泛型的通配符:?
可以对类型进行限定:? extends E :接收E类型或者E的子类型对象。上限
? super E:接收E类型或者E的父类型。下限
使用同一个方法操作泛型不同的对象时:< ? >
ArrayList和LinkedList的父类是Collection,故在操作时, printCollection(Collection al)应该是Collection
package com.vv.generic.advance.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.vv.bean.Student;
import com.vv.bean.Worker;
public class GenericAdvanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Worker("worker",12));
al.add(new Worker("worker2",32));
LinkedList al2 = new LinkedList();
al.add(new Worker("student",12));
al.add(new Worker("student2",12));
printCollection(al);
printCollection(al2);
}
private static void printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
当方法时静态的时候,泛型限定也可以改为:此时it.next()就可以有返回值,但若是?形式,则不能进行it.next()
private static void printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
l str = it.next();
System.out.println(it.next());
}
如上,一般都采用第一种,只有当需要操作返回值时才需要进行使用第二种:
private static l printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
l str = it.next();
return str;
}
如何使用泛型操作一部分,即只能存储person的子类,即泛型的限定;像LinkedList
这种方式进行添加数据时编译会报错,因为只能存储Person的子类,
package com.vv.generic.advance.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.vv.bean.Person;
import com.vv.bean.Student;
import com.vv.bean.Worker;
public class GenericAdvanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Worker("worker",12));
al.add(new Worker("worker2",32));
LinkedList al2 = new LinkedList();
al.add(new Worker("student",12));
al.add(new Worker("student2",12));
LinkedList al3 = new LinkedList();
al3.add(5);
al3.add(5);
printCollection(al);
printCollection(al2);
printCollection(al3);
}
private static void printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
上限:
如下情况,迭代器接收数据时,就可以进行使用Person父类进行数据的输出
package com.vv.generic.advance.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.vv.bean.Person;
import com.vv.bean.Student;
import com.vv.bean.Worker;
public class GenericAdvanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Worker("worker",12));
al.add(new Worker("worker2",32));
LinkedList al2 = new LinkedList();
al.add(new Worker("student",12));
al.add(new Worker("student2",12));
printCollection(al);
printCollection(al2);
}
private static void printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p = it.next();
// System.out.println(it.next());
System.out.println(p.getName()+p.getAge());
}
}
}
下限:
即泛型中存储时只能存储Student和它的父类
private static void printCollection(Collection al) {
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
一般在存储元素的时候都是使用上限,因为这样取出都是按照上限类型进行运算的,不会出现类型安全隐患
如下 ArrayList
将泛型定义为Person时才可以编译成功,
上限:存什么用什么类型进行接收
package com.vv.generic.advance.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.vv.bean.Person;
import com.vv.bean.Student;
import com.vv.bean.Worker;
public class GenericAdvanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al1 = new ArrayList();
al1.add(new Worker("worker",12));
al1.add(new Worker("worker2",32));
LinkedList al2 = new LinkedList();
al2.add(new Student("student",12));
al2.add(new Student("student2",2));
ArrayList al3 = new ArrayList();
al3.add(new Person("person",11));
al3.add(new Person("person2",21));
ArrayList al4 = new ArrayList();
al4.addAll(al1);
}
}
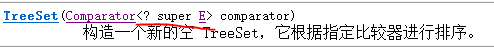
下限:
通常对集合中的元素进行取出操作时,即取什么类型使用什么的父类进行接收
package com.vv.generic.advance.demo;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.vv.bean.Person;
import com.vv.bean.Student;
import com.vv.bean.Worker;
public class GenericAdvanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet al1 = new TreeSet(new CompByName());
al1.add(new Worker("worker",12));
al1.add(new Worker("worker2",32));
TreeSet al2 = new TreeSet(new CompByName());
al2.add(new Student("student",12));
al2.add(new Student("student2",2));
TreeSet al3 = new TreeSet(new CompByName());
al3.add(new Person("person",11));
al3.add(new Person("person2",21));
TreeSet al4 = new TreeSet();
// al4.addAll(al2);
// al4.addAll(al1);
// al4.addAll(al3);
// System.out.println(al4.size());
Iterator it = al2.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
// Person p = it.next();
System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(p.getName()+p.getAge());
}
}
}
class CompByName implements Comparator{
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
int temp = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
return temp==0? o1.getAge()-o2.getAge():temp;
}
}