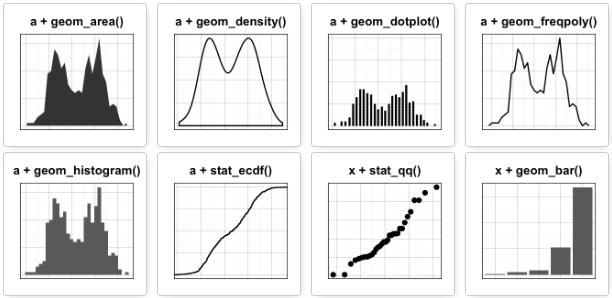
写在前面
ggplot2 是一个功能强大且灵活的R包 ,由Hadley Wickham 编写,其用于生成优雅的图形。ggplot2中的gg 表示图形语法(Grammar of Graphics),这是一个通过使用“语法”来绘图的图形概念。
根据ggplot2的画图理念,一个图可以分为不同的基本部分:
Plot = data + Aesthetics + Geometry 。
每个图形的主要组成部分定义如下:
data:数据集,主要是数据框
Aesthetics :映射,用来表示变量x和y,还可以用来控制颜色 ,点的大小或形状,条的高度等
Geometry :几何对象,即各种图形类型(直方图、箱线图、线图、直方图、点图等 )
ggplot2 包中提供了两个用于绘图的函数:qplot() 和ggplot() 。
qplot() :是一个快速绘图函数,用于绘制简单图形。
ggplot() :比qplot更灵活,更强大,可以分图层逐步绘图。
生成的图形可以保存为变量,然后可以用print()函数随时打印出来。
创建图形后,另外两个重要函数是:
last_plot() :返回要修改的最后一个图形
ggsave(“plot.png”,width = 5,height = 5) :保存当前工作目录中的最后一个图形。
数据可视化的图形类型
根据数据集的不同,ggplot2提供不同的图形类型。ggplot2提供了以下数据结构的绘图方法:
- 一个变量-x :连续的或离散的
- 两个变量-x和y :连续和/或离散
- 连续双变量分布 - x和y (均为连续)
- 连续函数
- 误差棒
- 地图
- 三个变量
安装和加载ggplot2包
安装ggplot2的三种姿势:
#直接安装tidyverse包
install.packages("tidyverse")
#直接安装ggplot2
install.packages("ggplot2")
#从Github上安装最新的版本,先安装devtools(如果没安装的话)
devtools::install_github("tidyverse/ggplot2")
加载ggplot2:
library(ggplot2)
数据格式和数据准备
注意:数据集应为数据框格式
下面例子中将使用数据集mtcars。
#加载数据
data(mtcars)
df <- mtcars[, c("mpg","cyl","wt")]
#将cyl转换为因子型
df$cyl <- as.factor(df$cyl)
head(df)
## mpg cyl wt
## Mazda RX4 21.0 6 2.620
## Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 2.875
## Datsun 710 22.8 4 2.320
## Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 3.215
## Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 3.440
## Valiant 18.1 6 3.460
qplot():使用ggplot2快速绘图
qplot() 函数与R中基本绘图函数plot() 类似,可以快速绘制一些简单的图形:散点图 、箱线图 、小提琴图 、直方图 、和密度图等。
但是,plot函数与qplot函数之间还有一些重要的区别 :
- qplot()不是泛型函数 :当不同类型的R对象传入qplot()时,它并不会匹配默认的函数调用。而ggplot()是一个泛型函数,从而可以对任意类型的R对象进行可视化操作。
- 一般的,可以将一个变量传递给图形属性,这样该变量将进行标度转换并显示在图例上。比如让点的颜色变为红色,则可以使用
I()函数:colour = I("red")。 - ggplot2中的图形属性名称(如colour,shape和size)比基础绘图系统中的名称(如col,pch和cex)
- 在基础绘图系统中,可以通过
points(),lines()和text()函数来向已有的图形中添加更多的元素。而在ggplot2中,需要在当前的图形中加入额外的图层。
qplot函数的绘图格式为:
qplot(x, y=NULL, data, geom="auto")
其中:
x,y :分别为x和y值。参数y是可选的,具体取决于要创建的图形的类型。
data :数据框
geom :几何对象,变量x和y同时指定默认为散点图,仅指定x默认为直方图。
其他参数如main,xlab和ylab也可用于向图形添加主标题和轴标签。
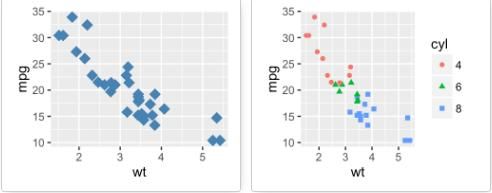
散点图
下面的R代码使用参数geom =“point”创建基本散点图,也可以组合不同的几何对象(例如:geom = c(“point”,“smooth”))。
# 基本散点图
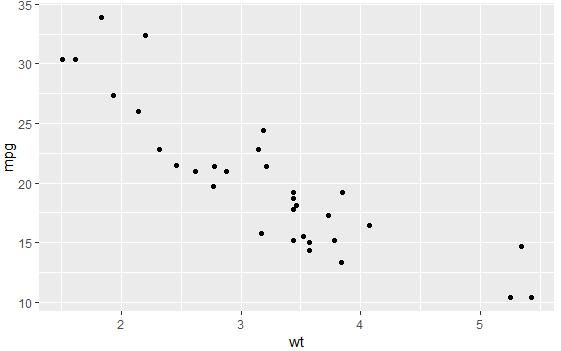
qplot(x = mpg, y = wt, data = df, geom = "point")
# 添加平滑曲线
qplot(mpg, wt, data = df, geom = c("point", "smooth"))
以下R代码将按组更改点的颜色和形状。列cyl将用作分组变量,即点的颜色和形状将由cyl的大小决定。
qplot(mpg, wt, data = df, colour = cyl, shape = cyl)
箱线图、小提琴图和点图
下面的R代码生成一些按性别分列的数据集(M为男性; F为女性):
set.seed(1234)
wdata = data.frame(
sex = factor(rep(c("F", "M"), each=200)),
weight = c(rnorm(200, 55), rnorm(200, 58)))
head(wdata)
## sex weight
## 1 F 53.79293
## 2 F 55.27743
## 3 F 56.08444
## 4 F 52.65430
## 5 F 55.42912
## 6 F 55.50606
# 基本箱线图
qplot(sex, weight, data = wdata, geom= "boxplot", fill = sex)
# 小提琴图
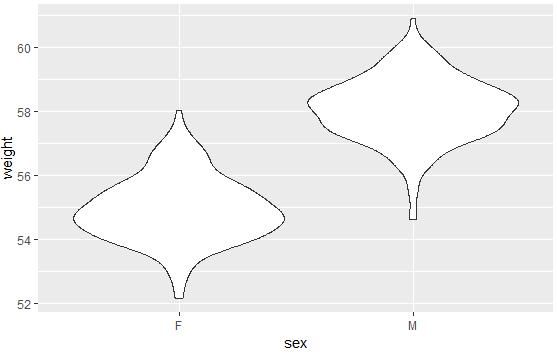
qplot(sex, weight, data = wdata, geom = "violin")
# 点图
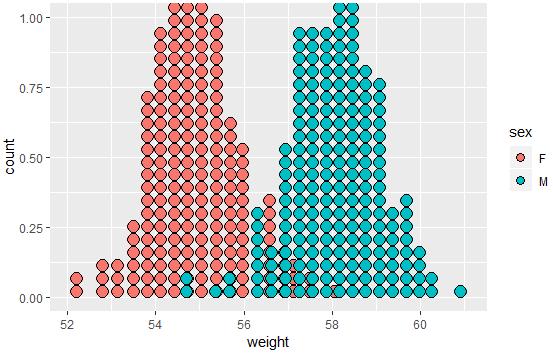
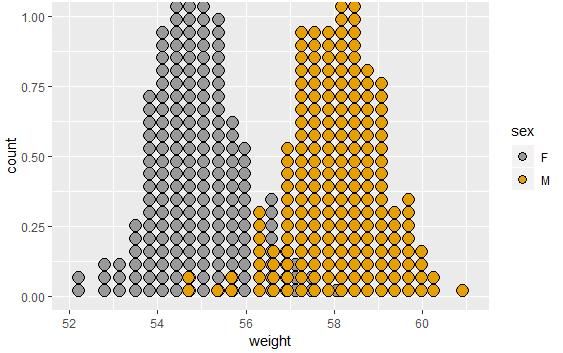
qplot(sex, weight, data = wdata, geom = "dotplot",stackdir = "center", binaxis = "y", dotsize = 0.5)
直方图和密度图
直方图和密度图用于显示数据的分布情况。
# 直方图
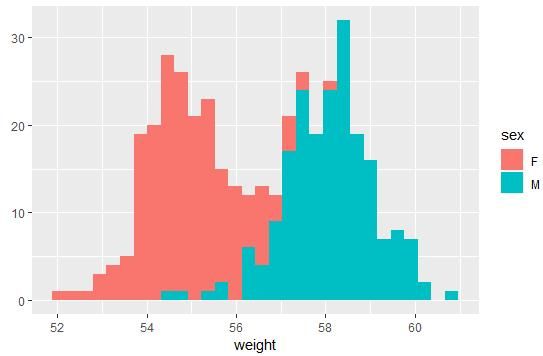
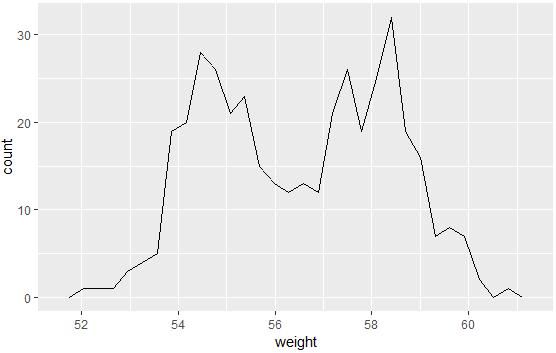
qplot(weight, data = wdata, geom = "histogram",fill = sex)
# 密度图
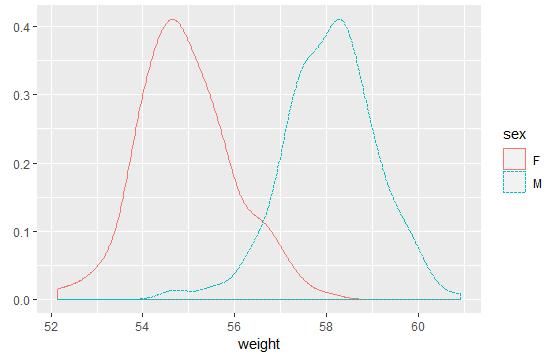
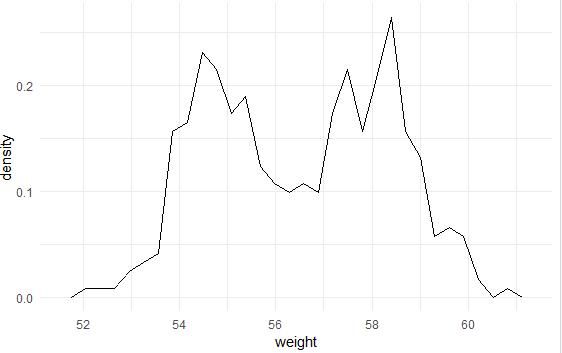
qplot(weight, data = wdata, geom = "density", color = sex, linetype = sex)
ggplot():逐层绘图
下面以绘制一个散点图来说明函数ggplot() 的使用,函数aes() 用来指定映射,另外还可以选择使用函数aes_string() ,它可以生成字符串的映射。
# 散点图
ggplot(data = mtcars, aes(x = wt, y = mpg)) + geom_point()
# 改变点大小和形状
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x = wt, y = mpg)) + geom_point(size = 2, shape = 23)
函数aes_string()的使用如下:
ggplot(mtcars, aes_string(x = "wt", y = "mpg")) + geom_point(size = 2, shape = 23)
画图过程中的原始数据集往往要经过转换( transformation) ,这时添加图层的另一种方式是使用stat_*() 函数。
下例中的 geom_density() 与stat_density() 函数的功能是等价的:
ggplot(wdata, aes(x = weight)) + geom_density()
ggplot(wdata, aes(x = weight)) + stat_density()
对于每一种图形类型,ggplot2几乎都提供了geom()和对应的stat()。
一个变量:连续型
下面将使用先前生成的数据集wdata。
head(wdata)
## sex weight
## 1 F 53.79293
## 2 F 55.27743
## 3 F 56.08444
## 4 F 52.65430
## 5 F 55.42912
## 6 F 55.50606
计算不同性别的体重平均值:
library(plyr)
mu <- ddply(wdata, "sex", summarise, grp.mean=mean(weight))
head(mu)
## sex grp.mean
## 1 F 54.94224
## 2 M 58.07325
首先绘制一个图层a,然后逐渐添加图层。
a <- ggplot(wdata, aes(x = weight))
可能添加的图层有:
- 对于一个连续变量:
- 面积图geom_area()
- 密度图geom_density()
- 点图geom_dotplot()
- 频率多边图geom_freqpoly()
- 直方图geom_histogram()
- 经验累积密度图stat_ecdf()
- QQ图stat_qq()
- 对于一个离散变量:
- 条形图geom_bar()
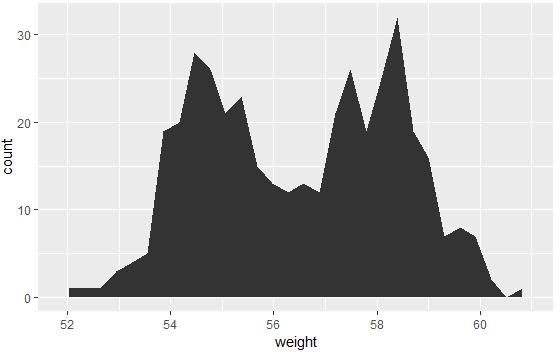
