我们知道一个程序的瓶颈在于数据库,我们也知道内存的速度是大大快于硬盘的速度的。当我们需要重复地获取相同的数据的时候,我们一次又一次的请求数据库或者远程服务,导致大量的时间耗费在数据库查询或者远程方法调用上,导致程序性能的恶化,这便是数据缓存要解决的问题。
Spring缓存支持
Spring定义了org.springframework.cache.CacheManager和org.springframework.cache.Cache接口用来统一不同的缓存的技术。其中,CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术抽象接口,Cache接口包含缓存的各种操作(增加、删除、获得缓存,我们一般不会直接和此接口打交道)。
1.Spring支持的CacheManager
针对不同的缓存技术,需要实现不同的CacheManager,Spring定义了如表所示的CacheManager实现。
| CacheManager | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SimpleCacheManager | 使用简单的Collection来存储缓存,主要用来测试 |
| ConcurrentMapCacheManager | 使用ConcurrentMap来存储缓存 |
| NoOpCacheManager | 仅测试用,不会实际存储缓存 |
| EhCacheCacheManager | 使用EhCache作为缓存技术 |
| GuavaCacheManager | 使用google guava的GuavaCache作为缓存技术(在1.5版本弃用了) |
| HazelcastCacheManager | 使用Hazelcast作为缓存技术 |
| JCacheCacheManager | 支持JCache(JSR-107)标准的实现作为缓存技术,如Apache Commons JCS |
| RedisCacheManager | 使用redis来作为缓存技术 |
在我们使用任意一个实现的CacheManager的时候,需注册实现的CacheManager的Bean,例如:
@Bean
public EhCacheCacheManager cacheManager(CacheManager ehCacheCacheManager) {
return new EhCacheCacheManager(ehCacheCacheManager);
}
当然,每种缓存技术都有很多的额外配置,但配置cacheManager是必不可少的。
2.声名式缓存注解
Spring提供了4个注解来声明缓存规则(又是使用注解式的AOP的一个生动例子)。这四个注解如表所示。
| 注解 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @Cacheable | 在方法执行前,Spring先检查缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据就直接返回缓存中的数据;如果没有就调用方法,并将返回值放入缓存。 |
| @CachePut | 无论怎么样,都会将方法的返回值放到缓存中。@CachePut的属性和@Cacheable保持一致 |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
| @Caching | 可以通过该注解,组合多个注解策略在一个方法上 |
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvit都有value属性,指定的是要使用的缓存名称;key属性指定的是数据在缓存中的存储的键。
3.开启声名式缓存支持
开启声名式缓存支持十分简单,只需在配置类上使用@EnableCaching注解即可,例如:
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class AppConfig {
}
Spring Boot的支持
在Spring中使用缓存技术的关键是配置CacheManager,而Spring Boot为我们自动配置了多个CacheManager的实现。
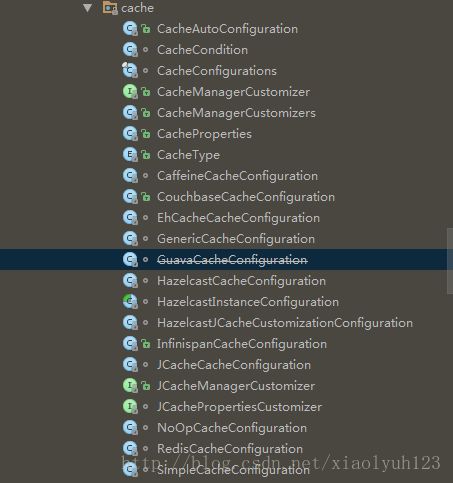
Spring Boot的CacheManager的自动配置放置在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache包中,如图所示。
通过图我们可以看出,Spring Boot为我们自动配置了EhCacheCacheConfiguration(使用EhCache)、GenericCacheConfiguration(使用Collection)、GuavaCacheConfiguration(使用Guava)、HazelcastCacheConfiguration(使用Hazelcast)、InfinispanCacheConfiguration(使用Infinispan)、JCacheCacheConfiguration(使用JCache)、NoOpCacheConfiguration(不使用存储)、RedisCacheConfiguration(使用Redis)、SimpleCacheConfiguration(使用ConcurrentMap)。在不做任何额外配置的情况下,默认使用的是SimpleCacheConfiguration,即使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager。
/*
* Copyright 2012-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* Simplest cache configuration, usually used as a fallback.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker;
SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
}
@Bean // 默认使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
}
Spring Boot支持以“spring.cache”为前缀的属性来配置缓存。
spring.cache.type= # 可选generic, ehcache, hazelcast, infinispan, jcache, redis, guava, simple, none
spring.cache.cache-names= # 程序启动时创建缓存名称
spring.cache.ehcache.config= # ehcache配置文件地址
spring.cache.hazelcast.config= # hazelcast 配置文件地址
spring.cache.infinispan.config= # infinispan 配置文件地址
spring.cache.jcache.config= # jcache 配置文件地址
spring.cache.jcache.provider= #当多个 jcache实现在类路径中的时候,指定jcache实现
spring.cache.guava.spec= # guava specs
在Spring Boot环境下,使用缓存技术只需在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并在配置类使用@EnableCaching开启缓存支持即可。
为监控而生的多级缓存框架 layering-cache这是我开源的一个多级缓存框架的实现,如果有兴趣可以看一下