.id,t1.sname,t2.stitle,t3.score
from students t1,subjects t2,scores t3
where t3.stuid=t1.id and t3.subid=t2.id;
-- 方法二
select t1.id,t1.sname,t2.stitle,t3.score
from scores t3
inner join students t1
on t3.stuid = t1.id
inner join subjects t2
on t3.subid = t2.id;
-- 方法三
select t1.id,t1.sname,t2.stitle,t3.score
from students t1
inner join scores t3
on t3.stuid = t1.id
inner join subjects t2
on t3.subid = t2.id;
-- 查询学生的姓名、平均分
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
group by students.sname;
-- 查询男生的姓名、总分
select students.sname,sum(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
where students.sex='男'
group by students.sname;
-- 查询科目的名称、平均分
select subjects.stitle,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id
group by subjects.stitle;
外联结
1、左外连接(LEFT OUTER JOIN)
概述:指将左表的所有记录与右表符合条件的记录,返回的结果除内连接的结果,还有左表不符合条件的记录,并在右表相应列中填NULL。
2、右外连接(RIGHT OUTER JOIN)
概述:与左外连接相反,指将右表的所有记录与左表符合条件的记录,返回的结果除内连接的结果,还有右表不符合条件的记录,并在左表相应列中填NULL。
学生姓名来源于students表,科目名称来源于subjects,分数来源于scores表
当查询结果来源于多张表时,需要使用连接查询
当查询结果来源于多张表时,需要使用连接查询
关键:找到表间的关系,当前的关系是
students表的id---scores表的stuid
subjects表的id---scores表的subid
select students.sname,subjects.stitle,scores.score
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id;
- 连接查询分类如下:
- 表A inner join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中
- 表A left join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表A中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 表A right join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表B中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 在查询或条件中推荐使用“表名.列名”的语法
- 如果多个表中列名不重复可以省略“表名.”部分
- 如果表的名称太长,可以在表名后面使用' as 简写名'或' 简写名',为表起个临时的简写名称
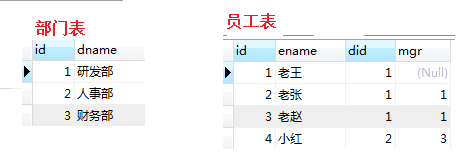
用一个部门表,员工表演示一下内外连接查询
-- 部门表,员工表
drop table if exists emp;
drop table if exists dept;
create table dept(
id int auto_increment primary key,
dname varchar(20)
);
create table emp(
id int auto_increment primary key,
ename varchar(20),
did int not null,
mgr int,
foreign key(did) references dept(id),
foreign key(mgr) references emp(id)
);
insert into dept(dname) values('研发部');
insert into dept(dname) values('人事部');
insert into dept(dname) values('财务部');
insert into emp(ename,did,mgr) values('老王',1,null);
insert into emp(ename,did,mgr) values('老张',1,1);
insert into emp(ename,did,mgr) values('老赵',1,1);
insert into emp(ename,did,mgr) values('小红',2,3);
insert into emp(ename,did,mgr) values('小丽',2,3);
/*查询员工额编号,姓名,上级的姓名*/
-- 1
select t1.id,t1.ename,t2.ename
from emp t1,emp t2
where t1.mgr = t2.id;
-- 2inner join
select t1.id,t1.ename,t2.ename
from emp t1
inner join emp t2
on t1.mgr = t2.id;
-- 3左外连接
select t1.id,t1.ename,t2.ename
from emp t1
left join emp t2
on t1.mgr = t2.id;
-- 4右外连接
select t1.id,t1.ename,t2.ename
from emp t1
right join emp t2
on t1.mgr = t2.id;
自关联
概述:指用表的别名实现表自身的连接。
在员工表中mgr列中代表了他们的上级
/*查询员工额编号,姓名,上级的姓名*/
select 员工表.id,员工表.ename 员工,上级表.ename 上级 from emp 员工表,emp 上级表
where 员工表.mgr = 上级表.id;
子查询
查询支持嵌套使用
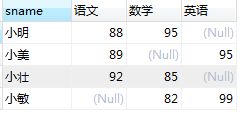
查询各学生的语文、数学、英语的成绩
-- 查询各学生的语文、数学、英语的成绩
select sname,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id
where sub.stitle='语文' and stuid=stu.id) as 语文,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id
where sub.stitle='数学' and stuid=stu.id) as 数学,
(select sco.score from scores sco inner join subjects sub on sco.subid=sub.id
where sub.stitle='英语' and stuid=stu.id) as 英语
from students stu;
内置函数
字符串函数
-- 查看字符的ascii码值ascii(str),str是空串时返回0
select ascii('a');
-- 查看ascii码值对应的字符char(数字)
select char(97);
-- 拼接字符串concat(str1,str2...)
select concat(12,34,'ab');
-- 包含字符个数length(str)
select length('abc');
-- 截取字符串
-- left(str,len)返回字符串str的左端len个字符
-- right(str,len)返回字符串str的右端len个字符
-- substring(str,pos,len)返回字符串str的位置pos起len个字符
select substring('abc123',2,3);
-- 去除空格
-- ltrim(str)返回删除了左空格的字符串str
-- rtrim(str)返回删除了右空格的字符串str
-- trim([方向 remstr from str)返回从某侧删除remstr后的字符串str,
-- 方向词包括both、leading、trailing,表示两侧、左、右
select trim(' bar ');
select trim(leading 'x' FROM 'xxxbarxxx');
select trim(both 'x' FROM 'xxxbarxxx');
select trim(trailing 'x' FROM 'xxxbarxxx');
-- 返回由n个空格字符组成的一个字符串space(n)
select space(10);
-- 替换字符串replace(str,from_str,to_str)
select replace('abc123','123','def');
-- 大小写转换,函数如下
-- lower(str)
-- upper(str)
select lower('aBcD');
数学函数
-- 求绝对值abs(n)
select abs(-32);
-- 求m除以n的余数mod(m,n),同运算符%
select mod(10,3);
select 10%3;
-- 地板floor(n),表示不大于n的最大整数
select floor(2.3);
-- 天花板ceiling(n),表示不小于n的最大整数
select ceiling(2.3);
-- 求四舍五入值round(n,d),n表示原数,d表示小数位置,默认为0
select round(1.6);
-- 求x的y次幂pow(x,y)
select pow(2,3);
-- 获取圆周率PI()
select PI();
-- 随机数rand(),值为0-1.0的浮点数
select rand();
-- 还有其它很多三角函数,使用时可以查询文档
日期时间函数
获取子值,语法如下
year(date)返回date的年份(范围在1000到9999)
month(date)返回date中的月份数值
day(date)返回date中的日期数值
hour(time)返回time的小时数(范围是0到23)
minute(time)返回time的分钟数(范围是0到59)
second(time)返回time的秒数(范围是0到59)
select year('2016-12-21');
日期计算,使用+-运算符,数字后面的关键字为year、month、day、hour、minute、second
select '2016-12-21'+interval 1 day;
获取年%Y,返回4位的整数
获取年%y,返回2位的整数
获取月%m,值为1-12的整数
获取日%d,返回整数
获取时%H,值为0-23的整数
获取时%h,值为1-12的整数
获取分%i,值为0-59的整数
获取秒%s,值为0-59的整数
/*日期-->字符串*/
select date_format('2017-10-20','%Y年%m月%d日')
/*字符串-->日期*/
select str_to_date('2017年10月20日','%Y年%m月%d日')
当前日期current_date()
select current_date();
当前时间current_time()
select current_time();
当前日期时间now()
select now();