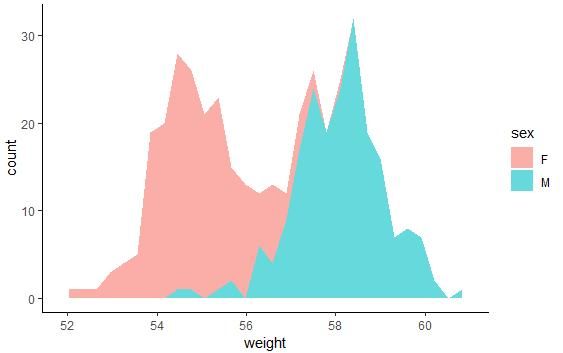
geom_area():创建面积图
# 面积图
a + geom_area(stat = "bin")
# 改变颜色
a + geom_area(aes(fill = sex), stat ="bin", alpha=0.6) + theme_classic()
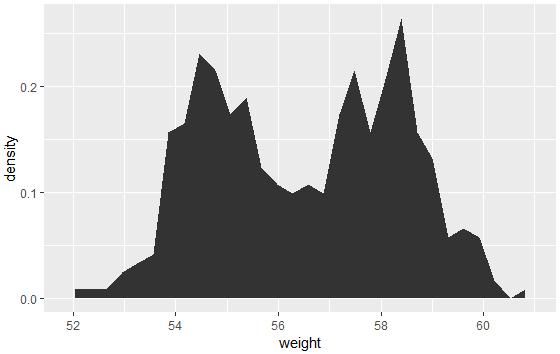
注意:y轴默认为变量weight的数量即count,如果y轴要显示密度,可用以下代码:
a+geom_area(aes(y=..density..), stat = "bin")
可以通过修改不同属性如透明度、填充颜色、大小、线型等自定义图形。
另一相同功能的函数:stat_bin()
a + stat_bin(geom = "area")
geom_density():创建密度图
下面将使用如下函数:
- geom_density():绘制密度图
- geom_vline():添加竖直线
- scale_color_manual():手动修改颜色
# 密度图
a + geom_density()
# 改变线的颜色
a + geom_density(aes(color = sex))
# 修改填充色及透明度
a + geom_density(aes(fill = sex), alpha=0.4)
# 添加均值线及手动修改颜色
a + geom_density(aes(color = sex)) + geom_vline(data=mu, aes(xintercept=grp.mean, color=sex), linetype="dashed") + scale_color_manual(values=c("#999999", "#E69F00"))
另一相同功能的函数:stat_density()
a + stat_density()
geom_dotplot():点图
在点图中,每个点代表一个观察点。
# 点图
a + geom_dotplot()
# 改变填充色
a + geom_dotplot(aes(fill = sex))
# 手动改变填充色
a + geom_dotplot(aes(fill = sex)) + scale_fill_manual(values=c("#999999", "#E69F00"))
geom_freqpoly():频率多边形
# 频率多边图
a + geom_freqpoly()
# 将y轴变为密度值
# 改变主题
a + geom_freqpoly(aes(y = ..density..)) + theme_minimal()
# 改变颜色和线型
a + geom_freqpoly(aes(color = sex, linetype = sex)) + theme_minimal()
另一相同功能的函数:stat_bin()
geom_histogram():直方图
# 直方图
a + geom_histogram()
# 改变线颜色
a + geom_histogram(aes(color = sex), fill = "white", position = "dodge")
# 将y轴变为密度值
a + geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..))
另一相同功能的函数:stat_bin()
a + stat_bin(geom = "histogram")
stat_ecdf():经验累积密度图
a + stat_ecdf()
stat_qq():QQ图
ggplot(mtcars, aes(sample=mpg)) + stat_qq()
一个变量:离散型
函数geom_bar()可用于一个离散变量的可视化。
data(mpg)
b <- ggplot(mpg, aes(fl))
# 直方图
b + geom_bar()
# 改变填充色
b + geom_bar(fill = "steelblue", color ="steelblue") + theme_minimal()
另一相同功能的函数:stat_count()
b + stat_count()
两个变量:X,Y皆连续
下面将使用数据集mtcars。
data(mtcars)
mtcars$cyl <- as.factor(mtcars$cyl)
head(mtcars[, c("wt", "mpg", "cyl")])
## wt mpg cyl
## Mazda RX4 2.620 21.0 6
## Mazda RX4 Wag 2.875 21.0 6
## Datsun 710 2.320 22.8 4
## Hornet 4 Drive 3.215 21.4 6
## Hornet Sportabout 3.440 18.7 8
## Valiant 3.460 18.1 6
首先绘制一个图层b,然后逐层添加。
可能添加的图层有:
- geom_point():散点图
- geom_smooth():平滑线
- geom_quantile():分位线
- geom_rug():边际地毯线
- geom_jitter():避免重叠
- geom_text():添加文本注释
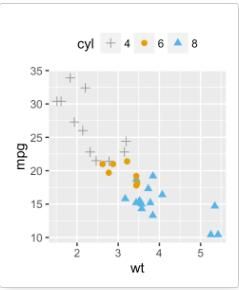
geom_point():散点图
# 散点图
b + geom_point()
# 改变点形状和颜色
b + geom_point(aes(color = cyl, shape = cyl))
# 手动修改点颜色
b + geom_point(aes(color = cyl, shape = cyl)) + scale_color_manual(values = c("#999999", "#E69F00", "#56B4E9")) + theme_minimal()
geom_smooth():平滑线
要在散点图上添加回归线,函数geom_smooth()将与参数method = lm结合使用。lm代表线性模型。
# 添加回归曲线
b + geom_smooth(method = lm)
# 散点图+回归线
b + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = lm, se = FALSE)
# 使用loess方法
b + geom_point() + geom_smooth()
# 改变颜色和形状
b + geom_point(aes(color=cyl, shape=cyl)) +
geom_smooth(aes(color=cyl, shape=cyl), method=lm, se=FALSE, fullrange=TRUE)
另一相同功能的函数:stat_smooth()
b + stat_smooth(method = "lm")
geom_quantile():分位线
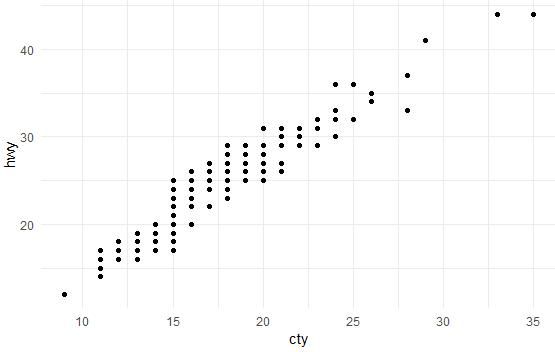
ggplot(mpg, aes(cty, hwy)) + geom_point() + geom_quantile() + theme_minimal()
另一相同功能的函数:stat_quantile()
ggplot(mpg, aes(cty, hwy)) +
geom_point() + stat_quantile(quantiles = c(0.25, 0.5, 0.75))
geom_rug():边际地毯线
下面使用数据集faithful。
ggplot(data = faithful, aes(x=eruptions, y=waiting))+
geom_point()+geom_rug()
geom_jitter():避免重叠
函数geom_jitter() 是函数geom_point(position = ‘jitter’) 的简化形式,下面的例子将使用数据集mpg。
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(displ, hwy))
# 添加散点图
p + geom_point()
# 避免重叠
p + geom_jitter(position = position_jitter(width = 0.5, height = 0.5))
可以使用函数position_jitter() 中的width 和width 参数来调整抖动的程度:
- width:x轴方向的抖动幅度
- height:y轴方向的抖动幅度
geom_text():文本注释
参数label 用来指定注释标签。
b + geom_text(aes(label = rownames(mtcars)))
两个变量:连续二元分布
下面将使用数据集diamonds。
data(diamonds)
head(diamonds[, c("carat", "price")])
## carat price
## 1 0.23 326
## 2 0.21 326
## 3 0.23 327
## 4 0.29 334
## 5 0.31 335
## 6 0.24 336
首先绘制一个图层c,然后再逐层添加。
c <- ggplot(diamonds, aes(carat, price))
可能添加的图层有:
- geom_bin2d(): 二维封箱热图
- geom_hex(): 六边形封箱图
- geom_density_2d(): 二维等高线密度图
geom_bin2d():二维封箱热图
geom_bin2d() 将点的数量用矩形封装起来,通过颜色深浅来反映点密度。
# 二维封箱热图
c + geom_bin2d()
# 改变bin的数量
c + geom_bin2d(bins = 15)
另一相同功能的函数:stat_bin_2d(), stat_summary_2d()
c + stat_bin_2d()
c + stat_summary_2d(aes(z = depth))
geom_hex():六边形封箱图
geom_hex()依赖于另一个R包hexbin,所以没安装的先安装:
install.packages("hexbin")
geom_hex()函数的用法如下:
require(hexbin)
# 六边形封箱图
c + geom_hex()
# 改变bin的数量
c + geom_hex(bins = 10)
另一相同功能的函数:stat_bin_hex(), stat_summary_hex()
c + stat_bin_hex()
c + stat_summary_hex(aes(z = depth))
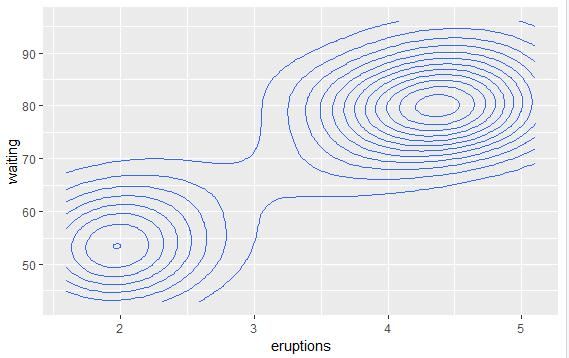
