Megacli是一款管理维护硬件RAID的工具,有LSI公司提供,LSI公司的raid卡,使用的比较广泛。我们可以通过megacli了解当前raid卡的所有信息,包括raid卡的型号,raid的阵列类型,raid上的磁盘状态,也可以通过它来直接创建阵列,在线添加磁盘等。
一,Megacli工具安装
可以在LSI公司的官网直接下载工具:
ftp://download2.boulder.ibm.com/ecc/sar/CMA/XSA/ibm_utl_sraidmr_megacli-8.00.48_linux_32-64.zip
下载完成之后,是一个zip包,然后解压,安装:
# unzip MegaCli_Linux.zip
# cd MegaCli_Linux
# ls
megacli_8.07.08-1_all.deb MegaCli-8.07.08-1.noarch.rpm MegaSAS.log
# rpm -ivh MegaCli-8.07.08-1.noarch.rpm
安装成功之后,命令的默认安装路径为:
# /opt/MegaRAID/MegaCli/MegaCli64
二,查看磁盘的状态
作用:显示Raid卡型号,Raid设置,整列类型,Disk相关信息
# /opt/MegaRAID/MegaCli/MegaCli64 -cfgdsply -aALL|less
1,查看raid整列类型和大小
如上图所示:
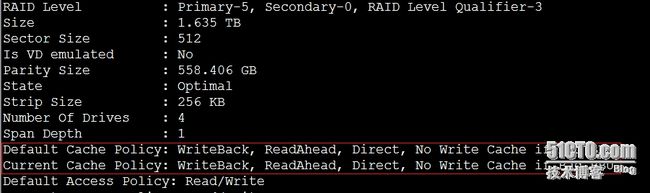
(1)通过RAID Level字段得知,disk group 0做的是一个raid5。
RAID Level对应关系:
RAID级别一般通过 Primary 字段值来判断,还需要结合Span Depth的值来判断值为1表示为 RAID-1,不为1表示 RAID-10; 还有一种情况:Primary-1, Secondary-3, RAID LevelQualifier-0 也是表示 RAID-10;
RAIDLevel : Primary-0, Secondary-0, RAID Level Qualifier-0 对应RAID 0
RAIDLevel : Primary-1, Secondary-0, RAID Level Qualifier-0 对应RAID 1
RAIDLevel : Primary-5, Secondary-0, RAID Level Qualifier-3 对应RAID 5
RAIDLevel : Primary-1, Secondary-3, RAID Level Qualifier-0 对应RAID 10
(2)disk group 0的大小为1.6TB;
2,查看raid的cache策略
如上图所示,raid的默认以及当前生效的cache策略为writeback(还有一种cache策略为WriteThrough)
策略说明:
(1). 第一段: WriteBack, WriteThrough
* WriteBack:进行写操作时,将数据写入RAID卡缓存,并直接返回,RAID卡控制器将在系统负载低或者Cache满了的情况下把数据写入硬盘。该设置会大大提升RAID卡写性能,绝大多数的情况下会降低系统IO负载。 数据的可靠性由RAID卡的BBU(Battery Backup Unit)进行保证。大多数情况下,我们都使用这种策略。
* WriteThrough: 数据写操作不使用缓存,数据直接写入磁盘。RAID卡写性能明显下降,在大多数情况下该设置会造成系统IO负载上升。特别对于io负载很大的服务,表现特别明显。
(2). 第二段: ReadAheadNone, ReadAdaptive, ReadAhead.
* ReadAheadNone: 不开启预读。这是默认的设置
* ReadAhead: 在读操作时,预先把后面顺序的数据加载入Cache,在顺序读取时,能提高性能,相反会降低随机读的性能。
* ReadAdaptive: 自适应预读,当Cache memory和IO空闲时,采取顺序预读,平衡了连续读性能及随机读的性能,需要消耗一定的计算能力。
(3). 第三段: Direct, Cached.
* Direct: Direct IO模式,读操作不缓存到cache memory中,数据将同时传输到cache中和应用,如果接下来要读取相同的数据块,则直接从Cache memory中获取. 这是默认的设置
* Cached: Cached IO模式,所有读操作都会缓存到cache memory中。
(4). 第四段: Write Cache OK if Bad BBU, No Write Cache if Bad BBU
* Write Cache OK if Bad BBU: 在BBU有问题时(如电池失效), 依旧使用Write Cache, 有一定的数据丢失风险.
