【原创博文,转载请注明出处!】
根据在项目开发中的长期积累和学习,本文所涉及的三种设计架构,我都会通过Objective-C语言在iOS开发环境下给出可运行demoGithub demo地址。
<一>、MVC
MVC架构在iOS开发中有两种形式的体现:
- 1 、Apple 版本的MVC
- 2、变种的MVC(iOS开发中常见)
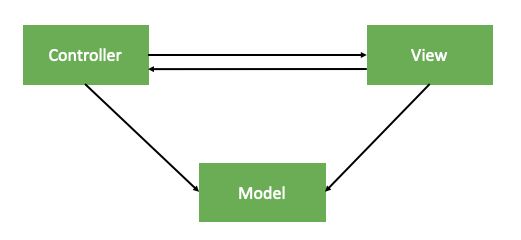
A. 首先我们看一下Apple版本的MVC 中,M、V、C三个模块之间的关系图:
上图可见:Apple版本的MVC中,Model和View是完全隔绝的。Model与View之间通过Controller作为桥梁进行沟通。
图中四个指向箭头的关系解释如下:
a. Controller同时指向Model和View表明Controller拥有Model和View;
b. Model指向Controller,意味着Model数据的改变需要通知到Controller,由Controller来刷新View的显示状态;
c. View指向Controller,View里面的事件需要通知到控制器去处理(如:Block、代理、通知)。
这种形式的MVC被UITableView发挥得淋漓尽致,举个例子:
// Student.h文件
@interface Student : NSObject
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *price;
@end
// StudentViewController.m文件
#import "StudentViewController.h"
#import "Student.h"
@interface StudentViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSMutableArray *newsData;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSMutableArray *studentData;
@end
@implementation StudentViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self loadStudent];
}
- (void)loadStudent
{
self.studentData = [NSMutableArray array];
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Student *student = [[Student alloc] init];
student.name = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"姓名-%d", I];
student.price = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"学号:%d", I];
[self.studentData addObject:student];
}
}
#pragma mark - Table view data source
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return self.studentData.count;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@"NewsCell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
Student *student = self.studentData[indexPath.row];
cell.detailTextLabel.text = student.price;
cell.textLabel.text = student.name;
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
NSLog(@"1111");
}
@end
这种MVC,view与model完全隔离,view不依赖model,所以优点是:view和model可以重复利用,也可以单独使用。
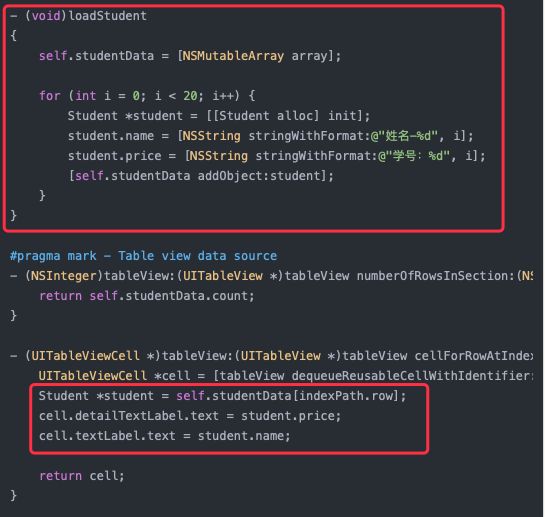
再来看看缺点(下图红框所示):
缺点:model数据需要在Controller中加载,另外view上面的控件赋值也需要逐一在控制器中赋值,所以控制器中代码很臃肿。
B. 让我们再来看一下项目中常见的变种MVC 中,M、V、C三个模块之间的关系图:
这种MVC,View拥有Model(Model通常作为View的一个实例对象),所以View能第一时间知道Model的变化,这样我们就可以将View的内部实现隐蔽起来,也就是无需对外暴露View内部控件API。
// MVCModel.h
#import
@interface MVCModel : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *imageName;
@end
// MVCView.h
#import
@class MVCModel, MVCView;
@protocol MVCViewDelegate
@optional
- (void)mvcViewDidClicked:(MVCView *)view;
@end
@interface MVCView : UIView
@property (nonatomic, strong) MVCModel *mvcModel;
@property (nonatomic, weak) id delegate;
@end
// MVCView.m
#import "MVCView.h"
#import "MVCModel.h"
@interface MVCView ()
@property (nonatomic, weak) UIImageView *imageView;
@property (nonatomic, weak) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation MVCView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 120, 150)];
[self addSubview:imageView];
_imageView = imageView;
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(20, 150, 100, 60)];
[self addSubview:label];
_label = label;
}
return self;
}
- (void)setMvcModel:(MVCModel *)mvcModel{
_mvcModel = mvcModel;
self.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"monkey1.png"];
self.label.text = mvcModel.name;
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(mvcViewDidClicked:)]) {
[self.delegate mvcViewDidClicked:self];
}
}
@end
// MVCGeneralController.m
#import "MVCGeneralController.h"
#import "MVCModel.h"
#import "MVCView.h"
#define SCREEN_WIDTH ([UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width)
@interface MVCGeneralController ()
@end
@implementation MVCGeneralController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
MVCView *view = [[MVCView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 150, 200)];
view.center = CGPointMake(SCREEN_WIDTH / 2, 300);
[self.view addSubview:view];
view.delegate = self;
MVCModel *model = [[MVCModel alloc] init];