geom_density_2d():二维等高线密度图
geom_density_2d() 或 stat_density_2d() 可将二维等高线密度图添加到散点图上,下面首先绘制一个散点图:
sp <- ggplot(faithful, aes(x=eruptions, y=waiting))
# 添加二维等高线密度图
sp + geom_density_2d()
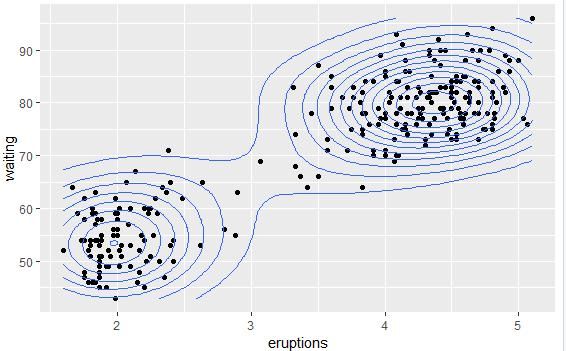
# 添加散点图
sp + geom_point() + geom_density_2d()
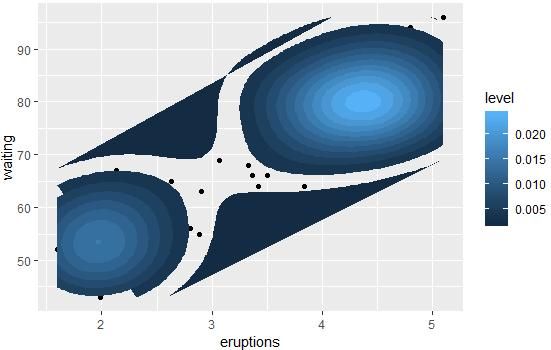
# 将默认图形改为多边形
sp + geom_point() +
stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom="polygon")
另一相同功能的函数:stat_density_2d()
sp + stat_density_2d()
两个变量:连续函数
在本节中,主要是关于如何用线来连接两个变量。
data(economics)
head(economics)
## date pce pop psavert uempmed unemploy
## 1 1967-07-01 507.4 198712 12.5 4.5 2944
## 2 1967-08-01 510.5 198911 12.5 4.7 2945
## 3 1967-09-01 516.3 199113 11.7 4.6 2958
## 4 1967-10-01 512.9 199311 12.5 4.9 3143
## 5 1967-11-01 518.1 199498 12.5 4.7 3066
## 6 1967-12-01 525.8 199657 12.1 4.8 3018
首先绘制一个图层d,然后逐层绘制。
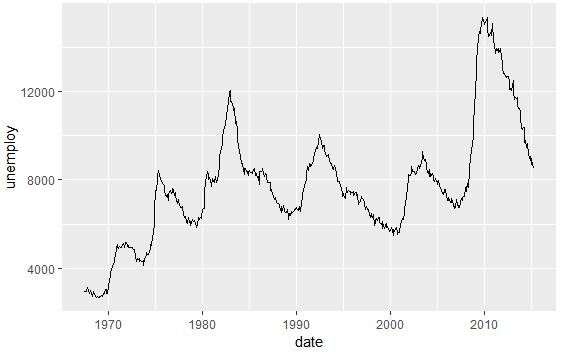
d <- ggplot(economics, aes(x = date, y = unemploy))
可能添加的图层有:
- geom_area():面积图
- geom_line():折线图
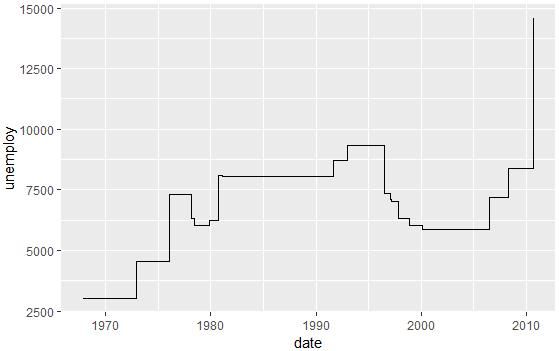
- geom_step(): 阶梯图
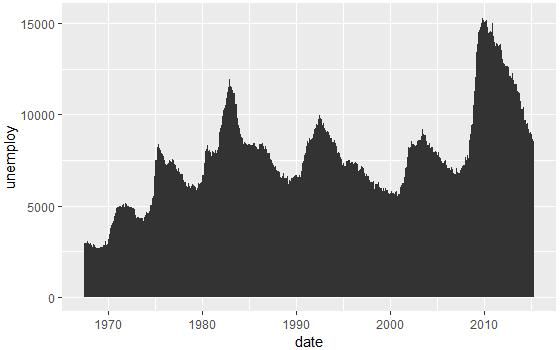
# 面积图
d + geom_area()
# 折线图
d + geom_line()
# 阶梯图
set.seed(1234)
ss <- economics[sample(1:nrow(economics), 20), ]
ggplot(ss, aes(x = date, y = unemploy)) + geom_step()
两个变量:x离散,y连续
下面将使用数据集ToothGrowth,其中的变量len(Tooth length)是连续变量,dose是离散变量。
data("ToothGrowth")
ToothGrowth$dose <- as.factor(ToothGrowth$dose)
head(ToothGrowth)
## len supp dose
## 1 4.2 VC 0.5
## 2 11.5 VC 0.5
## 3 7.3 VC 0.5
## 4 5.8 VC 0.5
## 5 6.4 VC 0.5
## 6 10.0 VC 0.5
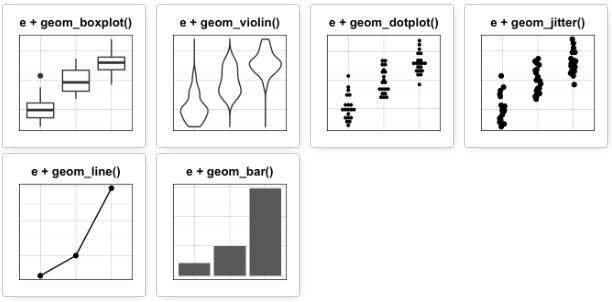
首先绘制一个图层e,然后逐层绘制。
e <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x = dose, y = len))
可能添加的图层有:
- geom_boxplot(): 箱线图
- geom_violin():小提琴图
- geom_dotplot():点图
- geom_jitter(): 带状图
- geom_line(): 线图
- geom_bar(): 条形图
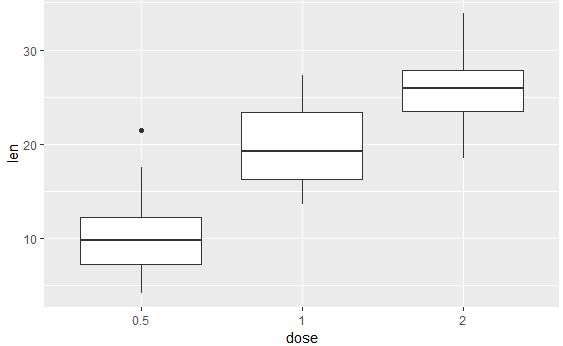
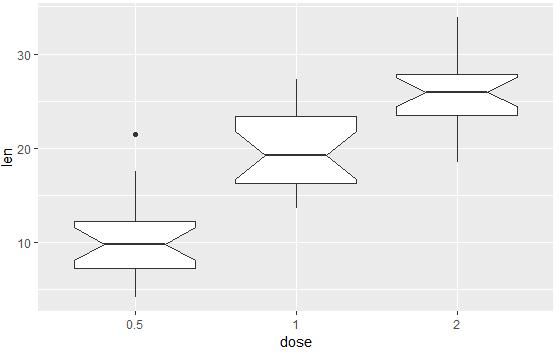
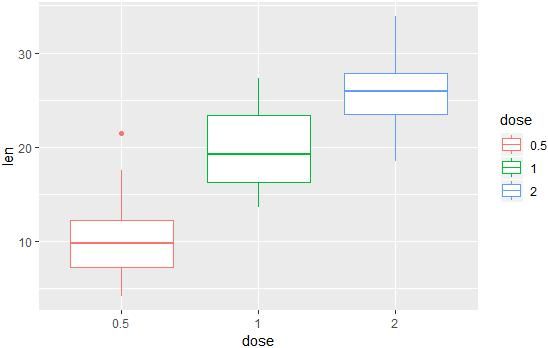
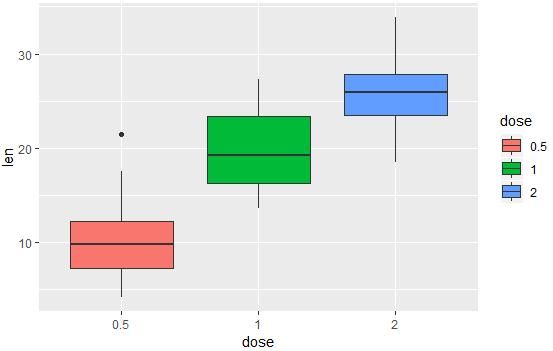
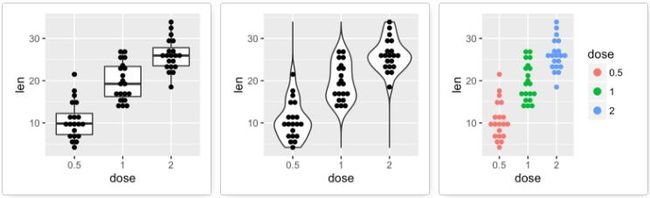
geom_boxplot():箱线图
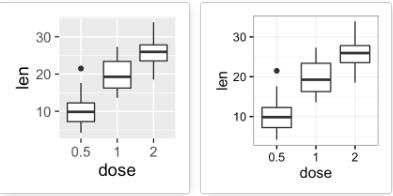
# 箱线图
e + geom_boxplot()
# 添加有缺口的箱线图
e + geom_boxplot(notch = TRUE)
# 改变颜色
e + geom_boxplot(aes(color = dose))
# 改变填充色
e + geom_boxplot(aes(fill = dose))
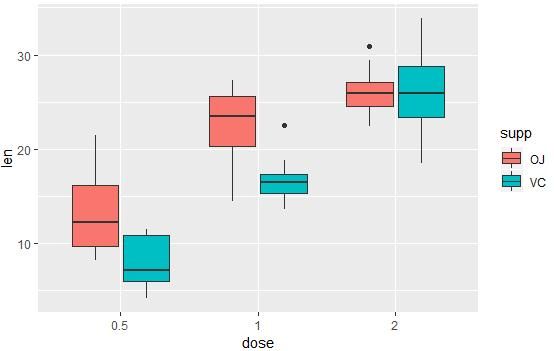
# 多组的箱线图
ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len, fill=supp)) +
geom_boxplot()
另一相同功能的函数:stat_boxplot()
e + stat_boxplot(coeff = 1.5)
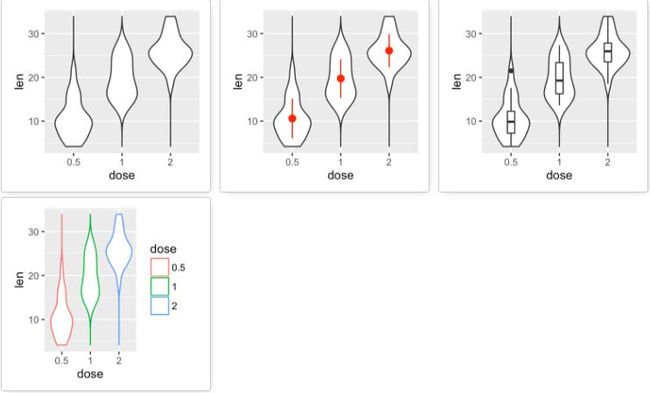
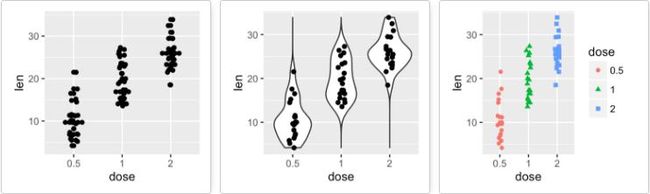
geom_violin():小提琴图
# 添加小提琴图
e + geom_violin(trim = FALSE)
# 添加中值点
e + geom_violin(trim = FALSE) +
stat_summary(fun.data="mean_sdl", fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="pointrange", color = "red")
# 与箱线图结合
e + geom_violin(trim = FALSE) +
geom_boxplot(width = 0.2)
# 将dose映射给颜色进行分组
e + geom_violin(aes(color = dose), trim = FALSE)
另一相同功能的函数:stat_ydensity()
e + stat_ydensity(trim = FALSE)
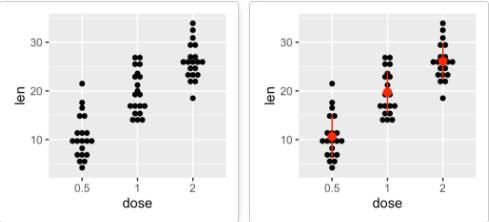
geom_dotplot():点图
# 添加点图
e + geom_dotplot(binaxis = "y", stackdir = "center")
# 添加中值点
e + geom_dotplot(binaxis = "y", stackdir = "center") +
stat_summary(fun.data="mean_sdl", fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="pointrange", color = "red")
# 与箱线图结合
e + geom_boxplot() +
geom_dotplot(binaxis = "y", stackdir = "center")
# 添加小提琴图
e + geom_violin(trim = FALSE) +
geom_dotplot(binaxis='y', stackdir='center')
# 将dose映射给颜色以及填充色
e + geom_dotplot(aes(color = dose, fill = dose),
binaxis = "y", stackdir = "center")
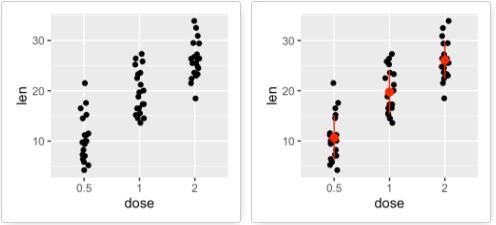
geom_jitter():带状图
带状图是一种一维散点图,当样本量很小时,与箱线图相当。
# 添加带状图
e + geom_jitter(position=position_jitter(0.2))
# 添加中值点
e + geom_jitter(position=position_jitter(0.2)) +
stat_summary(fun.data="mean_sdl", fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="pointrange", color = "red")
# 与点图结合
e + geom_jitter(position=position_jitter(0.2)) +
geom_dotplot(binaxis = "y", stackdir = "center")
# 与小提琴图结合
e + geom_violin(trim = FALSE) +
geom_jitter(position=position_jitter(0.2))
# 将dose映射给颜色和形状
e + geom_jitter(aes(color = dose, shape = dose),
position=position_jitter(0.2))
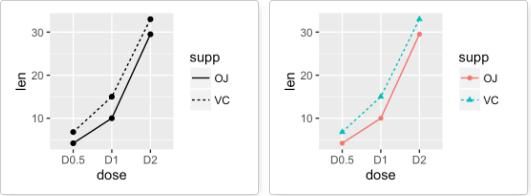
geom_line():线图
# 构造一个数据集
df <- data.frame(supp=rep(c("VC", "OJ"), each=3),
dose=rep(c("D0.5", "D1", "D2"),2),
len=c(6.8, 15, 33, 4.2, 10, 29.5))
head(df)
## supp dose len
## 1 VC D0.5 6.8
## 2 VC D1 15.0
## 3 VC D2 33.0
## 4 OJ D0.5 4.2
## 5 OJ D1 10.0
## 6 OJ D2 29.5
将supp变量映射给线型:
# 改变线型
ggplot(df, aes(x=dose, y=len, group=supp)) +
geom_line(aes(linetype=supp))+
geom_point()
# 修改线型、点的形状以及颜色
ggplot(df, aes(x=dose, y=len, group=supp)) +
geom_line(aes(linetype=supp, color = supp))+
geom_point(aes(shape=supp, color = supp))
