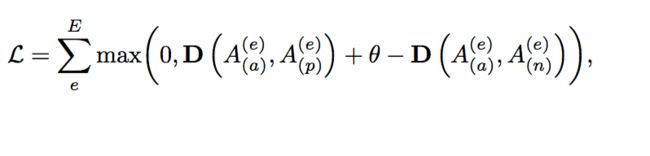ECCV 2016 person re-identification相关 第三篇
目前做person reID主要有两个方面:
- extracting and coding local invariant features to represent the visual appearance of a person
- learning a discriminative distance metric hence the distance of features from the same person can be smaller
在这篇文章中,作者聚焦于第一方面。在features方面,作者使用人的attribute,作者认为人的attribute属于mid level,这相对于color LBP这种low level的视觉特征,能更好的应对光照、角度、姿势等变化因素。但是人工标注attribute的数据比传统的标注数据的代价更为昂贵,所以目前还是以low level的特征为主。
作者提出的方法的优势在于:
- we propose a three- stage semi-supervised deep attribute learning algorithm, which makes learning a large set of human attributes from a limited number of labeled attribute data possible
- deep attributes achieve promising performance and generalization ability on four person ReID datasets
- deep attributes release the previous dependencies on local features, thus make the person ReID system more robust and efficient
作者使用dCNN来预测human attributes,并用于person reID,这是original的。
主要思想
作者的目的就是要学习一个attribute detector O:
其中I是输入图像,AI是binary的attribute。比如这个attribute是[有长发,女性,戴眼镜],那么对应就是[1,1,1]。如果是[短发,女性,没戴眼镜],那么就是[0,1,0]
前文提到了他们这是一个three-stage semi-supervised deep attribute learning algorithm,所以这里分为三个part来介绍
第一步
用AlexNet来训练,训练数据宝贵的有标注attribute的数据,一共N个sample,第n个sample tn的attribute是An。得到第一步训练的attribute detector O1
第二步
We denote the dataset with person ID labels as U = {u1, u2, ..., uM }, where M is the number of samples and each sample has a person ID label l, e.g., the m-th instance um has person ID lm.
可以理解为,这部分数据是没有attribute label标注的,但是有ID标注,就是标准的用于re ID 的数据,比如这一个sequence是谁,那个sequence是谁 。选一个sequence 作为anchor 一个sequence作为positive 再一个sequence作为negative a triplet [u(a),u(p),u(n)] is constructed 然后拿第一步里训练好的模型O1分别预测这三个sequence ,最小化anchor和positive之间的distance 最大化anchor 和 negative之间的distance 。
目标函数如下:
We denote the dataset with person ID labels as U = {u1, u2, ..., uM }, where M is the number of samples and each sample has a person ID label l, e.g., the m-th instance um has person ID lm. 可以理解为,这部分数据是没有attribute label标注的,但是有ID标注,就是标准的用于re ID 的数据,比如这一个sequence是谁,那个sequence是谁 。选一个sequence 作为anchor 一个sequence作为positive 再一个sequence作为negative a triplet [u(a),u(p),u(n)] is constructed 然后拿第一步里训练好的模型分别预测这三个sequence ,最小化anchor和positive之间的distance 最大化anchor 和 negative之间的distance loss function如下
However, the person ID label is not strong enough to train the dCNN with accurate attributes. Without proper constraints, the above loss function may generate meaningless attribute labels and easily over- fit the training dataset U. For example, imposing a large number meaningless attributes to two samples of a person may decrease the distance between their attribute labels, but does not help to improve the discriminative power of the dCNN. Therefore, we add several regularization terms and modify the original loss function as:
由此得到第二步训练的attribute detector O2
第三步
拿O2对第二步的数据库进行attribute的detect,得到一个有attribute标注的新的数据库,然后把这个数据库和第一步的数据库结合在一起,再对O2进行fine-tuning
NOTE:作者第一步用的数据库是PETA,第二步用的数据库是MOT