model.name = @"a Monkey";
model.imageName = @"monkey";
view.mvcModel = model;
}
-(void)mvcViewDidClicked:(MVCView *)view{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
@end
通过代码可见,变种的MVC架构下:
优点:相对于Apple的MVC而言,对Controller进行瘦身,将View内部的细节封装起来了,外界不知道View内部的具体实现;
缺点:View依赖于Model。
<二>、MVP
初看上去MVP与Apple版本的MVC很相似,仔细对比发现MVP中的P"取代"了MVC中的C功能,demo如下:
//
// MVP_ViewController.m
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "MVP_ViewController.h"
#import "Presenter.h"
@interface MVP_ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic, strong) Presenter *presenter;
@end
@implementation MVP_ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.presenter = [[Presenter alloc] initWithController:self];
}
@end
//
// MVP_Model.h
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
#import
@interface MVP_Model : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *imageName;
@end
//
// MVP_View.h
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import
@class MVP_View;
@protocol MVP_ViewDelegate
@optional
- (void)viewDidClicked:(MVP_View *)view;
@end
@interface MVP_View : UIView
@property (nonatomic, weak) id delegate;
- (void)setImageName:(NSString *)imageName introduction:(NSString *)introduction;
@end
//
// MVP_View.m
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "MVP_View.h"
@interface MVP_View ()
@property (nonatomic, weak) UIImageView *imageView;
@property (nonatomic, weak) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation MVP_View
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 120, 150)];
[self addSubview:imageView];
_imageView = imageView;
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(20, 150, 100, 60)];
[self addSubview:label];
_label = label;
}
return self;
}
- (void)setImageName:(NSString *)imageName introduction:(NSString *)introduction{
self.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:imageName];
self.label.text = introduction;
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(viewDidClicked:)]) {
[self.delegate viewDidClicked:self];
}
}
@end
//
// Presenter.h
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import
@interface Presenter : NSObject
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller;
@end
//
// Presenter.m
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "Presenter.h"
#import "MVP_View.h"
#import "MVP_Model.h"
#define SCREEN_WIDTH ([UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width)
@interface Presenter ()
@property (nonatomic, weak) UIViewController *controller;
@end
@implementation Presenter
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.controller = controller;
MVP_View *view = [[MVP_View alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 150, 200)];
view.center = CGPointMake(SCREEN_WIDTH / 2, 300);
[controller.view addSubview:view];
view.delegate = self;
MVP_Model *model = [[MVP_Model alloc] init];
model.name = @"a Monkey";
model.imageName = @"monkey1";
[view setImageName:model.imageName introduction:model.name];
}
return self;
}
- (void)viewDidClicked:(MVP_View *)view{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
@end
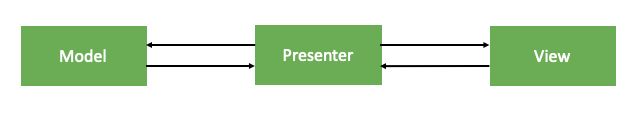
MVP架构下,之前控制器C需要负责的任务由Presenter去处理,Presenter可以理解为Controller的一个代理者,如果Controller中有很多复杂的UI,我们可以为这个Controller设计多个Presenter,这样每一部分的数据加载等任务分散到各自的Presenter中处理,Controller看起来非常干净。
MVP中,Model与View仍然可以做到绝对的隔离,没有依赖关系,所以Model与VIew也可以单独使用。
<三>、MVVM
从MVVM关系图中看上去,该架构与MVP架构很像,Model与View之间仍然是隔离的,可以单独使用,灵活性、复用性都很友好。ViewModel与View之间双向绑定,鉴于在iOS环境下的MVVM架构中,一般我们在View中通过监听ViewModel中属性的变化去更新View的显示效果,所以MVVM架构在iOS开发中一般搭配RAC框架使用(或者FB 推出的轻量级"NSObject+FBKVOController"框架)。该架构下:控制器Controller拥有ViewModel,ViewModel同时拥有View和Model,对于复杂的界面,一个Controller可以有多个ViewModel去实现各部分的业务逻辑,我将ViewModel理解为控制器的"代理",同MVP一样,MVVM大大解放了Controller职责,demo源码如下:
//
// MVVM_ViewController.m
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "MVVM_ViewController.h"