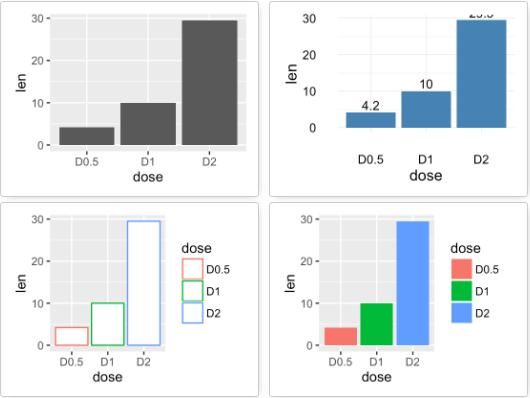
geom_bar():条形图
# 构造一个数据集
df <- data.frame(dose=c("D0.5", "D1", "D2"),
len=c(4.2, 10, 29.5))
head(df)
## dose len
## 1 D0.5 4.2
## 2 D1 10.0
## 3 D2 29.5
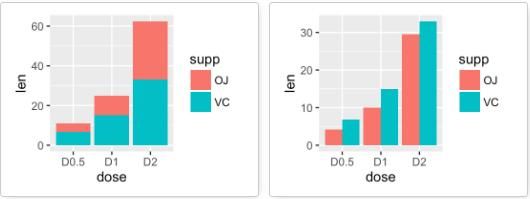
df2 <- data.frame(supp=rep(c("VC", "OJ"), each=3),
dose=rep(c("D0.5", "D1", "D2"),2),
len=c(6.8, 15, 33, 4.2, 10, 29.5))
head(df2)
## supp dose len
## 1 VC D0.5 6.8
## 2 VC D1 15.0
## 3 VC D2 33.0
## 4 OJ D0.5 4.2
## 5 OJ D1 10.0
## 6 OJ D2 29.5
绘制一个图层:
f <- ggplot(df, aes(x = dose, y = len))
# 添加条形图
f + geom_bar(stat = "identity")
# 修改填充色以及添加标签
f + geom_bar(stat="identity", fill="steelblue")+
geom_text(aes(label=len), vjust=-0.3, size=3.5)+
theme_minimal()
# 将dose映射给条形图颜色
f + geom_bar(aes(color = dose),
stat="identity", fill="white")
# 修改填充色
f + geom_bar(aes(fill = dose), stat="identity")
g <- ggplot(data=df2, aes(x=dose, y=len, fill=supp))
# 堆积条形图,position参数默认值为stack
g + geom_bar(stat = "identity")
# 修改position为dodge
g + geom_bar(stat="identity", position=position_dodge())
另一相同功能的函数: stat_identity()
g + stat_identity(geom = "bar")
g + stat_identity(geom = "bar", position = "dodge")
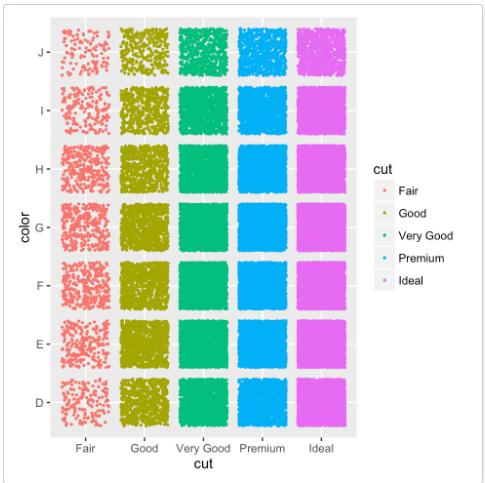
两个变量:X,Y皆离散
下面将使用数据集diamonds中的两个离散变量color以及cut。
ggplot(diamonds, aes(cut, color)) +
geom_jitter(aes(color = cut), size = 0.5)
两个变量:绘制误差图
df <- ToothGrowth
df$dose <- as.factor(df$dose)
head(df)
## len supp dose
## 1 4.2 VC 0.5
## 2 11.5 VC 0.5
## 3 7.3 VC 0.5
## 4 5.8 VC 0.5
## 5 6.4 VC 0.5
## 6 10.0 VC 0.5
下面这个函数用来计算每组的均值以及标准误。
data_summary <- function(data, varname, grps){
require(plyr)
summary_func <- function(x, col){
c(mean = mean(x[[col]], na.rm=TRUE),
sd = sd(x[[col]], na.rm=TRUE))
}
data_sum<-ddply(data, grps, .fun=summary_func, varname)
data_sum <- rename(data_sum, c("mean" = varname))
return(data_sum)
}
df2 <- data_summary(df, varname="len", grps= "dose")
# 将dose转换为因子型变量
df2$dose=as.factor(df2$dose)
head(df2)
## dose len sd
## 1 0.5 10.605 4.499763
## 2 1 19.735 4.415436
## 3 2 26.100 3.774150
创建一个图层f。
f <- ggplot(df2, aes(x = dose, y = len,
ymin = len-sd, ymax = len+sd))
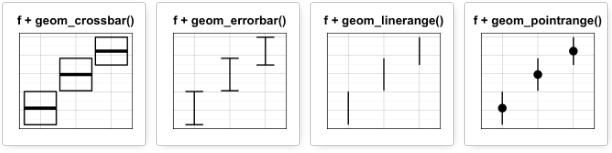
可添加的图层有:
- geom_crossbar(): 空心柱,上中下三线分别代表ymax、mean、ymin
- geom_errorbar(): 误差棒
- geom_errorbarh(): 水平误差棒
- geom_linerange():竖直误差线
- geom_pointrange():中间为一点的误差线
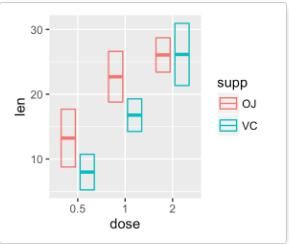
geom_crossbar():空心柱,上中下三线分别代表ymax、mean、ymin
# 添加空心柱
f + geom_crossbar()
# 将dose映射给颜色
f + geom_crossbar(aes(color = dose))
# 手动修改颜色
f + geom_crossbar(aes(color = dose)) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("#999999", "#E69F00", "#56B4E9"))+
theme_minimal()
# 修改填充色
f + geom_crossbar(aes(fill = dose)) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("#999999", "#E69F00", "#56B4E9"))+
theme_minimal()
构造数据集df3。
df3 <- data_summary(df, varname="len", grps= c("supp", "dose"))
head(df3)
## supp dose len sd
## 1 OJ 0.5 13.23 4.459709
## 2 OJ 1 22.70 3.910953
## 3 OJ 2 26.06 2.655058
## 4 VC 0.5 7.98 2.746634
## 5 VC 1 16.77 2.515309
## 6 VC 2 26.14 4.797731
f <- ggplot(df3, aes(x = dose, y = len,
ymin = len-sd, ymax = len+sd))
# 将supp映射给颜色
f + geom_crossbar(aes(color = supp))
# 避免重叠
f + geom_crossbar(aes(color = supp),
position = position_dodge(1))
geom_crossbar()的一个替代方法是使用函数stat_summary()。在这种情况下,可以自动计算平均值和标准误。
f <- ggplot(df, aes(x = dose, y = len, color = supp))
f + stat_summary(fun.data="mean_sdl", fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="crossbar", width = 0.6,
position = position_dodge(0.8))
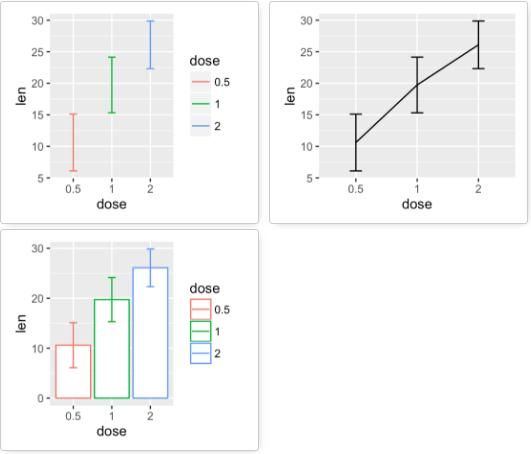
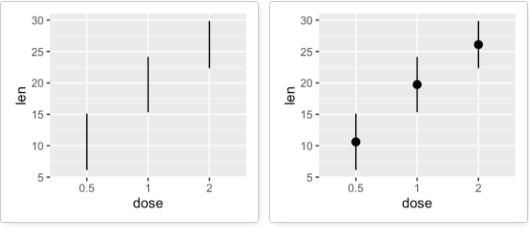
geom_errorbar():误差棒
创建一个图层f。
f <- ggplot(df2, aes(x = dose, y = len,
ymin = len-sd, ymax = len+sd))
# 将dose映射给颜色
f + geom_errorbar(aes(color = dose), width = 0.2)
# 与折线图结合
f + geom_line(aes(group = 1)) +
geom_errorbar(width = 0.2)
# 与条形图结合,并将dose映射给颜色
f + geom_bar(aes(color = dose), stat = "identity", fill ="white") +
geom_errorbar(aes(color = dose), width = 0.2)
geom_errorbarh():水平误差棒
构造数据集df2。
df2 <- data_summary(ToothGrowth, varname="len", grps = "dose")
df2$dose <- as.factor(df2$dose)
head(df2)
## dose len sd
## 1 0.5 10.605 4.499763
## 2 1 19.735 4.415436
## 3 2 26.100 3.774150
创建一个图层f。
f <- ggplot(df2, aes(x = len, y = dose ,
xmin=len-sd, xmax=len+sd))
参数xmin与xmax用来设置水平误差棒。
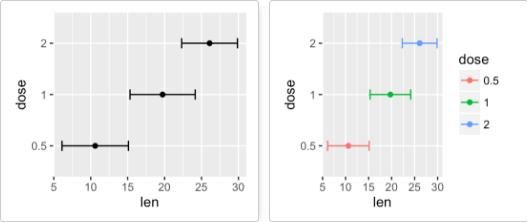
f+geom_errorbarh()
通过映射实现分组。
f+geom_errorbarh(aes(color=dose))
geom_linerange():竖直误差线
f <- ggplot(df2, aes(x = dose, y = len,
ymin=len-sd, ymax=len+sd))
# Line range
f + geom_linerange()
geom_pointrange():中间为一点的误差线
# Point range
f + geom_pointrange()
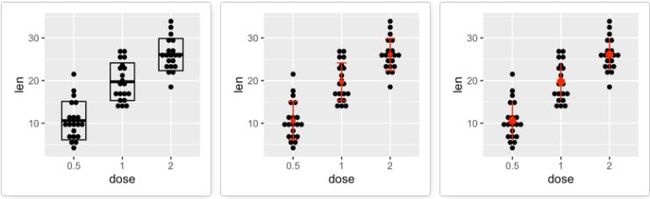
点图+误差棒
创建一个图层g。
g <- ggplot(df, aes(x=dose, y=len)) +