* No Write Cache if Bad BBU: 在BBU有问题时, 不使用Write Cache
策略自动切换的问题由于MegaSAS RAID卡默认采用No Write Cache if Bad BBU的设置,将可能发生Write Cache策略变更的情况(由WriteBack变成WriteThrough),导致写性能下降,如果该自动变更发生在业务高峰且系统Io负载高的时候,可能会引发不可预测的问题,如卡机。以下原因将造成Write Cache策略的变更.
(1). RAID卡进入BBU Learn Cycle: 详细介绍见下面
(2). 检测到某些电池故障,如电池容量过低等,一般是电池老化带来的影响,IBM建议一年更换一次RAID卡电池
(3). 没有安装电池, 部分服务器购买时不带电池,导致被自动设置为WriteThrough
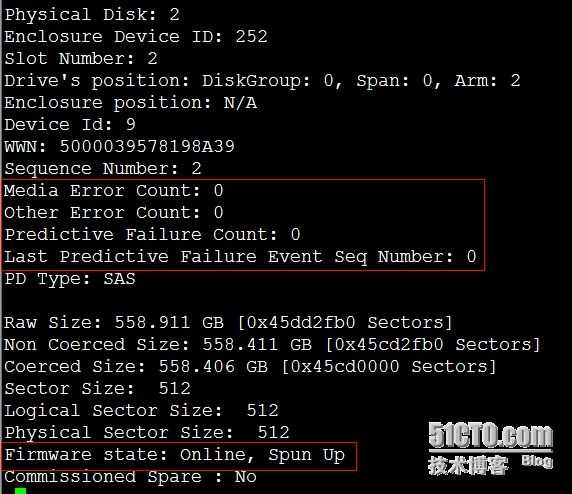
3,判定磁盘是否损坏
如上图所示,我们一般通过如上5个值,来判断磁盘是否应该报修:
1,Media Error
磁盘存在错误,可能是磁盘有坏道。值越大,越危险。根据磁盘状况,一般大于100报修更换。
2,Other Error
磁盘存在未知的错误,可能是磁盘松动,需要重新再插入。根据磁盘状况,一般大于100报修更换。
3,Predictive Failure Count
磁盘的预警数。一般大于0,就报修更换。
4,Last Predictive Failure Event Seq Number
最后一条预警的时间序列号。这个值不为0,肯定Predictive Failure Count也不为0
5,Firmware state
磁盘目前的状态。一般有9种,即
(1)Unconfigured Good – A drive accessible to the RAID controller but not configured as a part of
a virtual drive or as a hot spare.
(2)Online – A drive that can be accessed by the RAID controller and will be part of the virtual
drive.
(3)Rebuild – A drive to which data is being written to restore full redundancy for a virtual drive.
(4)Failed – A drive that was originally configured as Online or Hot Spare, but on which the
firmware detects an unrecoverable error.
(5)Unconfigured Bad – A drive on which the firmware detects an unrecoverable error; the drive
was Unconfigured Good or the drive could not be initialized.
(6)Missing – A drive that was Online, but which has been removed from its location.
(7)Offline – A drive that is part of a virtual drive but which has invalid data as far as the RAID
configuration is concerned.
(8)Hot Spare – A drive that is configured as a hot spare.
(9)None – A drive with an unsupported flag set. An Unconfigured Good or Offline drive that has
completed the prepare for removal operation.
(10)还有一种特殊的状态copyback:
从磁盘组中把数据复制到非磁盘组的磁盘中,然后等failed的盘更换之后,再从这个非磁盘组的磁盘中把数据给copyback回来。
做hot spare的盘,会出现这种情况:即原来的hot spare盘只是临时存放了数据,等failed的盘更换之后,把数据从hotspare的盘中复制回来,正常使用的还是新更换的盘,hot spare的盘永久做hot spare。
三,获取linux服务器的Serial Number
# dmidecode -t 1|grep 'Serial Number'
通常磁盘维修的时候,需要向机房硬件工程师包对应机器的SN。