#import "ViewModel.h"
@interface MVVM_ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic, strong) ViewModel *viewModel;
@end
@implementation MVVM_ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.viewModel = [[ViewModel alloc] initWithController:self];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
@end
//
// ViewModel.h
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import
@interface ViewModel : NSObject
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller;
@end
//
// ViewModel.m
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "ViewModel.h"
#import "MVVM_Model.h"
#import "MVVM_View.h"
#define SCREEN_WIDTH ([UIScreen mainScreen].bounds.size.width)
@interface ViewModel ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) UIViewController *controller;
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *imageName;
@property (weak, nonatomic) UIView *view;
@end
@implementation ViewModel
- (instancetype)initWithController:(UIViewController *)controller{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.controller = controller;
MVVM_View *view = [[MVVM_View alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 150, 200)];
view.center = CGPointMake(SCREEN_WIDTH / 2, 300);
[controller.view addSubview:view];
view.viewModel = self;
view.delegate = self;
MVVM_Model *model = [[MVVM_Model alloc] init];
model.name = @"a Monkey";
model.imageName = @"monkey";
self.name = model.name;
self.imageName = model.imageName;
}
return self;
}
- (void)viewDidClicked:(MVVM_View *)view{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
self.imageName = [self.imageName isEqualToString:@"monkey1"] ? @"monkey" : @"monkey1";
}
@end
//
// MVVM_View.h
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import
@class MVVM_View, ViewModel;
@protocol MVVM_ViewDelegate
@optional
- (void)viewDidClicked:(MVVM_View *)view;
@end
@interface MVVM_View : UIView
@property (nonatomic, weak) ViewModel *viewModel;
@property (nonatomic, weak) id delegate;
@end
//
// MVVM_View.m
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import "MVVM_View.h"
#import "NSObject+FBKVOController.h"
@interface MVVM_View ()
@property (nonatomic, weak) UIImageView *imageView;
@property (nonatomic, weak) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation MVVM_View
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame{
if (self = [super initWithFrame:frame]) {
UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 120, 150)];
[self addSubview:imageView];
_imageView = imageView;
UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(20, 150, 100, 60)];
[self addSubview:label];
_label = label;
}
return self;
}
- (void)setViewModel:(ViewModel *)viewModel{
_viewModel = viewModel;
__weak typeof(self) waekSelf = self;
[self.KVOController observe:viewModel keyPath:@"name" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew block:^(id _Nullable observer, id _Nonnull object, NSDictionary * _Nonnull change) {
waekSelf.label.text = change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey];
}];
[self.KVOController observe:viewModel keyPath:@"imageName" options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew block:^(id _Nullable observer, id _Nonnull object, NSDictionary * _Nonnull change) {
waekSelf.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey]];
}];
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{
if ([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(viewDidClicked:)]) {
[self.delegate viewDidClicked:self];
}
}
@end
//
// MVVM_Model.h
// MVC_MVP_MVVM
//
// Created by Rephontil.Zhou. on 2018/12/1.
// Copyright © 2018 Rephontil.Zhou. All rights reserved.
//
#import
@interface MVVM_Model : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *imageName;
@end
Demo中,我引入了FB的轻量级KVO框架FBKVOController,在View中监听ViewModel属性的变化,以便及时更新View。
写了这么多,可能还不是很好理解。Demo运行一遍应该就一目了然了。