geom_dotplot(binaxis='y', stackdir='center')
# 添加空心柱
g + stat_summary(fun.data="mean_sdl", fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="crossbar", width=0.5)
# 添加误差棒
g + stat_summary(fun.data=mean_sdl, fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="errorbar", color="red", width=0.2) +
stat_summary(fun.y=mean, geom="point", color="red")
# 添加中间为一点的误差线
g + stat_summary(fun.data=mean_sdl, fun.args = list(mult=1),
geom="pointrange", color="red")
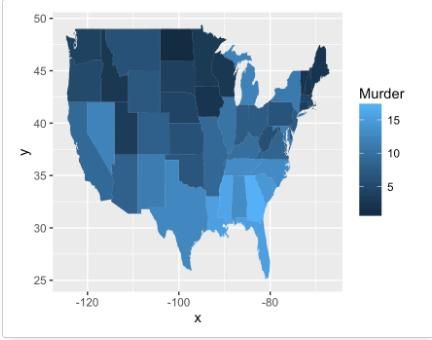
两个变量:绘制地图
geom_map()函数可用于绘制地图,首先需要安装map包。
install.packages("map")
下面将绘制美国地图,并采用数据集USArrests。
# 数据准备
crimes <- data.frame(state = tolower(rownames(USArrests)),
USArrests)
library(reshape2) # for melt
crimesm <- melt(crimes, id = 1)
# 获取地图数据
require(maps)
map_data <- map_data("state")
# 绘制地图,使用Murder进行着色
ggplot(crimes, aes(map_id = state)) +
geom_map(aes(fill = Murder), map = map_data) +
expand_limits(x = map_data$long, y = map_data$lat)
三个变量
使用数据集mtcars,首先计算一个相关性矩阵。
数据准备:
df <- mtcars[, c(1,3,4,5,6,7)]
# 计算相关性矩阵
cormat <- round(cor(df),2)
require(reshape2)
cormat <- melt(cormat)
head(cormat)
## Var1 Var2 value
## 1 mpg mpg 1.00
## 2 disp mpg -0.85
## 3 hp mpg -0.78
## 4 drat mpg 0.68
## 5 wt mpg -0.87
## 6 qsec mpg 0.42
创建一个图层g。
g <- ggplot(cormat, aes(x = Var1, y = Var2))
在此基础上可添加的图层有:
- geom_tile(): 瓦片图
- geom_raster(): 光栅图,瓦片图的一种,只不过所有的tiles都是一样的大小
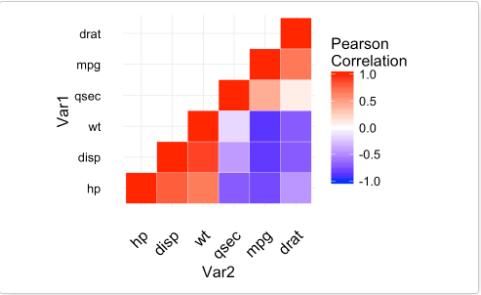
现在使用geom_tile()绘制相关性矩阵图。
# 计算相关性矩阵
cormat <- round(cor(df),2)
# 对相关性矩阵进行重新排序
hc <- hclust(as.dist(1-cormat)/2)
cormat.ord <- cormat[hc$order, hc$order]
# 获得矩阵的上三角
cormat.ord[lower.tri(cormat.ord)]<- NA
require(reshape2)
melted_cormat <- melt(cormat.ord, na.rm = TRUE)
# 绘制矩阵图
ggplot(melted_cormat, aes(Var2, Var1, fill = value))+
geom_tile(color = "white")+
scale_fill_gradient2(low = "blue", high = "red", mid = "white",
midpoint = 0, limit = c(-1,1), space = "Lab",
name="Pearson\nCorrelation") + # Change gradient color
theme_minimal()+ # minimal theme
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, vjust = 1,
size = 12, hjust = 1))+
coord_fixed()
其他图形类型
饼图
生存曲线
图形元件:多边形、路径、带状、射线(线段)、矩形等
本节主要是关于如何添加图形元件,可能会用到以下函数:
- geom_polygon():添加多边形
- geom_path(): 路径
- geom_ribbon(): 带状
- geom_segment(): 射线、线段
- geom_curve(): 曲线
- geom_rect(): 二维矩形
-
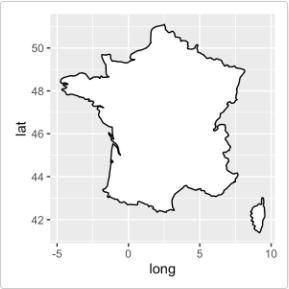
下面使用geom_polygon()函数绘制了一张法国地图:
require(maps) france = map_data('world', region = 'France') ggplot(france, aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group)) + geom_polygon(fill = 'white', colour = 'black') -
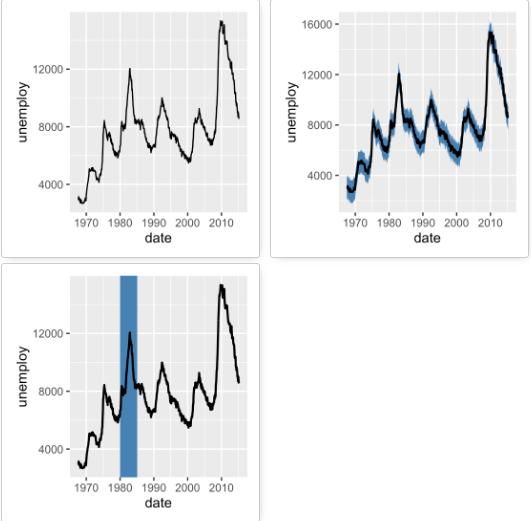
下面使用econimics 数据绘制了折线图,并添加了条带和矩形。
h <- ggplot(economics, aes(date, unemploy)) # 折线图 h + geom_path() # 添加条带 h + geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = unemploy-900, ymax = unemploy+900), fill = "steelblue") + geom_path(size = 0.8) # 添加矩形 h + geom_rect(aes(xmin = as.Date('1980-01-01'), ymin = -Inf, xmax = as.Date('1985-01-01'), ymax = Inf), fill = "steelblue") + geom_path(size = 0.8) -
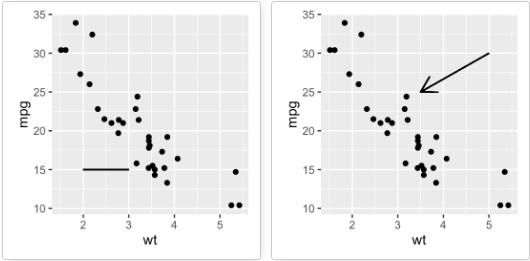
在点之间添加线段:
# 绘制散点图 i <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(wt, mpg)) + geom_point() # 添加线段 i + geom_segment(aes(x = 2, y = 15, xend = 3, yend = 15)) # 添加箭头 require(grid) i + geom_segment(aes(x = 5, y = 30, xend = 3.5, yend = 25), arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.5, "cm"))) -
在点之间添加曲线:
i + geom_curve(aes(x = 2, y = 15, xend = 3, yend = 15))
图形参数
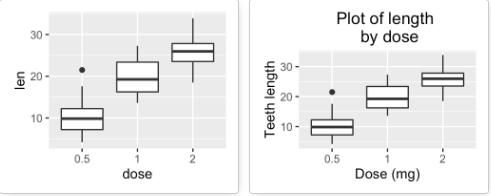
主标题、轴标签和图例标题
# 创建图层
ToothGrowth$dose <- as.factor(ToothGrowth$dose)
p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len)) + geom_boxplot()
修改标题以及标签的函数有:
- ggtitle(“New main title”): 添加主标题
- xlab(“New X axis label”): 修改x轴标签
- ylab(“New Y axis label”): 修改y轴标签
- labs(title = “New main title”, x = “New X axis label”, y = “New Y axis label”): 可同时添加主标题以及坐标轴标签,另外,图例标题也可以用此函数修改
-
修改主标题及轴标签
print(p) p <- p +labs(title="Plot of length \n by dose", x ="Dose (mg)", y = "Teeth length")+ theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5)) p -
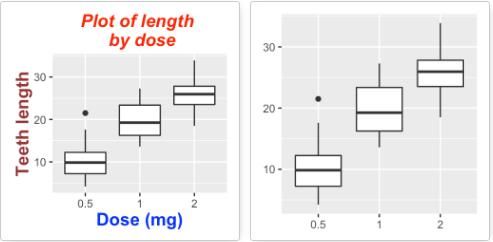
修改标签的外观
要修改标签的外观(颜色,大小和字体),可以使用函数theme()和element_text(),函数element_blank()可以隐藏标签。
p + theme( plot.title = element_text(color="red", size=14, face="bold.italic",hjust = 0.5), axis.title.x = element_text(color="blue", size=14, face="bold"), axis.title.y = element_text(color="#993333", size=14, face="bold") ) p + theme(plot.title = element_blank(), axis.title.x = element_blank(), axis.title.y = element_blank()) -
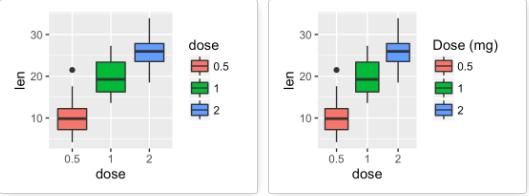
修改图例标题
p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len, fill=dose))+ geom_boxplot() p p + labs(fill = "Dose (mg)")
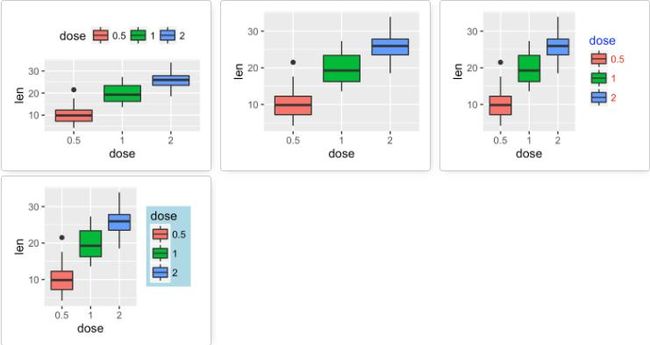
图例位置及外观
-
绘制箱线图
ToothGrowth$dose <- as.factor(ToothGrowth$dose) p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len, fill=dose))+ geom_boxplot() -
修改图例位置及外观
# 修改图例位置: "left","top", "right", "bottom", "none" p + theme(legend.position="top") # 去掉图例 p + theme(legend.position = "none") # 修改图例标题和标签的外观 p + theme(legend.title = element_text(colour="blue"), legend.text = element_text(colour="red")) # 修改图例背景 p + theme(legend.background = element_rect(fill="lightblue")) -
利用scale()函数自定义图例
scale_x_discrete():修改图例标签顺序
-
scale_fill_discrete(): 修改图例标题以及标签
# Change the order of legend items p + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("2", "0.5", "1")) # Set legend title and labels p + scale_fill_discrete(name = "Dose", labels = c("A", "B", "C"))
自动/手动修改颜色
ToothGrowth$dose <- as.factor(ToothGrowth$dose)
mtcars$cyl <- as.factor(mtcars$cyl)
# 箱线图
bp <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len))
# 散点图
sp <- ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg))
-
修改填充色、轮廓线颜色
# 箱线图 bp + geom_boxplot(fill='steelblue', color="red") # 散点图 sp + geom_point(color='darkblue') -
通过映射分组修改颜色
# 箱线图 bp <- bp + geom_boxplot(aes(fill = dose)) bp # 散点图 sp <- sp + geom_point(aes(color = cyl)) sp -
手动修改颜色
- scale_fill_manual(): 填充色
- scale_color_manual():轮廓色,如点线
# 箱线图 bp + scale_fill_manual(values=c("#999999", "#E69F00", "#56B4E9")) # 散点图 sp + scale_color_manual(values=c("#999999", "#E69F00", "#56B4E9")) -
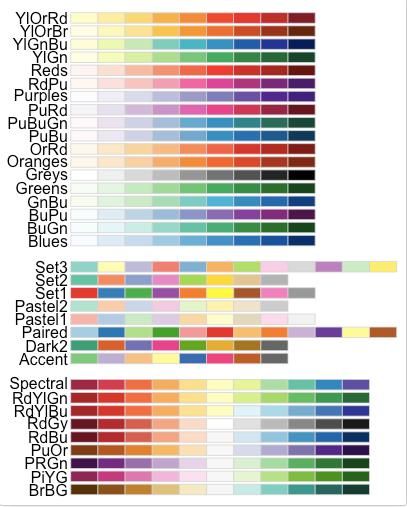
使用RColorBrewer调色板
- scale_fill_brewer(): 填充色
- scale_color_brewer():轮廓色,如点线
# 箱线图 bp + scale_fill_brewer(palette="Dark2") # 散点图 sp + scale_color_brewer(palette="Dark2")RColorBrewer包提供以下调色板:
-
使用灰度调色板
- scale_fill_grey(): 填充色
- scale_color_grey():轮廓色,如点线
# 箱线图 bp + scale_fill_grey() + theme_classic() # 散点图 sp + scale_color_grey() + theme_classic() -
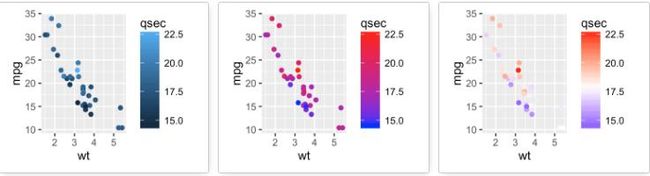
梯度或连续颜色
有时我们会将某个连续变量映射给颜色,这时修改这种梯度或连续型颜色就可以使用以下函数:
- scale_color_gradient(), scale_fill_gradient():两种颜色的连续梯度
- scale_color_gradient2(), scale_fill_gradient2():不同梯度
- scale_color_gradientn(), scale_fill_gradientn():多种颜色梯度
# Color by qsec values sp2<-ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_point(aes(color = qsec)) sp2 # Change the low and high colors # Sequential color scheme sp2+scale_color_gradient(low="blue", high="red") # Diverging color scheme mid<-mean(mtcars$qsec) sp2+scale_color_gradient2(midpoint=mid, low="blue", mid="white", high="red", space = "Lab" )
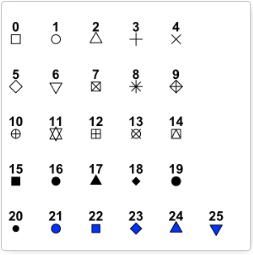
点的颜色、大小和形状
R中常用的点形状如下图所示:
# Convert cyl as factor variable
mtcars$cyl <- as.factor(mtcars$cyl)
# Basic scatter plot
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) +
geom_point(shape = 18, color = "steelblue", size = 4)
# Change point shapes and colors by groups
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) +
geom_point(aes(shape = cyl, color = cyl))
也可通过以下方法对点的颜色、大小、形状进行修改:
- scale_shape_manual() : to change point shapes
- scale_color_manual() : to change point colors
- scale_size_manual() : to change the size of points
# Change colors and shapes manually
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg, group=cyl)) +
geom_point(aes(shape=cyl, color=cyl), size=2)+
scale_shape_manual(values=c(3, 16, 17))+
scale_color_manual(values=c('#999999','#E69F00', '#56B4E9'))+
theme(legend.position="top")
添加文本注释
对图形添加文本注释有以下几个函数:
- geom_text(): 文本注释
- geom_label(): 文本注释,类似于geom_text(),只是多了个背景框
- annotate(): 文本注释
- annotation_custom(): 分面时可以在所有的面板进行文本注释
set.seed(1234)
df <- mtcars[sample(1:nrow(mtcars), 10), ]
df$cyl <- as.factor(df$cyl)
# Scatter plot
sp <- ggplot(df, aes(x=wt, y=mpg))+ geom_point()
# Add text, change colors by groups
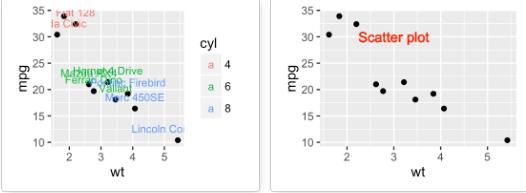
sp + geom_text(aes(label = rownames(df), color = cyl),
size = 3, vjust = -1)
# Add text at a particular coordinate
sp + geom_text(x = 3, y = 30, label = "Scatter plot",
color="red")
线型
R里的线型有七种:“blank”, “solid”, “dashed”, “dotted”, “dotdash”, “longdash”, “twodash”,对应数字0,1,2,3,4,5,6.
-
简单折线图
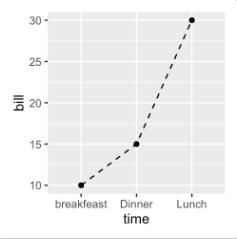
# Create some data df <- data.frame(time=c("breakfeast", "Lunch", "Dinner"), bill=c(10, 30, 15)) head(df)## time bill ## 1 breakfeast 10 ## 2 Lunch 30 ## 3 Dinner 15# Basic line plot with points # Change the line type ggplot(data=df, aes(x=time, y=bill, group=1)) + geom_line(linetype = "dashed")+ geom_point() -
多组折线图
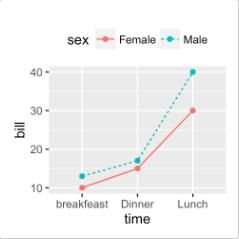
# Create some data df2 <- data.frame(sex = rep(c("Female", "Male"), each=3), time=c("breakfeast", "Lunch", "Dinner"), bill=c(10, 30, 15, 13, 40, 17) ) head(df2)## sex time bill ## 1 Female breakfeast 10 ## 2 Female Lunch 30 ## 3 Female Dinner 15 ## 4 Male breakfeast 13 ## 5 Male Lunch 40 ## 6 Male Dinner 17# Line plot with multiple groups # Change line types and colors by groups (sex) ggplot(df2, aes(x=time, y=bill, group=sex)) + geom_line(aes(linetype = sex, color = sex))+ geom_point(aes(color=sex))+ theme(legend.position="top")以下函数可对线的外观进行修改:
- scale_linetype_manual() : 改变线型
- scale_color_manual() : 改变线的颜色
- scale_size_manual() : 改变线的粗细
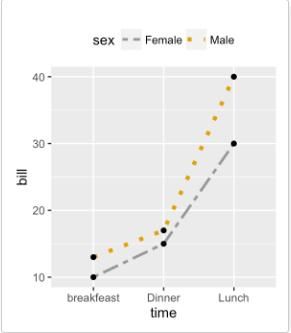
# Change line types, colors and sizes ggplot(df2, aes(x=time, y=bill, group=sex)) + geom_line(aes(linetype=sex, color=sex, size=sex))+ geom_point()+ scale_linetype_manual(values=c("twodash", "dotted"))+ scale_color_manual(values=c('#999999','#E69F00'))+ scale_size_manual(values=c(1, 1.5))+ theme(legend.position="top")
主题和背景色
# Convert the column dose from numeric to factor variable
ToothGrowth$dose <- as.factor(ToothGrowth$dose)
-
绘制箱线图
p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len)) + geom_boxplot() -
修改主题
ggplot2提供了两种主题:
- theme_gray(): 灰色背景加白色网格线
- theme_bw() : 白色背景加灰色网格线
p + theme_gray(base_size = 14) p + theme_bw()- heme_linedraw : 黑色网格线
- theme_light : 浅灰色网格线
p + theme_linedraw()
p + theme_light()
theme_minimal: 无背景色
-
theme_classic : 只有坐标轴没有网格线
p + theme_minimal() p + theme_classic()
坐标轴:最大与最小值
p <- ggplot(cars, aes(x = speed, y = dist)) + geom_point()
修改坐标轴范围有以下几种方式:
1、不删除数据
- p+coord_cartesian(xlim=c(5, 20), ylim=c(0, 50)):笛卡尔坐标系,这是设定修改不会删除数据
2、会删除部分数据:不在此范围内的数据都会被删除,因此在此基础上添加图层时数据是不完整的
- p+xlim(5, 20)+ylim(0, 50)
- p+scale_x_continuous(limits=c(5, 20))+scale_y_continuous(limits=c(0, 50))
3、扩展图形范围:expand()函数,扩大范围
- p+expand_limits(x=0, y=0):设置截距为0,即过原点
- p+expand_limits(x=c(5, 50), y=c(0, 150)):扩大坐标轴范围,这样图形显示就小了
# Default plot
print(p)
# Change axis limits using coord_cartesian()
p + coord_cartesian(xlim =c(5, 20), ylim = c(0, 50))
# Use xlim() and ylim()
p + xlim(5, 20) + ylim(0, 50)
# Expand limits
p + expand_limits(x = c(5, 50), y = c(0, 150))
坐标变换:log和sqrt
-
绘制散点图
p <- ggplot(cars, aes(x = speed, y = dist)) + geom_point() -
ggplot2中的坐标变换函数有以下几种:
- p+scale_x_log10(),p+scale_y_log10(): 绘图时对x,y取10的对数
- p+scale_x_sqrt(),p+scale_x_sqrt(): 开根号
- p+scale_x_reverse(),p+scale_x_reverse():坐标轴反向
- p+coord_trans(x =“log10”, y=“log10”): 同上,可以对坐标轴取对数、根号等
- p+scale_x_continuous(trans=”log2”),p+scale_x_continuous(trans=”log2”): 同上,取对数的另外一种方法
-
下面使用scale_xx_continuous()函数进行坐标变换:
# Default scatter plot print(p) # Log transformation using scale_xx() # possible values for trans : 'log2', 'log10','sqrt' p + scale_x_continuous(trans='log2') + scale_y_continuous(trans='log2') # Format axis tick mark labels require(scales) p + scale_y_continuous(trans = log2_trans(), breaks = trans_breaks("log2", function(x) 2^x), labels = trans_format("log2", math_format(2^.x))) # Reverse coordinates p + scale_y_reverse()
坐标刻度:刻度线、标签、顺序等
更改坐标轴刻度线标签的函数:
- element_text(face, color, size, angle): 修改文本风格
- element_blank(): 隐藏文本
p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len)) + geom_boxplot()
# print(p)
修改刻度标签等
# Change the style of axis tick labels
# face can be "plain", "italic", "bold" or "bold.italic"
p + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(face="bold", color="#993333",
size=14, angle=45),
axis.text.y = element_text(face="bold", color="blue",
size=14, angle=45))
# Remove axis ticks and tick mark labels
p + theme(
axis.text.x = element_blank(), # Remove x axis tick labels
axis.text.y = element_blank(), # Remove y axis tick labels
axis.ticks = element_blank()) # Remove ticks
自定义坐标轴:
- 离散非连续坐标轴
- scale_x_discrete(name, breaks, labels, limits)
- scale_y_discrete(name, breaks, labels, limits)
- 连续型坐标轴
- scale_x_conyinuous(name, breaks, labels, limits)
- scale_y_continuous(name, breaks, labels, limits)
详细情况如下:
- name: x,y轴的标题
- breaks: 刻度,分成几段
- labels:坐标轴刻度线标签
- limits: 坐标轴范围
其中scale_xx()函数可以修改坐标轴的如下参数:
- 坐标轴标题
- 坐标轴范围
- 刻度标签位置
- 手动设置刻度标签
离散坐标轴
# Change x axis label and the order of items
p + scale_x_discrete(name ="Dose (mg)",
limits=c("2","1","0.5"))
# Change tick mark labels
p + scale_x_discrete(breaks=c("0.5","1","2"),
labels=c("Dose 0.5", "Dose 1", "Dose 2"))
# Choose which items to display
p + scale_x_discrete(limits=c("0.5", "2"))
连续坐标轴
# Default scatter plot
# +++++++++++++++++
sp <- ggplot(cars, aes(x = speed, y = dist)) + geom_point()
sp
# Customize the plot
#+++++++++++++++++++++
# 1. Change x and y axis labels, and limits
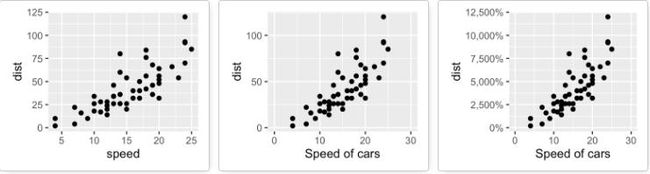
sp <- sp + scale_x_continuous(name="Speed of cars", limits=c(0, 30)) +
scale_y_continuous(name="Stopping distance", limits=c(0, 150))
# 2. Set tick marks on y axis: a tick mark is shown on every 50
sp + scale_y_continuous(breaks=seq(0, 150, 50))
# Format the labels
# +++++++++++++++++
require(scales)
sp + scale_y_continuous(labels = percent) # labels as percents
添加直线:水平,垂直和回归线
ggplot2提供以下方法为图形添加直线:
- geom_hline(yintercept, linetype, color, size): 添加水平线
- geom_vline(xintercept, linetype, color, size):添加竖直线
- geom_abline(intercept, slope, linetype, color, size):添加回归线
- geom_segment():添加线段
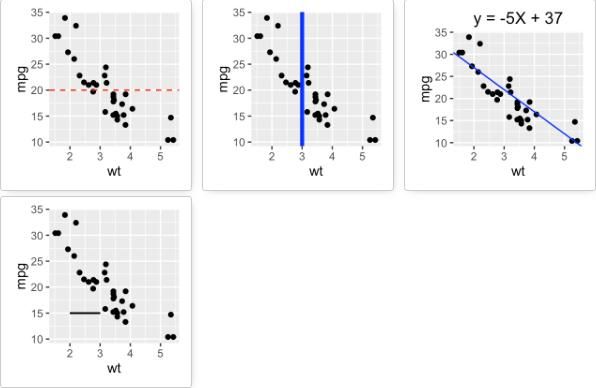
# Simple scatter plot
sp <- ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_point()
添加直线
# Add horizontal line at y = 2O; change line type and color
sp + geom_hline(yintercept=20, linetype="dashed", color = "red")
# Add vertical line at x = 3; change line type, color and size
sp + geom_vline(xintercept = 3, color = "blue", size=1.5)
# Add regression line
sp + geom_abline(intercept = 37, slope = -5, color="blue")+
ggtitle("y = -5X + 37")
# Add horizontal line segment
sp + geom_segment(aes(x = 2, y = 15, xend = 3, yend = 15))
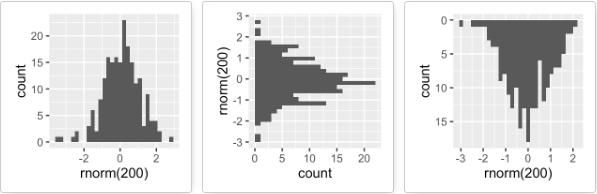
图形旋转:旋转、反向
主要是下面两个函数:
- coord_flip():创建水平方向图
- scale_x_reverse(),scale_y_reverse():坐标轴反向
set.seed(1234)
# Basic histogram
hp <- qplot(x=rnorm(200), geom="histogram")
hp
# Horizontal histogram
hp + coord_flip()
# Y axis reversed
hp + scale_y_reverse()
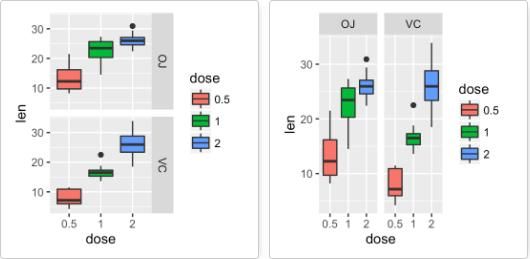
分面
分面就是根据一个或多个变量将图形分为几个图形以便于可视化,主要有两个方法实现:
- facet_grid()
- facet_wrap()
p <- ggplot(ToothGrowth, aes(x=dose, y=len, group=dose)) +
geom_boxplot(aes(fill=dose))
p
以下函数可以用来分面:
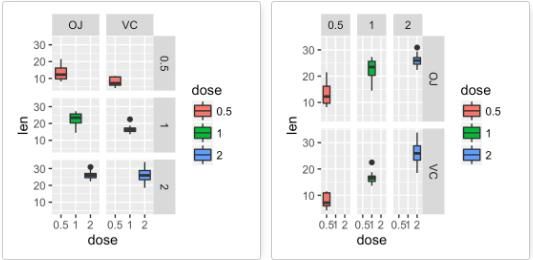
- p+facet_grid(supp~.): 按变量supp进行竖直方向分面
- p+facet_grid(.~supp): 按变量supp进行水平方向分面
- p+facet_wrap(dose~supp):按双变量supp和dose进行水平竖直方向分面
- p+facet_wrap(~fl): 将分成的面板边靠边置于一个矩形框内
-
按一个离散变量进行分面:
# Split in vertical direction p + facet_grid(supp ~ .) # Split in horizontal direction p + facet_grid(. ~ supp) -
按两个离散变量进行分面:
# Facet by two variables: dose and supp. # Rows are dose and columns are supp p + facet_grid(dose ~ supp) # Facet by two variables: reverse the order of the 2 variables # Rows are supp and columns are dose p + facet_grid(supp ~ dose)
可以通过设置参数scales来控制坐标轴比例:
p + facet_grid(dose ~ supp, scales='free')
位置调整
为了显示得更好,很多图形需要调整位置。
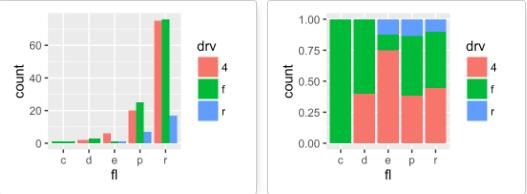
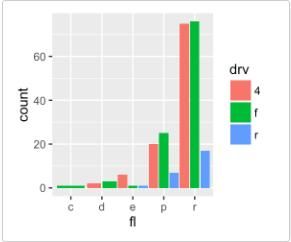
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(fl, fill = drv))
# Arrange elements side by side
p + geom_bar(position = "dodge")
# Stack objects on top of one another,
# and normalize to have equal height
p + geom_bar(position = "fill")
# Stack elements on top of one another
p + geom_bar(position = "stack")
# Add random noise to X and Y position
# of each element to avoid overplotting
ggplot(mpg, aes(cty, hwy)) +
geom_point(position = "jitter")
上面几个函数有两个重要的参数:heigth、weight。
- position_dodge(width, height)
- position_fill(width, height)
- position_stack(width, height)
- position_jitter(width, height)
p + geom_bar(position = position_dodge(width = 1))
坐标系
p <- ggplot(mpg, aes(fl)) + geom_bar()
ggplot2中的坐标系主要有:
- p+coord_cartesian(xlim=NULL, ylim=NULL):笛卡尔坐标系(默认)
- p+coord_fixed(ratio=1, clim=NULL, ylim=NULL):固定了坐标轴比例的笛卡尔坐标系。默认比例为1
- p+coord_flip(…):旋转笛卡尔坐标系
- p+coord_polar(theta=”x”, start=0, direction=1):极坐标系
- p+coord_trans(x,y,limx,limy):变换笛卡尔坐标系
- coord_map():地图坐标系
各个坐标系参数如下:
1、笛卡尔坐标系:coord_cartesian(), coord_fixed() and coord_flip()
- xlim:x轴范围
- ylim:y轴范围
- ratio:y/x
- …:其他参数
2、极坐标系:coord_polar()
- theta:外延坐标,x或y
- start:坐标开始的位置,默认为12点钟
- direction:方向:顺时针(1),逆时针(-1)
3、变换坐标系:coord_trans()
- x,y:变换的坐标轴
- limx,limy:坐标轴范围
p + coord_cartesian(ylim = c(0, 200))
p + coord_fixed(ratio = 1/50)
p + coord_flip()
p + coord_polar(theta = "x", direction = 1)
p + coord_trans(y = "sqrt")
ggplot2的扩展:R包和函数
- ggplot2官网,里面有十分详细的说明
- ggplot2扩展包
- factoextra :可以对多个变量进行可视化的一个R包
- easyggplot2:可以轻松并快速自定义绘制图形的R包
- ggplot2 - 快速进行图形组合:可以使用R包 gridExtra 和cowplot
- ggplot2: 绘制相关性矩阵热图:
- ggfortify: 对ggplot2包进行了扩展,从而可以绘制一些常用的R包,这些已经包含在了函数autoplot()中
- GGally: 提供了一些扩展函数,包括成对相关性矩阵、散点图矩阵、平行坐标图、生存曲线图和网络图的一些函数
- ggRandomForests: 使用randomForestSRC和ggplot2包对随机森林进行图形分析的R包
- ggdendro: 使用ggplot2来绘制树形图的R包
- ggmcmc: 从贝叶斯推理分析MCMC模拟的R包
- ggthemes: 提供一些额外主题的R包
- The R Graph Gallery
一些相关资源
书籍
- ggplot2: The Elements for Elegant Data Visualization in R
- Cookbook for R
- ggplot2:数据分析与图形艺术
- R in Action
- R for Data Science
- R语言资源汇总
博客
- Build a plot layer by layer
- R-bloggers
备忘单
- Data Visualization with ggplot2, RStudio cheat sheet
- Beautiful plotting in R: A ggplot2 cheatsheet
版本信息
以上全部代码运行环境为:R (ver. 3.5.1),ggplot2(ver 3.0.0) 。
参考资料
- ggplot2高效实用指南
- Be Awesome in ggplot2: A Practical Guide to be Highly Effective - R software and data visualization
- 《ggplot2:数据分析与图形艺术》